This document discusses gene pyramiding in chickpea to develop durable resistance to bacterial blight. It describes:
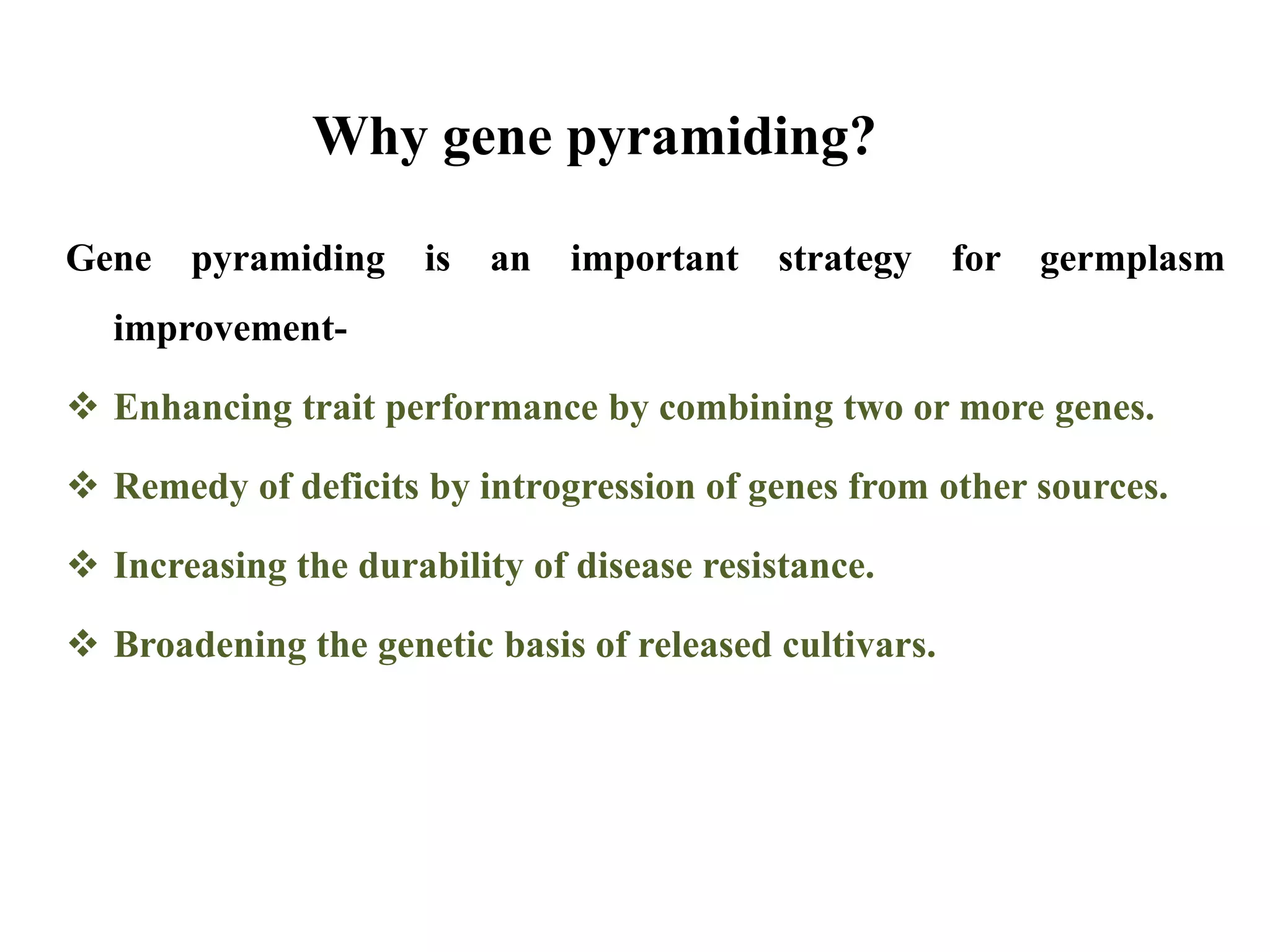
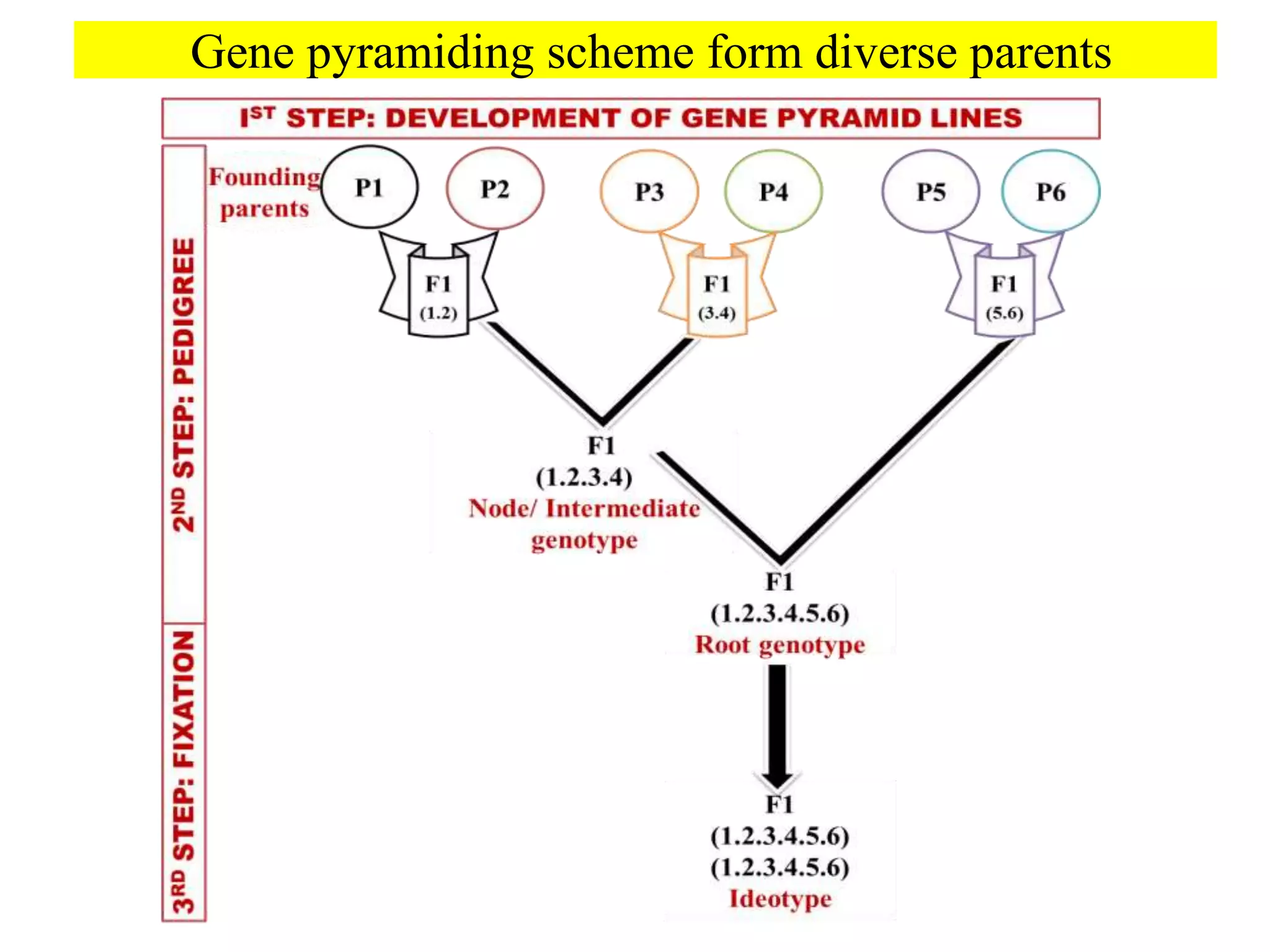
1) Gene pyramiding involves combining two or more genes from multiple parents into a single variety to enhance trait performance and increase durability of disease resistance.
