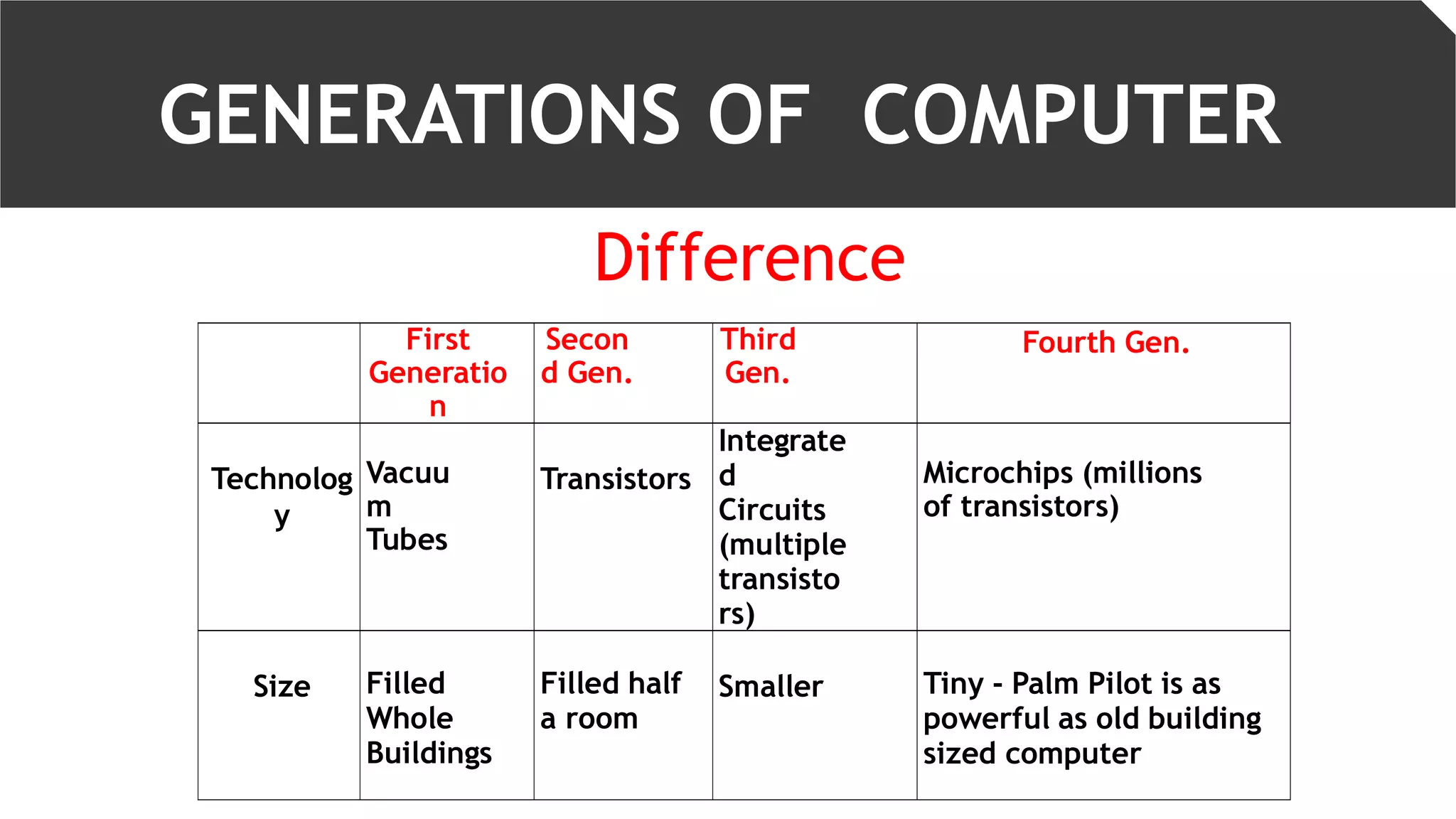
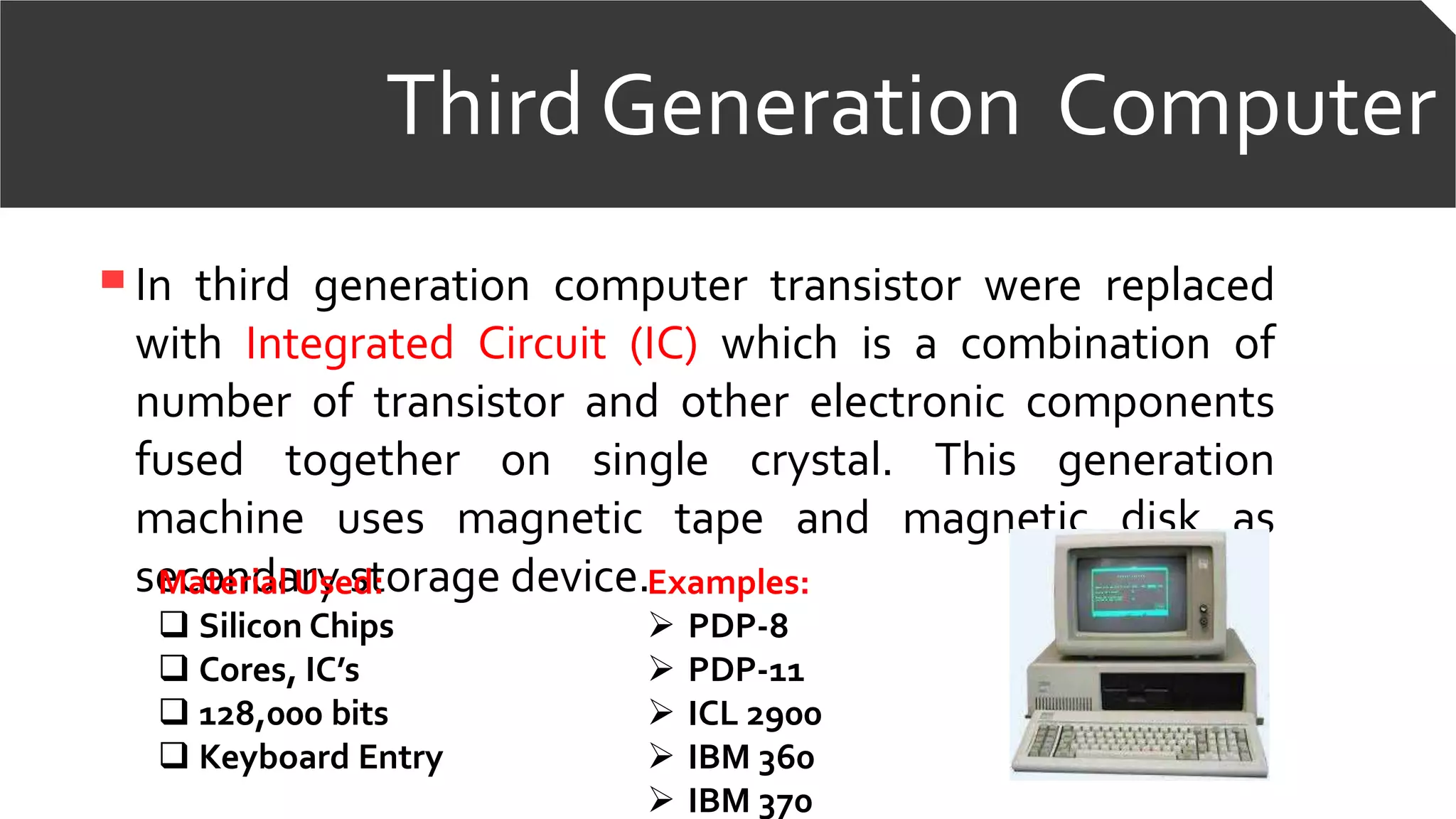
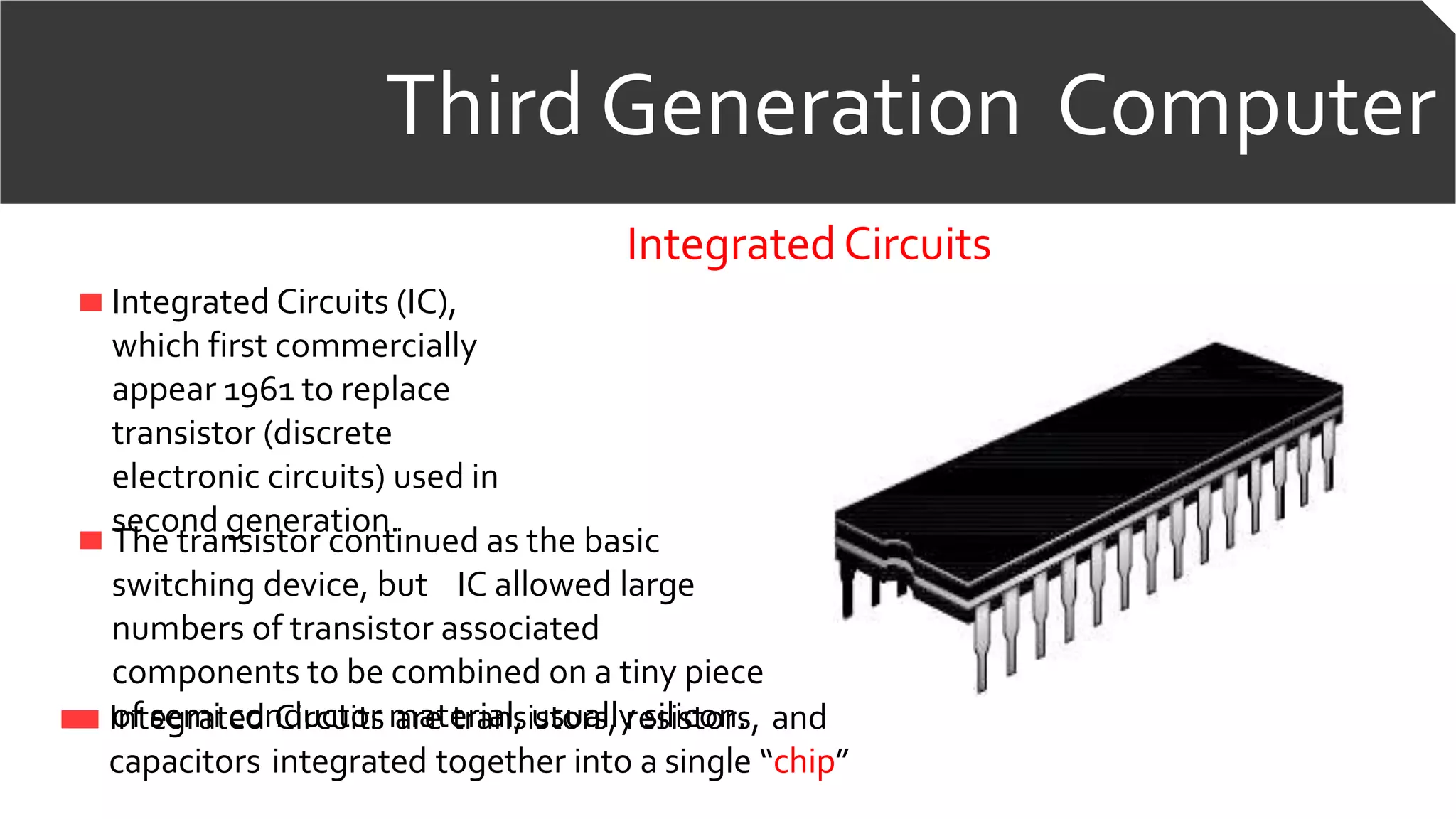
The document discusses the five generations of computers. The first generation used vacuum tubes and were very large in size. The second generation used transistors, which made computers smaller. The third generation used integrated circuits which further reduced size and improved performance. The fourth generation used microprocessors on a single chip. The fifth generation aims to develop artificial intelligence and robotics. Each generation brought improvements in size, performance and capabilities through technological advancements in components.


