Rice Diseases Introduction and BLB disease resistance
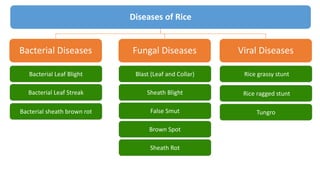
- 1. Diseases of Rice Bacterial Diseases Viral Diseases Fungal Diseases Bacterial Leaf Blight Bacterial Leaf Streak Bacterial sheath brown rot Blast (Leaf and Collar) Sheath Blight False Smut Brown Spot Sheath Rot Rice grassy stunt Rice ragged stunt Tungro
- 2. Severity of important biotic stresses that affect rice plants in India.
- 3. Bacterial Leaf Blight • Caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. • Wilting of seedlings and yellowing and drying of leaves. • Estimated to cause annual rice production losses of 20–30 percent throughout rice-growing countries in Asia (Kim et al., 2019) • It occurs in areas that have weeds and stubbles of infected plants. • It can occur in both tropical and temperate environments, particularly in irrigated and rainfed lowland areas. The disease favors temperatures at 25−34°C, with RH > 70%. • It is commonly observed when strong winds and continuous heavy rains occur, allowing the disease- causing bacteria to easily spread through ooze droplets on lesions of infected plants. • Bacterial blight can be severe in susceptible rice varieties under high nitrogen fertilization.
- 4. Bacterial Leaf Blight • The disease was fist reported from Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan in 1884. Subsequently, the disease was reported from East, South and Southeast Asian countries (Devadath 1992; Win et al. 2013) and Australia (Ou 1985). • In Africa, the disease was fist reported in West Africa by Buddenhagen et al. (1979) from Mali. Subsequently, it was reported from many other West African and some East African countries (Sere et al. 2013). • BLB has become a major problem in several West African countries like Burkina Faso, Niger and Mali causing 50–90 % yield loss (Sere et al. 2005; Basso et al. 2011). • Yield losses due to this disease ranging from 2 to 74 % depending on varieties, season, weather conditions, stages of infection and nitrogen application have been reported (Reddy 1989). Global distribution of bacterial blight of rice (Laha et al., 2017)
- 5. Disease life cycle • The ratoons and self-grown plants in lowlands constitute the primary source of inoculum. In double- cropped areas, infected straw and stubble, infected wild rice and living rice plants growing in ponds, ditches and irrigation channels during off season serve as a source of inoculum. • Staggered sowing and transplanting result in overlapping of crops, and in such scenario the spread of the disease is very easy and fast. • The pathogen surviving on some grasses like Leersia hexandra, Cyperus rotundus and Panicum repens and irrigation water contaminated with bacteria flowing through the fields also act as a source of primary inoculum. • Combination of cloudy and rainy weather or drizzling condition, floods, cyclone or strong winds, excess and late top dressing of nitrogenous fertilizer and moderate temperature of 28–30 °C favor the rapid buildup of the BB disease (Ezuka and Kaku 2000). Disease life cycle of the rice bacterial blight caused by bacteria- Xoo, including the influence of disease secondary host plant on disease severity.
- 6. Bacterial Leaf Blight • Application of chemicals or antibiotics is very costly and is not very effective. • Breeding and deployment of high-yielding varieties (HYVs) carrying major resistance genes (R genes) are the most effective approach for managing the disease. • To date, at least 42 BLB resistance genes have been identified, and some of them viz., Xa4, xa5, xa13, Xa21 have been extensively used for development of BB resistant rice varieties. • Large scale and long-term cultivation of varieties and hybrids with a single gene results in the breakdown of resistance due to a high degree of pathogenic variation. • Pyramiding of two or three Xa genes can enhance the durability and spectrum of resistance against BLB.