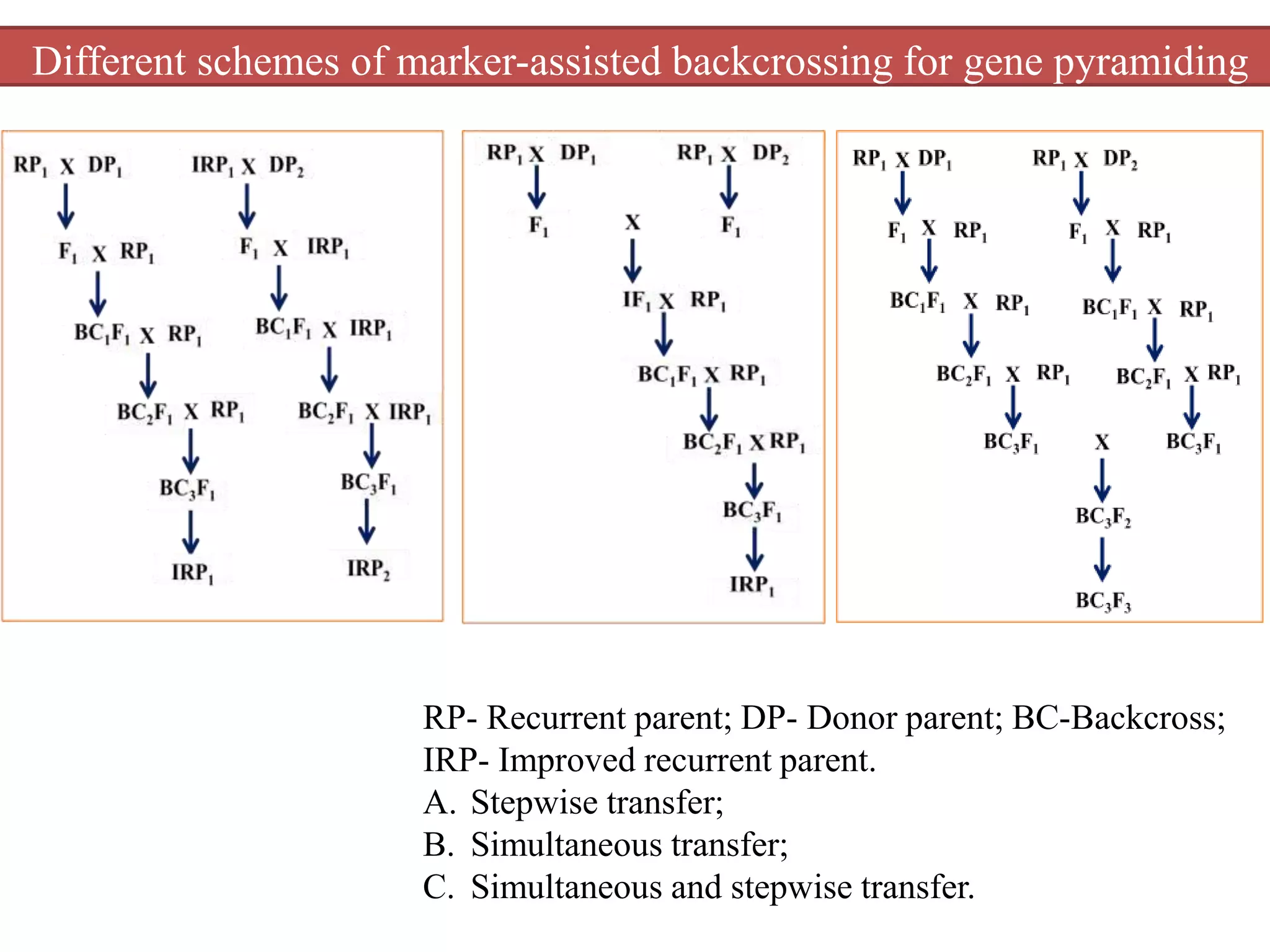
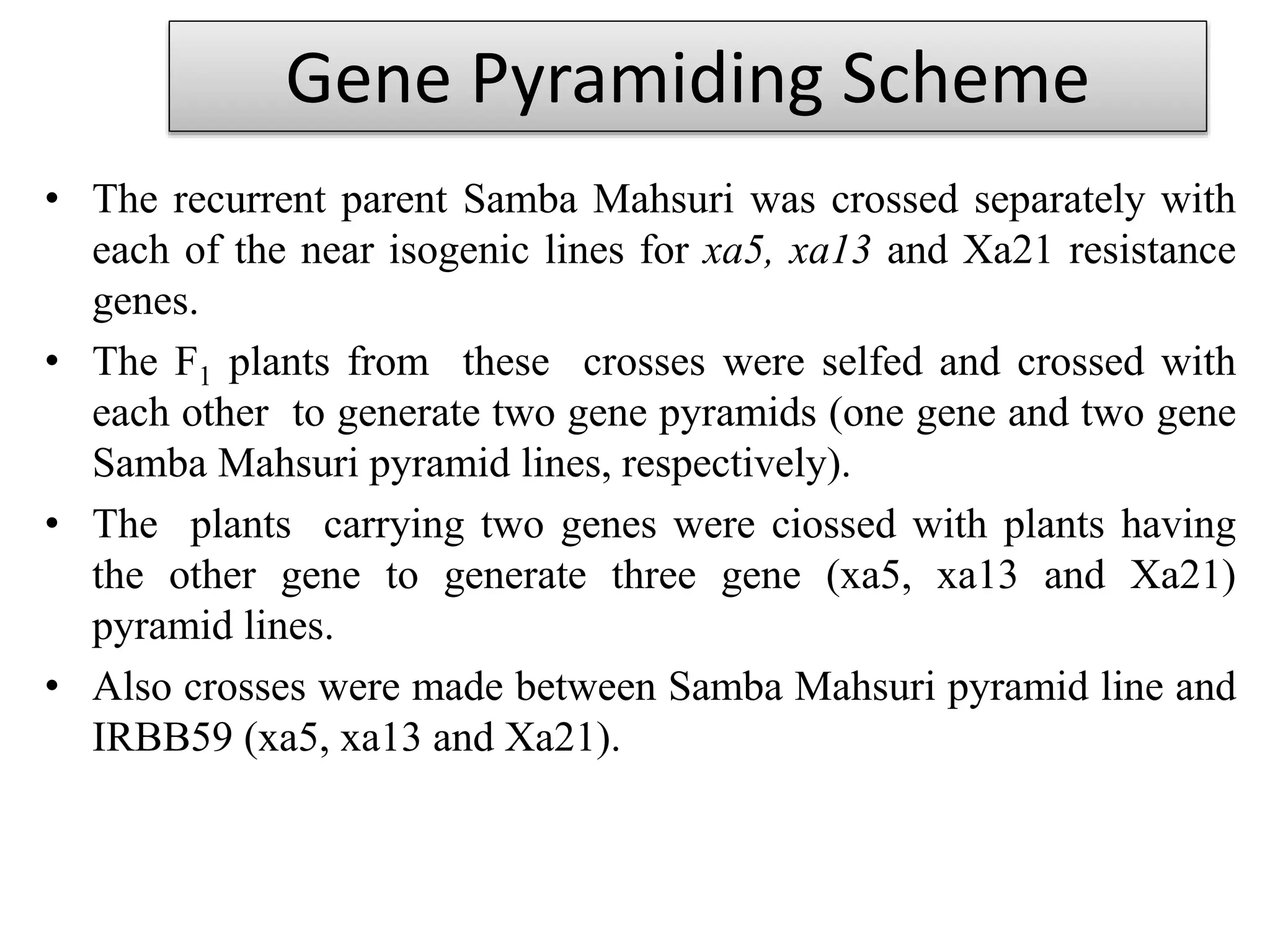
