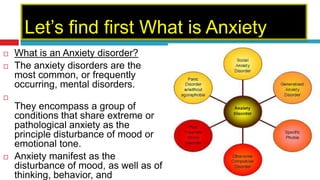
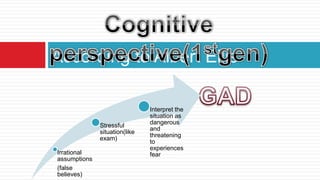
This document discusses generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). GAD is a common anxiety disorder characterized by excessive, uncontrollable worry about daily life events for at least six months. People with GAD may experience physical symptoms like restlessness, fatigue, difficulty sleeping, and increased heart rate. The document explores GAD from psychodynamic, humanistic, cognitive, and biological perspectives and their associated therapies, such as psychodynamic therapy focusing on childhood experiences, cognitive therapy challenging irrational thoughts, and biological therapy using medication.