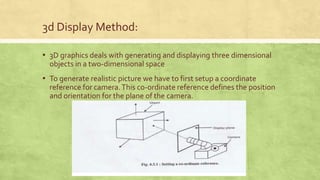
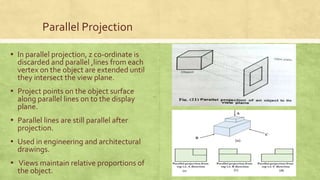
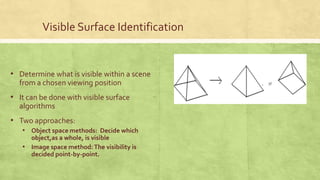
This presentation discusses 3D display methods. It is presented by 4 group members and covers topics such as parallel projection, perspective projection, depth cueing, visible line identification, visible surface identification, and surface rendering. Parallel projection discards the z-coordinate and extends parallel lines until they intersect the view plane, while perspective projection shows lines converging to give a realistic view. Depth cueing identifies the front and back of objects by varying intensity. Algorithms also determine which lines and surfaces are visible from the viewing position. Surface rendering sets intensities based on lighting and material properties.