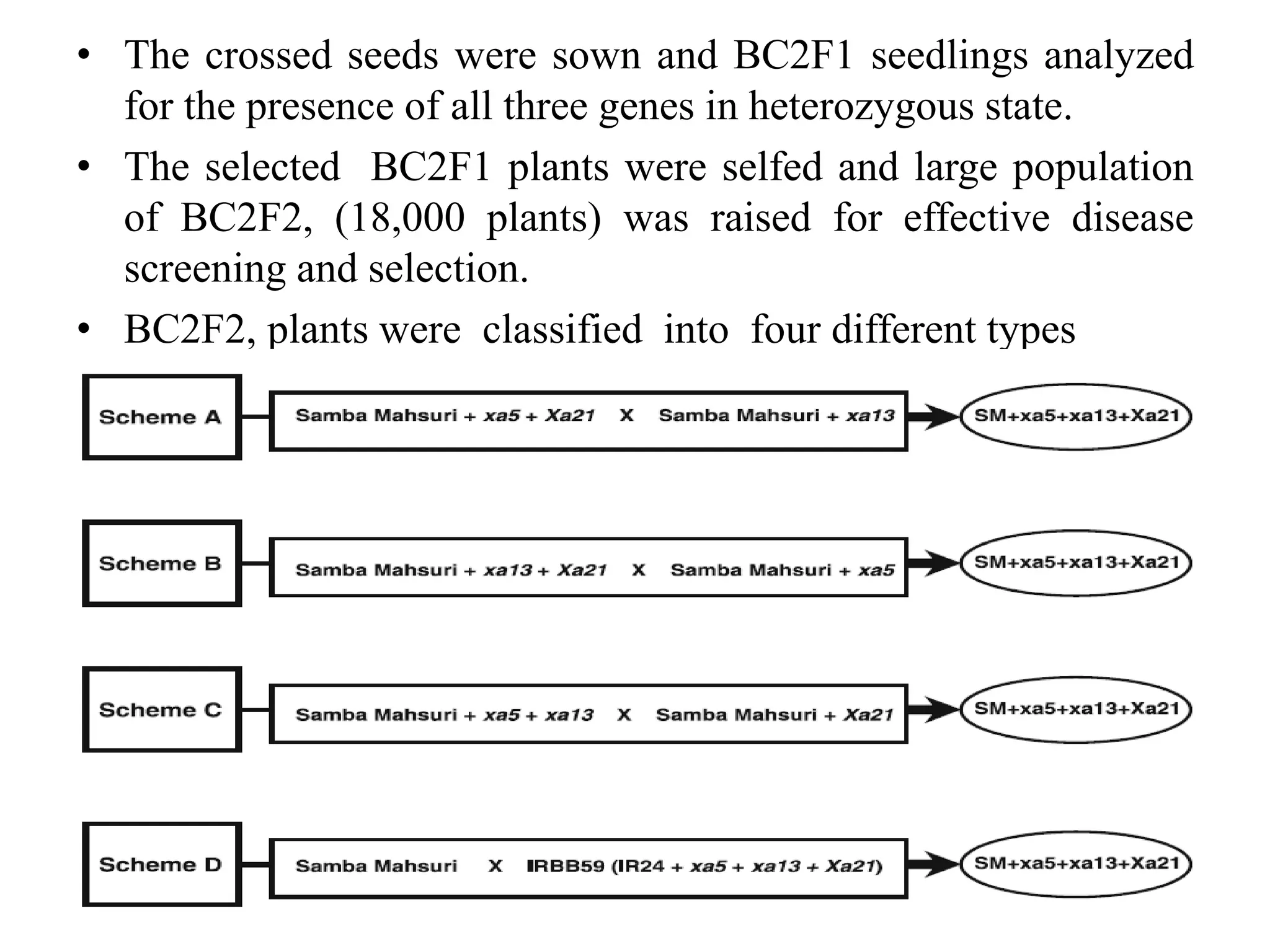
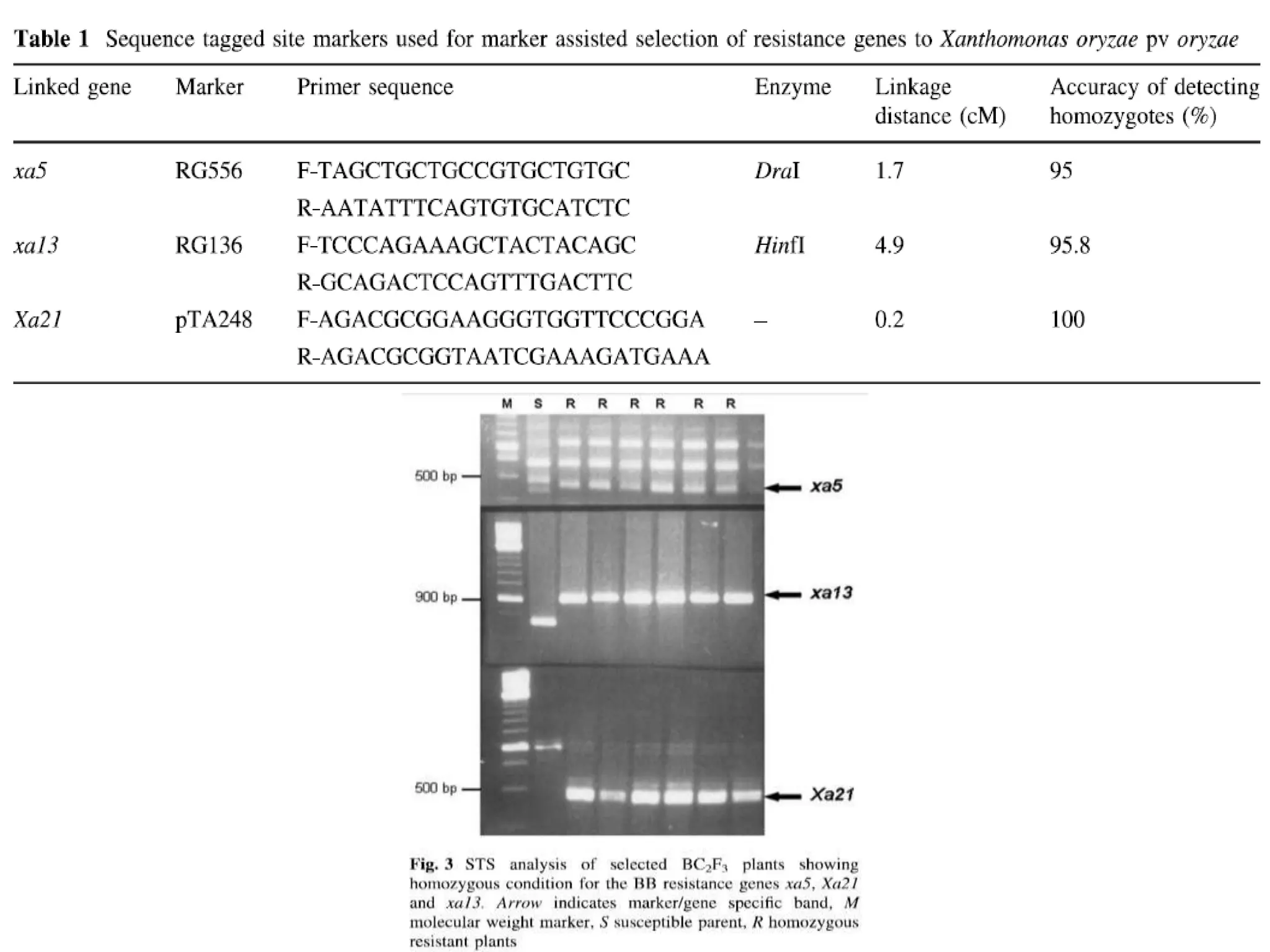
2) A study introgressed three bacterial blight resistance genes (xa5, xa13, and Xa21) into the rice variety Samba Mahsuri using marker-assisted backcrossing.