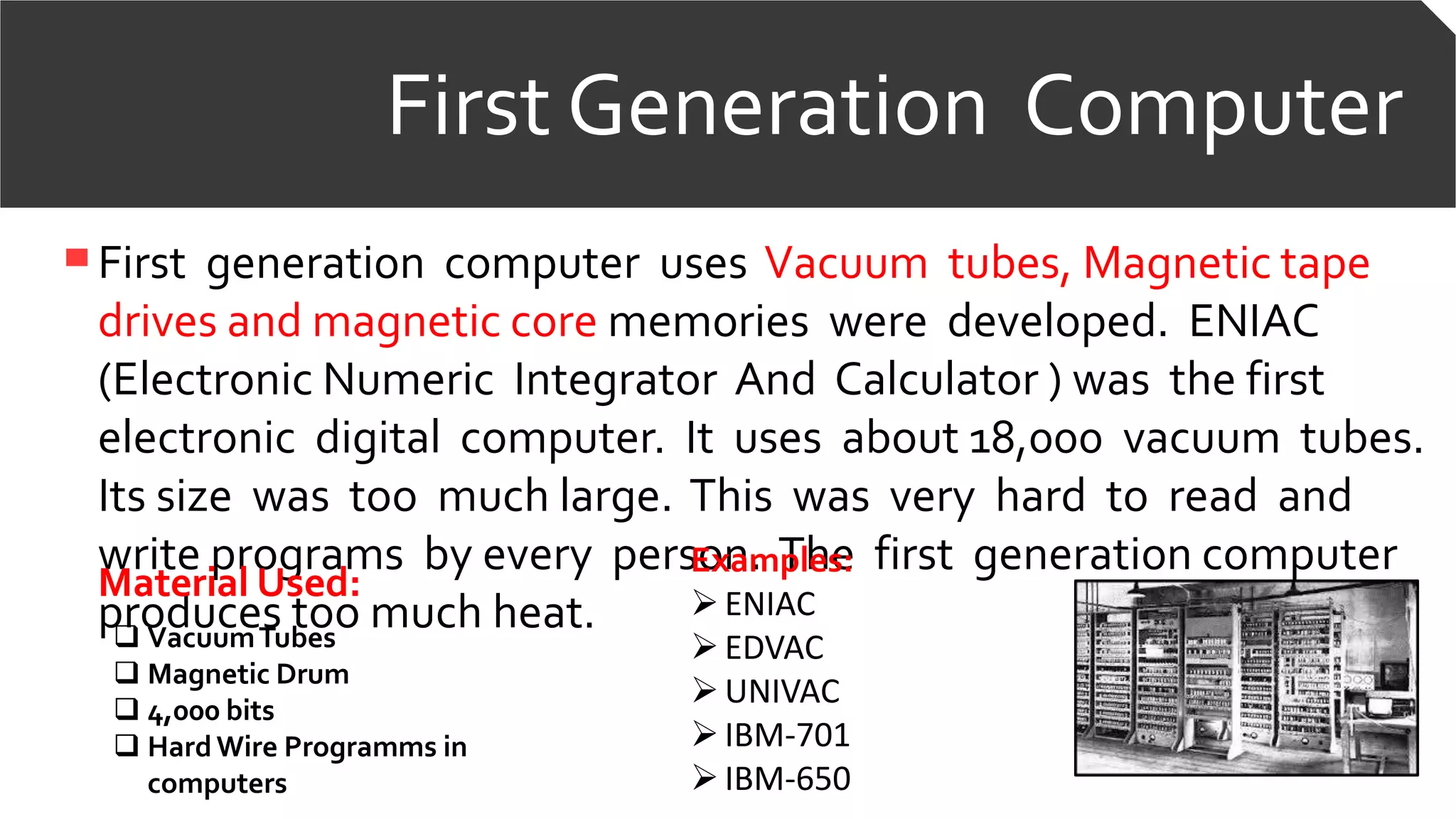
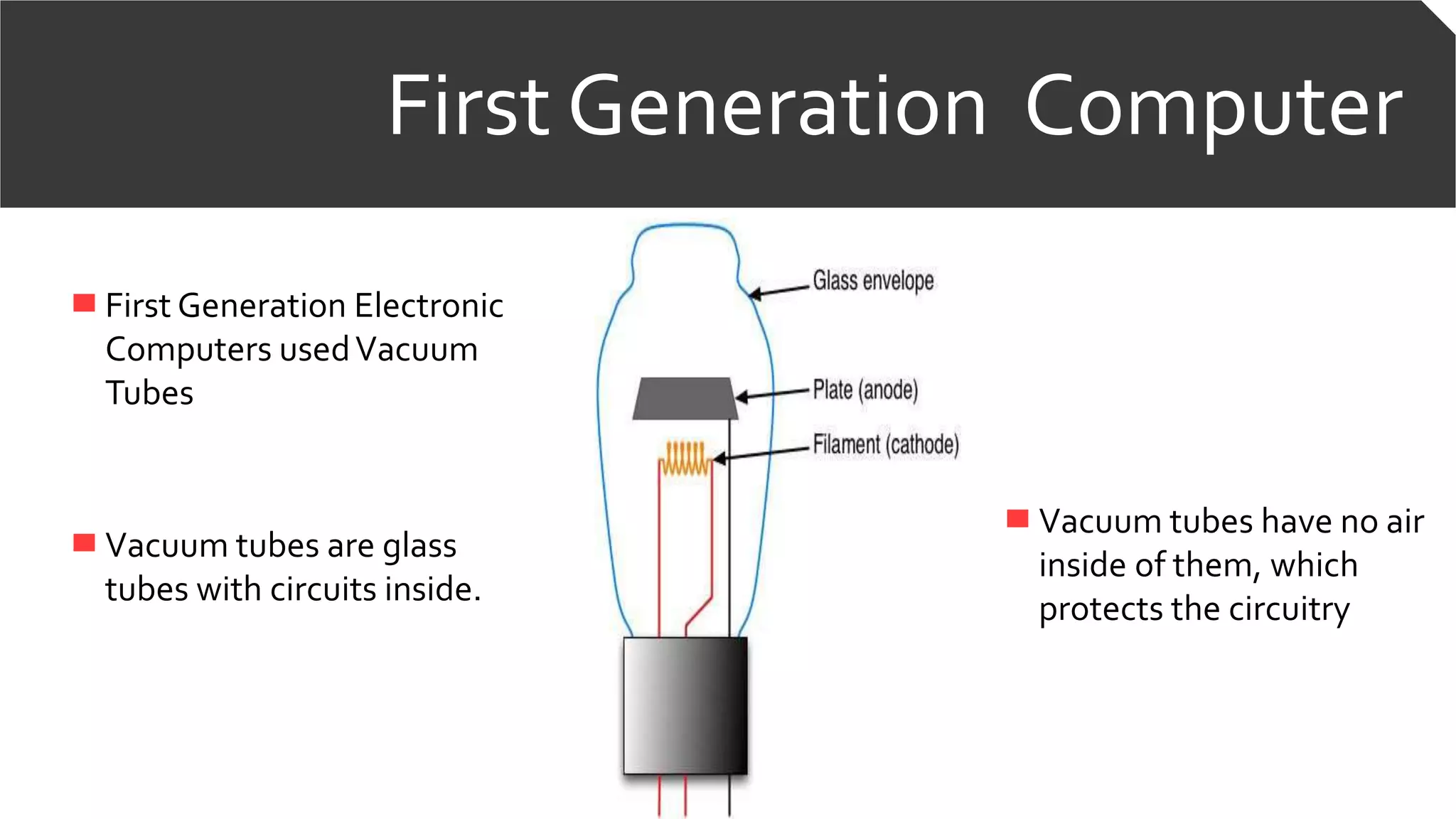
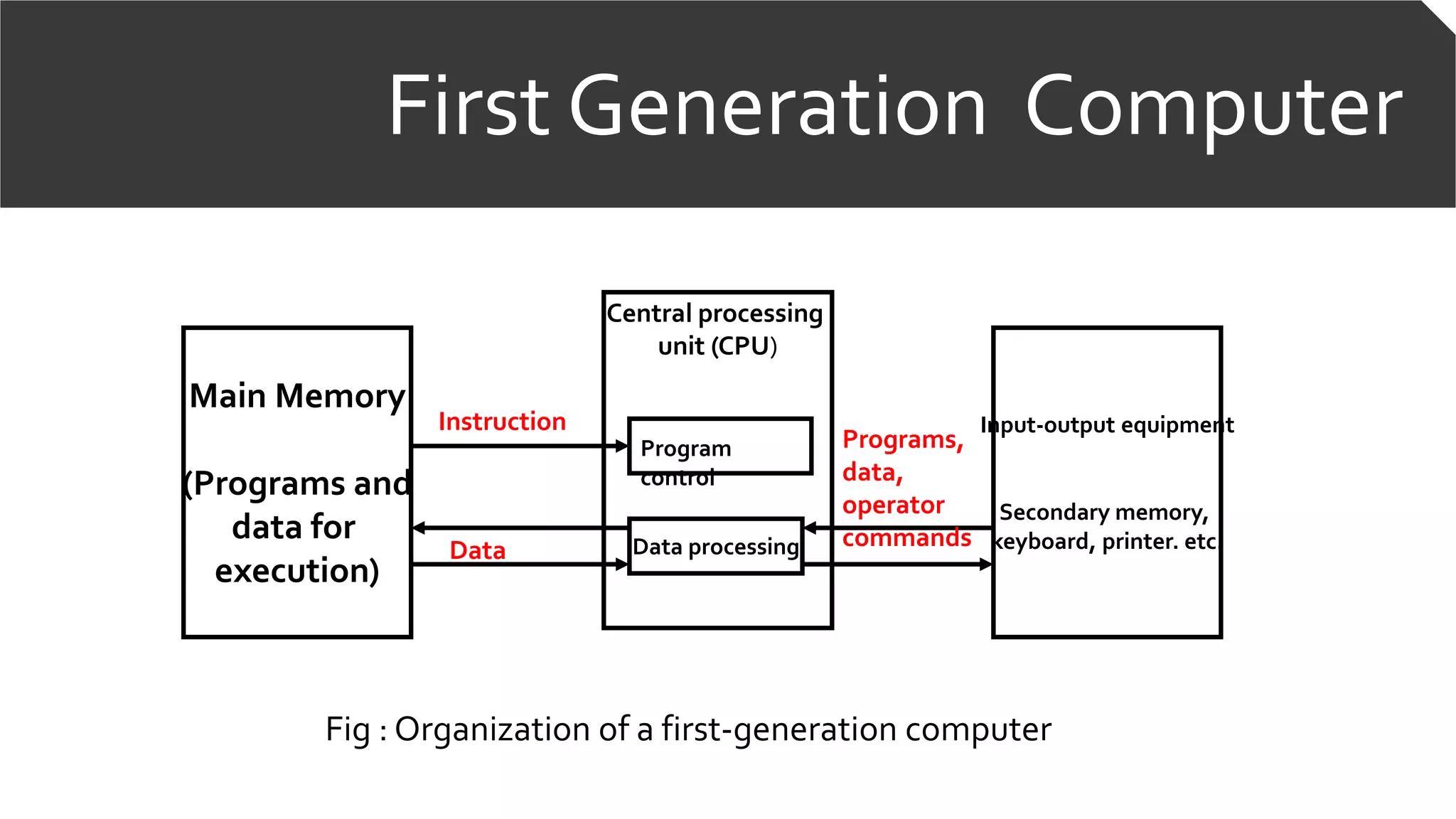
![First Generation Computer
First generation languages [1GL]
Represent the very early,
primitive computer
languages that consisted
entirely of 1's and 0's -
the actual language that
the computer
understands (machine
0101110
101
1010101
00
1110101
010
0011011
