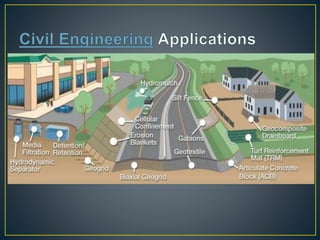
Geotextiles are versatile materials with applications in civil engineering, providing benefits such as separation, drainage, filtration, reinforcement, and protection against erosion. Their properties, including tensile strength and chemical resistance, make them suitable for use in roads, railroads, and various earth structures. Through effectively managing soil and water interactions, geotextiles enhance structural integrity in multiple construction contexts.