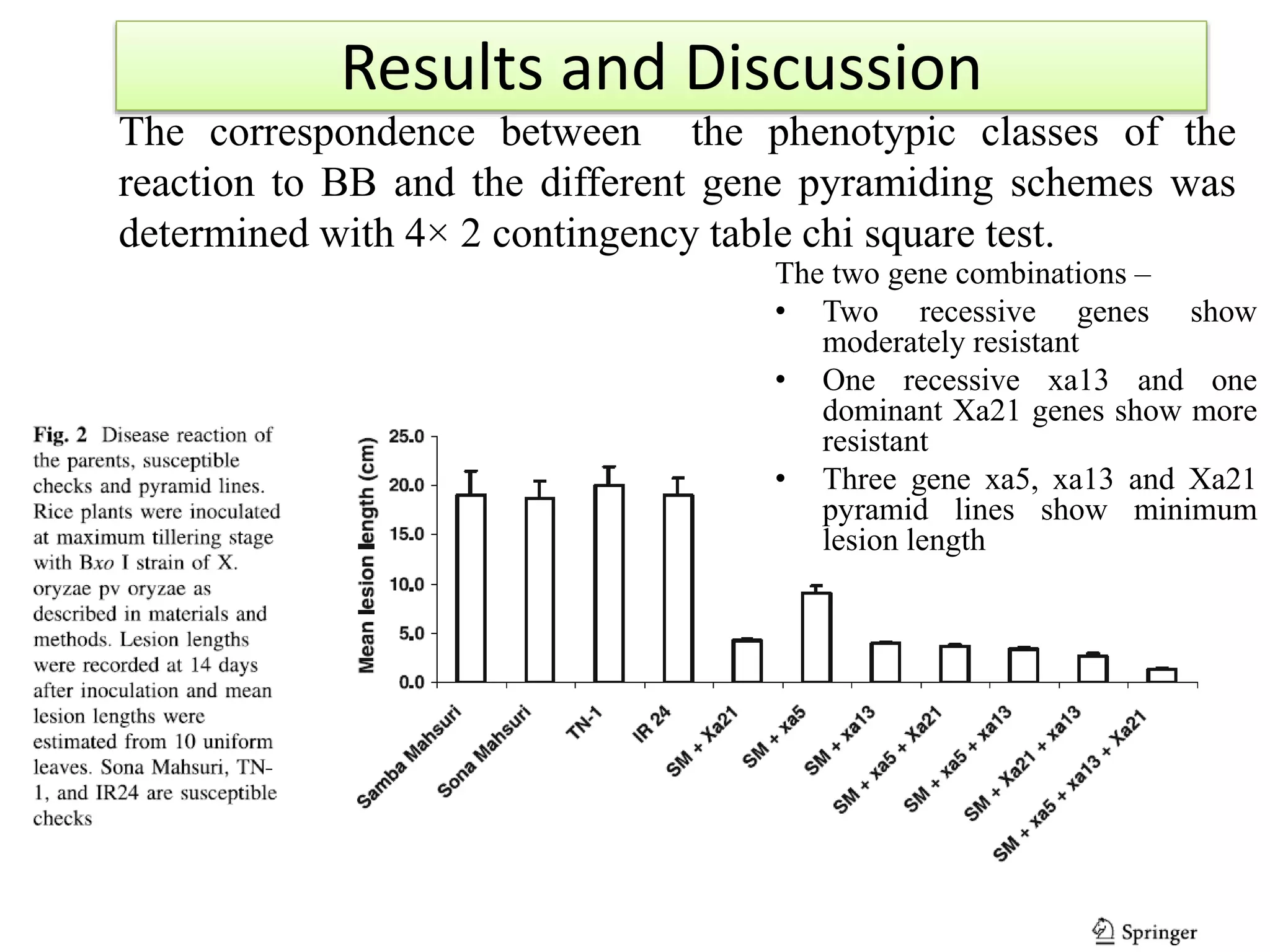
3) Two-gene and three-gene pyramid lines were developed and evaluated. The three-gene pyramid lines showed the highest resistance, with minimum lesion lengths after artificial inoculation.