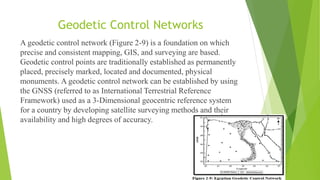
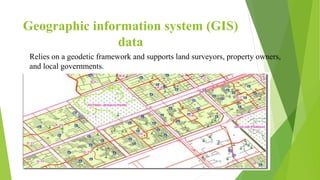
This document discusses geodesy and its types. Geodesy is the science of accurately measuring and understanding the Earth's geometric shape, orientation in space and gravitational field. It involves determining coordinates and land boundaries and is used for applications like engineering construction, topographic mapping, monitoring structures and crustal movement. The document outlines the responsibilities of geodesists and how the field has evolved with new technologies like GPS and satellites. It describes different types of geodesy including satellite geodesy and physical geodesy.