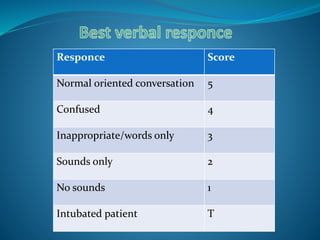
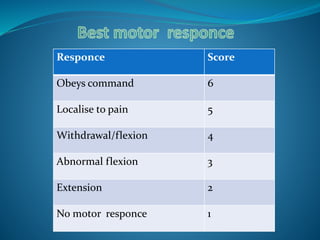
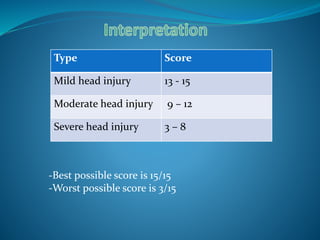
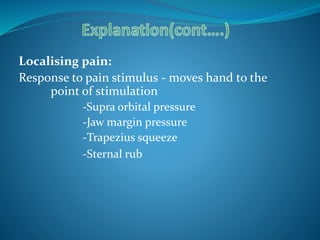
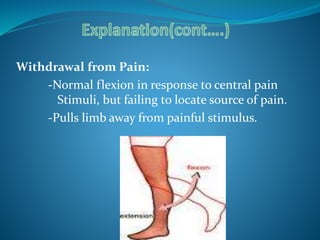
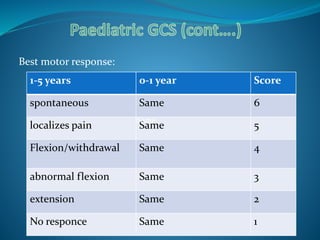
The Glasgow Coma Scale is a neurological scale used to assess a person's level of consciousness after brain injury. It was developed in 1974 by Graham Teasdale and Bryan Jennett. The scale consists of 3 components - eye opening, verbal response, and motor response - each of which are assigned a score between 1-5. The scores from each component are added to give a total score between 3-15, with lower scores indicating a worse level of consciousness. The Glasgow Coma Scale provides a standardized measure for initial assessment and ongoing monitoring of patients with brain injuries.