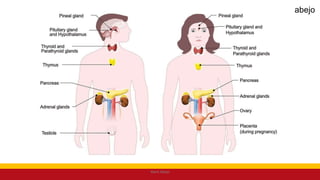
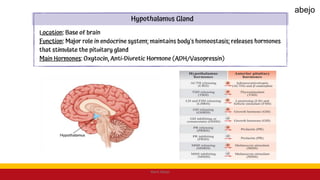
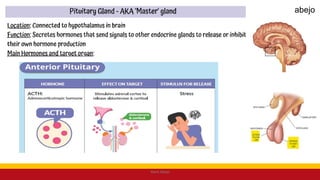
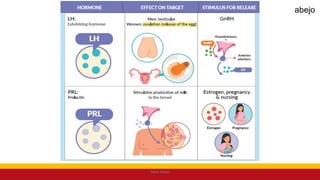
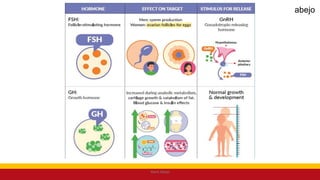
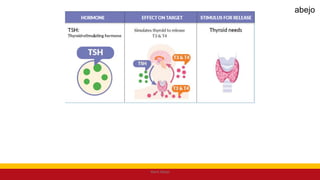
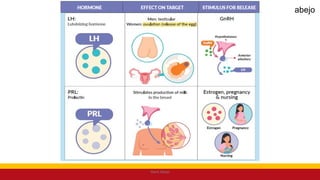
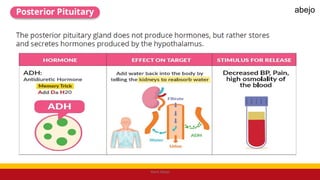
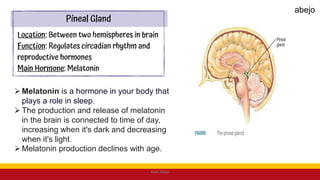
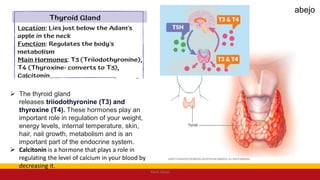
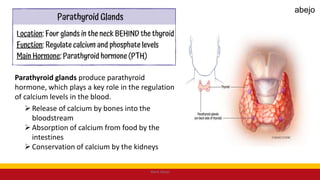
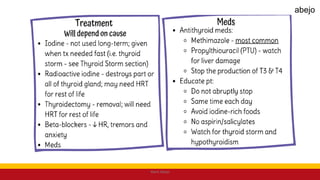
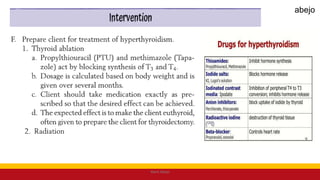
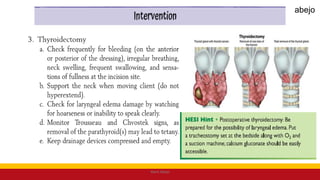
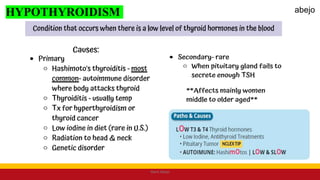
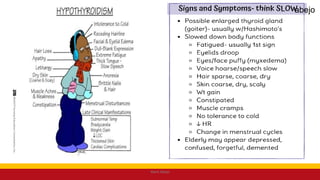
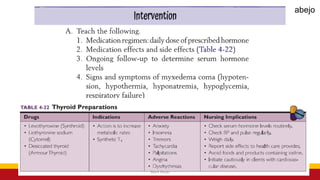
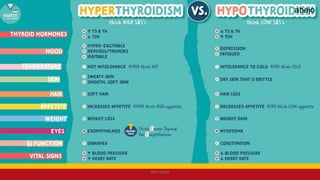
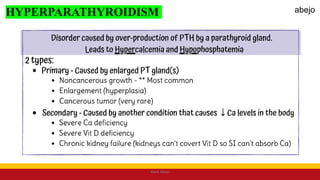
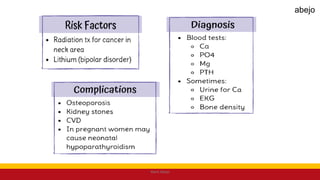
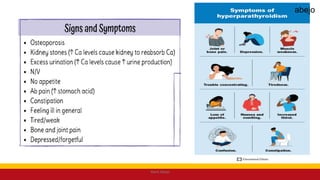
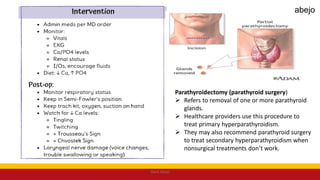
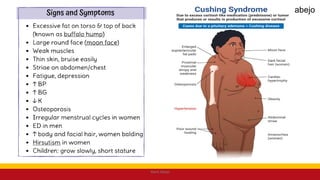
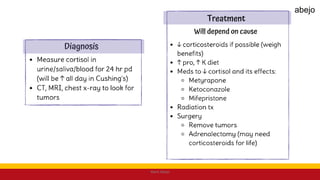
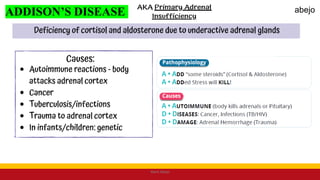
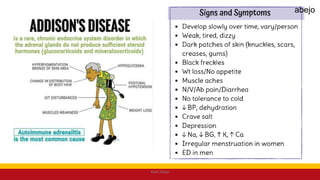
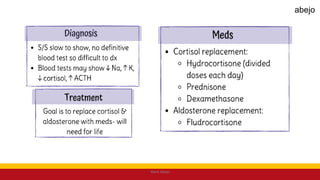
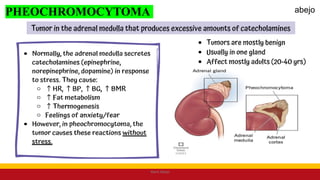