00
0101110
0101110
101
1010101
00
1110101
010
0011011
00
0101110](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abracadabra-180801170853/75/Generation-of-computer-9-2048.jpg)


![Third Generation ComputerThird Generation Computer
Third generation languages [3GL]
With the languages introduced
by the third generation of
computer programming, words
and commands (instead of
just symbols and numbers)
were being used.These
languages therefore, had syntax
that was much easier to
understand. Third generation
languages are known as "high
level languages" and include C,
C/C++,JAVA
…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abracadabra-180801170853/75/Generation-of-computer-19-2048.jpg)




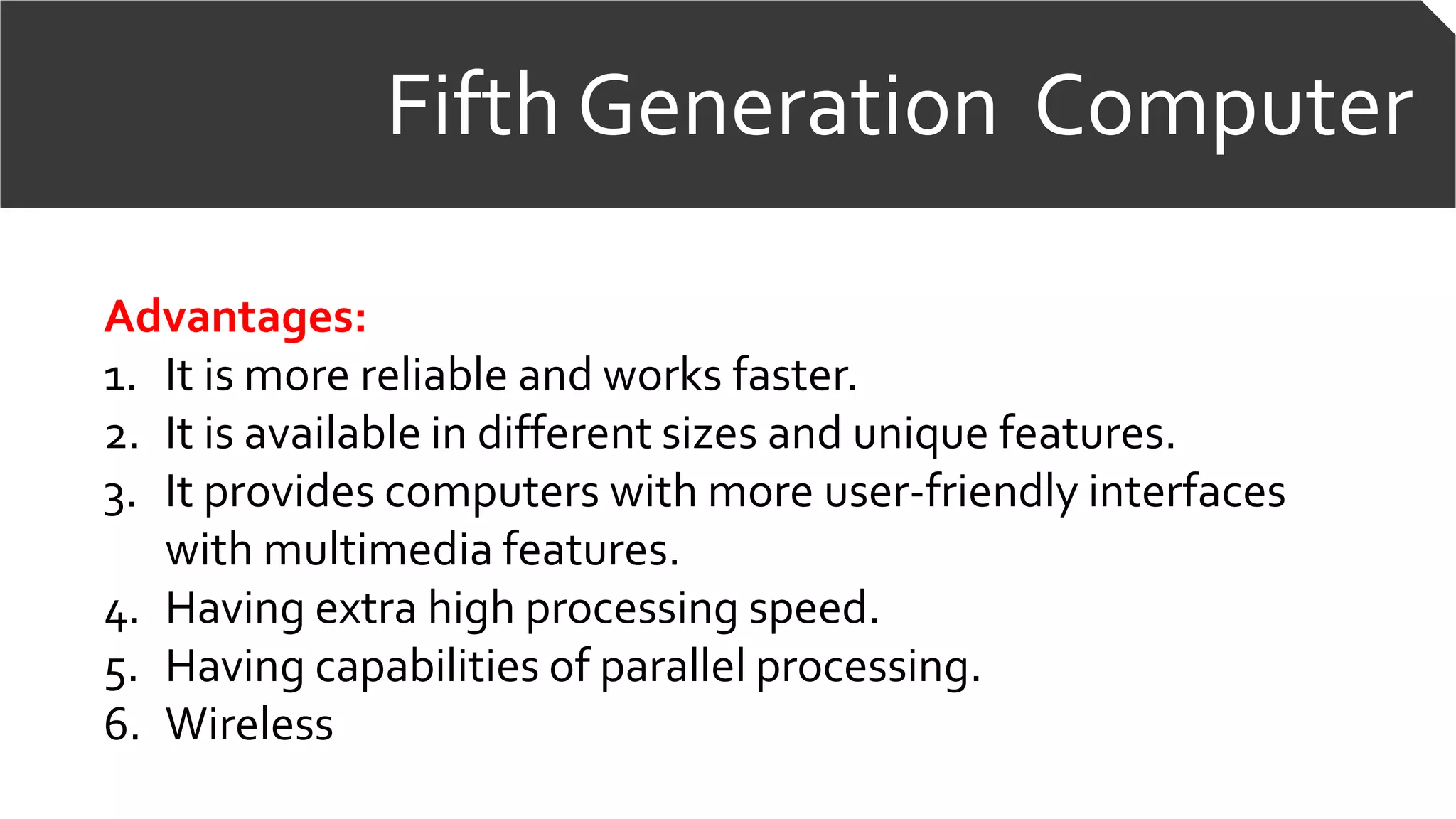
![Fifth Generation ComputerThird Generation ComputerFifth Generation Computer
Fifth generation languages [5GL]
Fifth generation languages are
currenty being used for neural
networks.A neural network is a
form of Artifical intelligence that
attempts to imitate how the
human mind works.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abracadabra-180801170853/75/Generation-of-computer-29-2048.jpg)