- 7. S. No Gene Chr# Resistance to Xoo race Donor cultivar 1 Xa1 4 Japanese race-I Kogyoku, IRBB1 2 Xa2 4 Japanese race-II IRBB2 3 Xa3/Xa26 11 Chinese, Philippine, and Japanese races Wase Aikoku 3, Minghui 63, IRBB3 4 Xa4 11 Philippine race-I TKM6, IRBB4 5 xa5 5 Philippine races I, II, III IRBB5 6 Xa6/xa3 11 Philippine race 1 Zenith 7 Xa7 6 Philippine races DZ78 8 xa8 7 Philippine races PI231128 9 Xa9 11 Philippine races Khao Lay Nhay and Sateng 10 Xa10 11 Philippine and Japanese races Cas 209 11 Xa11 3 Japanese races IB, II, IIIA, V IR8 12 Xa12 4 Indonesian race V Kogyoku, Java14 13 xa13 8 Philippine race 6 BJ1, IRBB13 14 Xa14 4 Philippine race 5 TN1 15 xa15 - Japanese races M41 mutant 16 Xa16 - Japanese races Tetep 17 Xa17 - Japanese races Asominori 18 Xa18 - Burmese races IR24, Miyang23, Toyonishiki 19 xa19 - Japanese races XM5 (mutant of IR24) 20 xa20 - Japanese races XM6 (mutant of IR24) 21 Xa21 11 Philippine and Japanese races O. longistaminata, IRBB21 S. No Gene Chr# Resistance to Xoo race Donor cultivar 22 Xa22(t) 11 Chinese races Zhachanglong 23 Xa23 11 Indonesian races O. rufipogon (CBB23) 24 xa24 2 Philippine and Chinese races DV86 25 xa25(t) 12 Chinese and Philippine races Minghui 63, HX-3 (somaclonal mutant of Minghui 63) 26 xa26(t) - Philippine races Nep Bha Bong 27 Xa27(t) 6 Chinese strains and Philippine race 2 to 6 O. minuta IRGC 101141, IRBB27 28 xa28(t) - Philippine race2 Lota sail 29 Xa29(t) 1 Chinese races O. officinalis(B5) 30 Xa30(t) 11 Indonesian races O. rufipogon (Y238) 31 xa31(t) 4 Chinese races Zhachanglong 32 xa32(t) 11 Philippine races Oryza australiensis (introgression line C4064) 33 Xa33 7 Thai races Ba7 34 Xa33(t) - O. nivara 35 xa34(t) - Thai races Pin Kaset xa34(t) O. brachyantha 36 Xa35(t) 11 Philippine races Oryza minuta (Acc. No.101133) 37 Xa36(t) Philippine races C4059 38 Xa38 Indian Punjab races O. nivara IRGC81825 39 Xa39 11 Chinese and Philippines races FF329 40 Xa40(t) 11 Korean BB races IR65482-7-216-1-2 41 xa41(t) Various Xoo strains Rice germplasm 42 xa42 3 Japanese Xoo races XM14, a mutant of IR24 Bacterial Leaf Blight resistance genes (Chukwu et al., 2019)
- 8. List of cloned rice R genes, cognate Xanthomonas oryzae Avr genes (Kumar et al., 2020)
- 9. The schematic representation for the molecular signaling involved during host and pathogen interaction Hijacking host key genes (SWEET11/13/14) by pathogen Utilization of host metabolic resources like Kreb’s intermediate by pathogen. (Kumar et al., 2020)
- 10. Resistance mechanism by BLB resistance genes • Xa1 encodes NB-LRR type protein and confers resistance to Xoo isolates by recognizing TALEs. Xa21 and Xa3/Xa26 encode plasma membrane localized LRR receptor like kinase proteins and confer race specific resistance to Xoo. • Xa4 encode cell wall associated protein kinase and boosts resistance to Xoo by strengthening the cell wall. The recessive gene xa5 encodes gamma subunit of the basal transcription factor IIA 5 (TFIIAg5) and is a substitution variant of a single amino acid V39E. The non-variant version of the basal transcription factor is required for survival of Xoo in rice. • The genes, xa13, xa25, and xa41, encode transmembrane proteins which are basically sugar transporters, and the dominant alleles of these genes are specifically induced by TALEs produced by the pathogen for establishing infection. Xa10 encodes an ER membrane protein, which elicits Ca2+ depletion in ER membrane inducing host cell death. • Xa23 is known to be an executor R gene that encodes a protein with 113 amino acid residues. The transcription of Xa23 is triggered by AvrXa23, a TALE from Xoo (Wang et al., 2015). Xa27 encodes apoplast protein, which triggers thickening of the secondary cell wall of the vascular bundle elements (Gu et al., 2004). • Both dominant and recessive like Xa1, Xa4, Xa21, xa5, and xa13 confer race specific resistance to Xoo, respectively, whereas the recessive alleles of genes such as xa1, xa4, and xa21 and dominant alleles of Xa5 and Xa13 are susceptible to Xoo (Zhang and Wang, 2013).