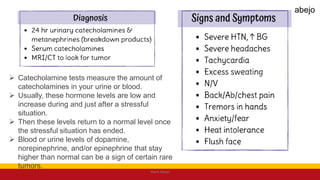
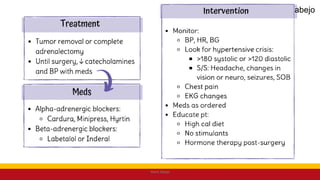
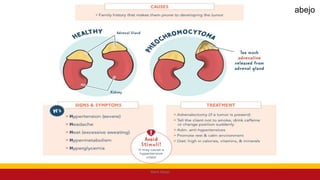
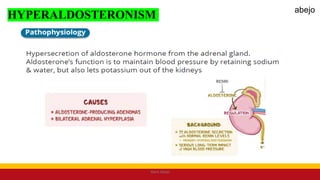
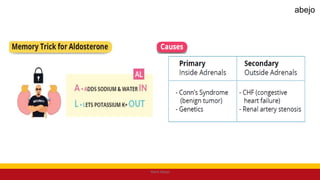
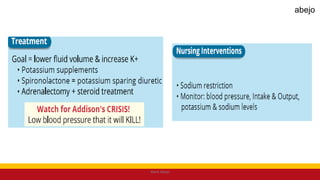
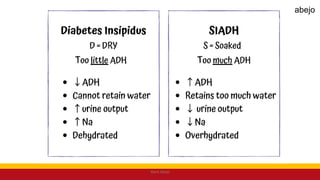
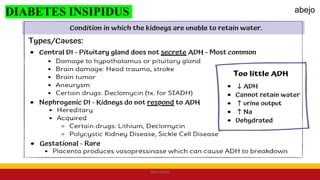
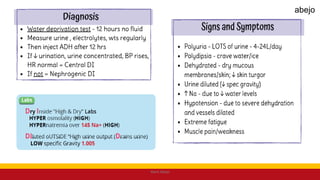
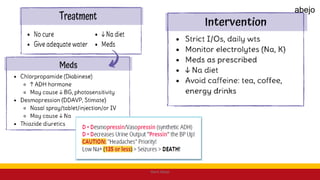
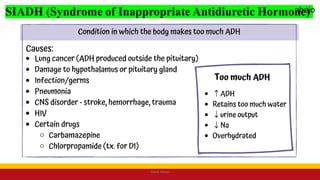
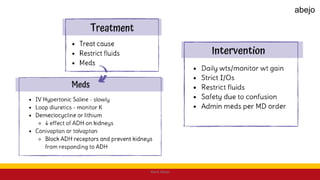
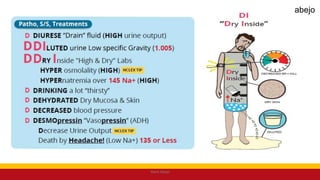
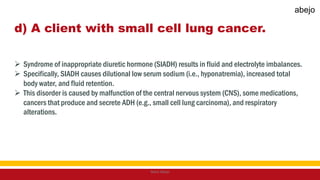
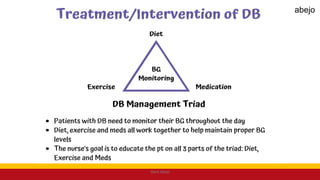
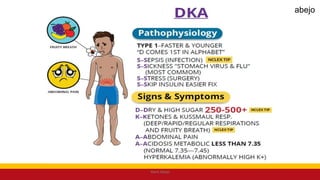
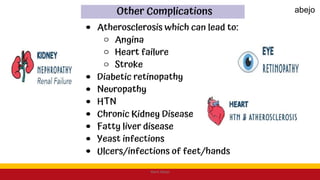
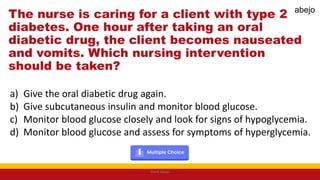
This Medical-Surgical Nursing PowerPoint lecture is designed to provide nursing students with a solid foundation in caring for patients with acute and chronic medical conditions. Covering essential topics such as pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic procedures, and evidence-based interventions, this lecture prepares nurses for real-world patient care in hospital and clinical settings.