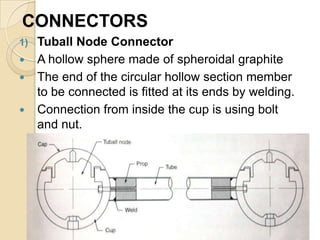
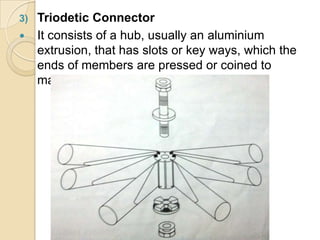
Space frames are three-dimensional structures composed of interconnected linear elements that transfer loads through a grid-like network. They are designed without intermediate columns, creating large open interior spaces. Space frames come in various types including two-way and three-way grids, and can be single, double, or triple-layered. They consist of tubular members and specialized connectors, such as tuball nodes, nodus connectors, and triodetic connectors. Space frames are light, economical, stiff structures that allow freedom in building design and easy integration of services. Examples include the San Siro Stadium in Milan and Stansted Airport in London.