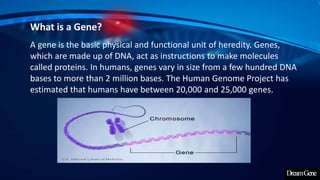
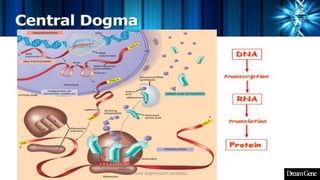
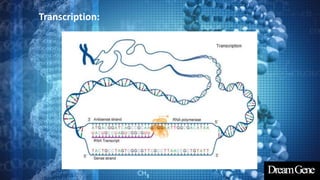
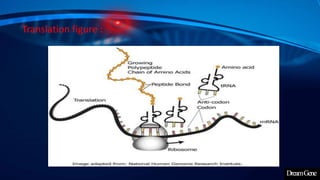
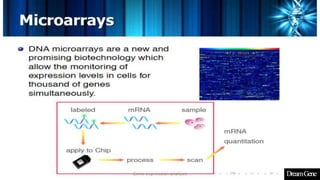
This presentation introduces gene expression analysis. It defines a gene as the basic unit of heredity made of DNA that codes for proteins. Gene expression analysis studies how genes are transcribed into RNA and translated into proteins. The central dogma of biology is explained as transcription of DNA to mRNA and translation of mRNA to proteins. Techniques for measuring gene expression at different levels like microarrays, RNA-Seq and reporter genes are also presented. Applications of gene expression analysis include cancer research and protein purification.