- 11. Host Differential X. oryzae pv. oryzae pathotypes a I II III IV V VI VII VIII IX X XI IRBB1 (Xa1) S S S S S S S S S R, M S IRBB3 (Xa3) S S S S S S S S S R S IRBB4 (Xa4) S S S S R, M M R, M R, M S R S IRBB5 (xa5) S S S S R, M R R R R R, M S IRBB7 (Xa7) S S S S S S S R R R, M S IRBB8 (xa8) S S R, M R, M R, M R R, M S S R S IRBB10 (Xa10) S S S S S S S S S R, M S IRBB13 (xa13) R R R R R S S S S R, M S IRBB21 (Xa21) R, M S R, M S R M R, M R R, M R S IR8 (Xa11) S S S S S R S S S R, M S IR24 S S S S S S S S S R, M S a Based on mean lesion lengths, the nature of responses were classified into susceptible (S) (above 10 cm), moderately resistant (MR) (between 5-10 cm) and resistant (R) (up to 5 cm). R, M is indicated when some isolates in the pathotype give a resistant reaction while other isolates give a moderately resistant reaction. Pathotype and Genetic Diversity amongst Indian Isolates of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Frequency of X. oryzae pv. oryzae pathotypes in India Effectiveness of Xa genes against Indian X. oryzae pv. oryzae isolates. Statewise distribution of X. oryzae pv. oryzae strains collected from India. (Mishra et al., 2013)
- 12. Gene Pyramidsb Xoo pathotypes a I II III IV V VI VII VIII IX X XI IRBB52 (Xa4 + Xa21) R Mc R S R Rc R R R R Mc IRBB54 (xa5 + Xa21) R S R Mc R R R R R R Mc IRBB55 (xa13 + Xa21) R R R R R Sd M R M R Mc IRBB58 (Xa4 + xa13 + Xa21) R R R R R M R R M R Mc IRBB59 (xa5 + xa13 + Xa21) R R R R R R R R R R Rc IRBB60 (Xa4 + xa5 + xa13 + Xa21) R R R R R R R R R R R Reactions of X. oryzae pv. oryzae pathotypes on Xa gene pyramid lines • A rice line with xa5, xa13 and Xa21 resistance genes is resistant to all strains collected from different locations of India. • This three gene combination appears to be the most suitable Xa gene combination to be deployed in Indian rice cultivars. (Mishra et al., 2013)
- 13. Molecular Breeding for BLB Resistance in Rice • Efforts have been made to improve resistance of rice against BLB through conventional and modern breeding techniques. • This is achieved through standard crossing and/or backcrossing an elite rice variety/hybrid with the genotype carrying the resistance gene to BLB. • The practice not only reduces the use of chemical pesticides but also offers a sustainable way for management of this disease. • The incorporation of several resistance (R) genes has been facilitated through marker-assisted backcrossing (MABC) or conventional backcross breeding, and resistance breeding has played a significant role in defending rice from the attack by the pathogen.
- 14. Cultivars improved for bacterial blight resistance through breeding/marker-assisted breeding (Kumar et al., 2020)
