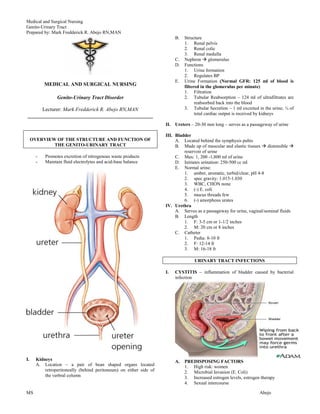
The document summarizes the structure and function of the genitourinary tract. It discusses the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. It describes urine formation and the roles of the kidneys in regulating blood pressure and fluid/electrolyte balance. Common genitourinary disorders are also outlined, including urinary tract infections like cystitis and pyelonephritis. Acute and chronic renal failure are summarized as well as conditions like nephrolithiasis. Nursing management of related issues is briefly discussed.