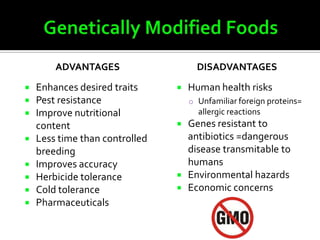
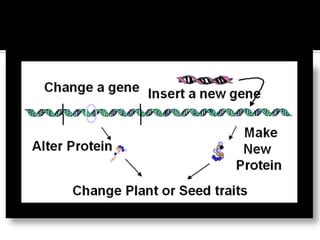
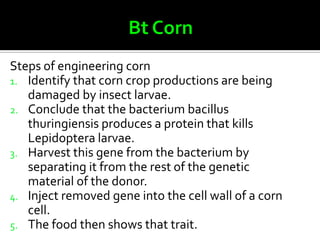
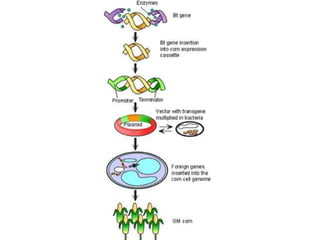
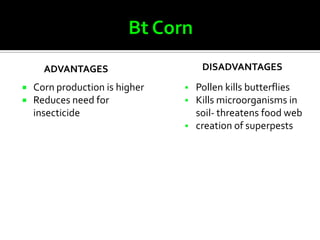
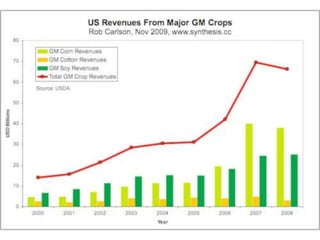
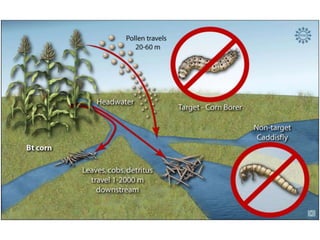
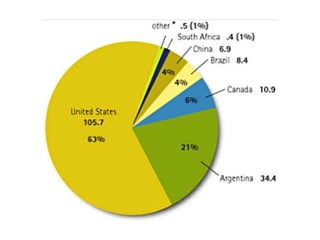
The document discusses genetically modified foods (GMOs). It defines GMOs as foods that have been genetically enhanced through molecular biology techniques such as transferring genes from donor organisms. The document outlines the process of genetic engineering and provides examples of commonly genetically modified crops like corn, soybeans and cotton. It notes both potential advantages of GMOs, like pest resistance and higher yields, and disadvantages such as possible human health and environmental risks.