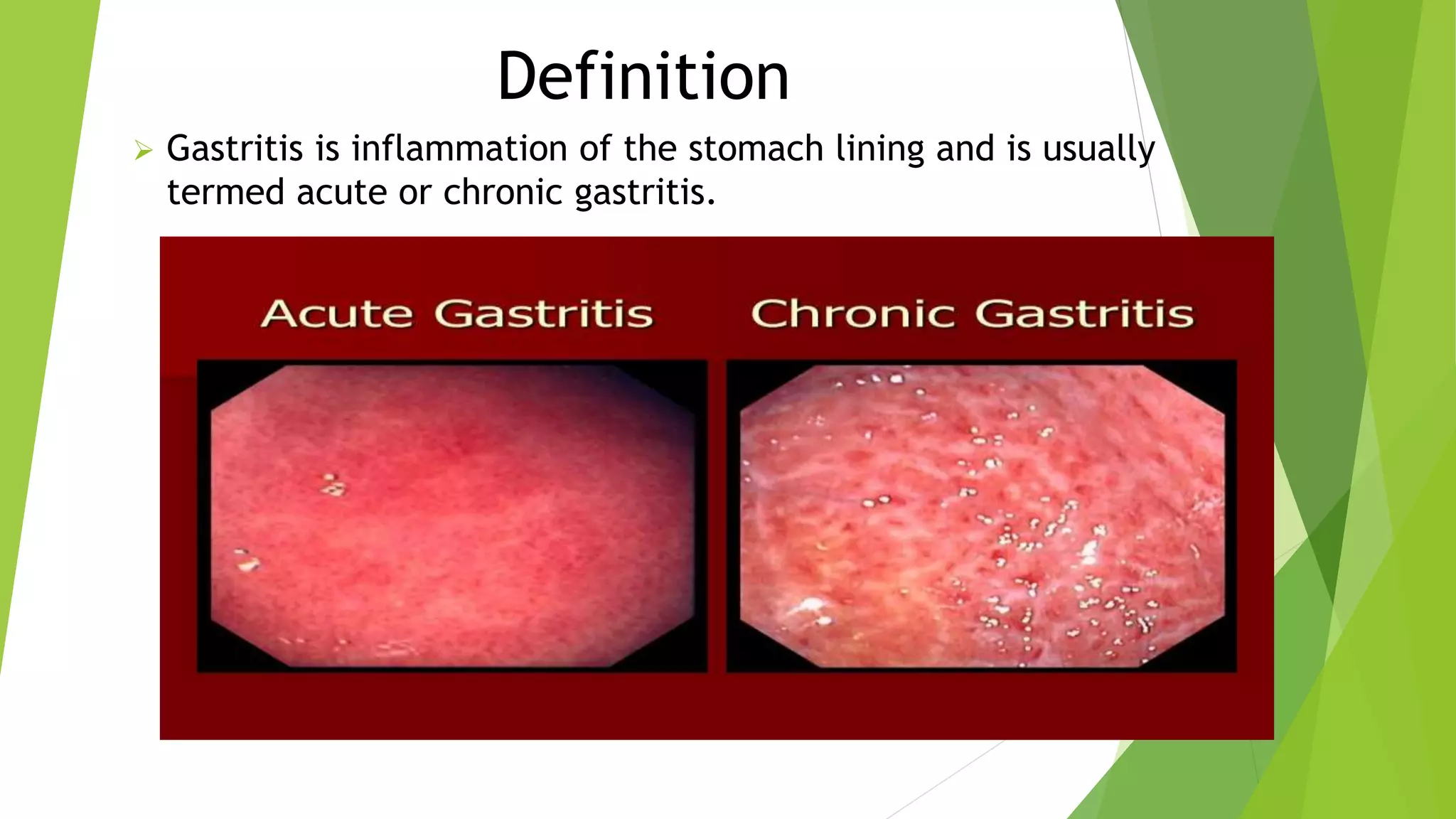
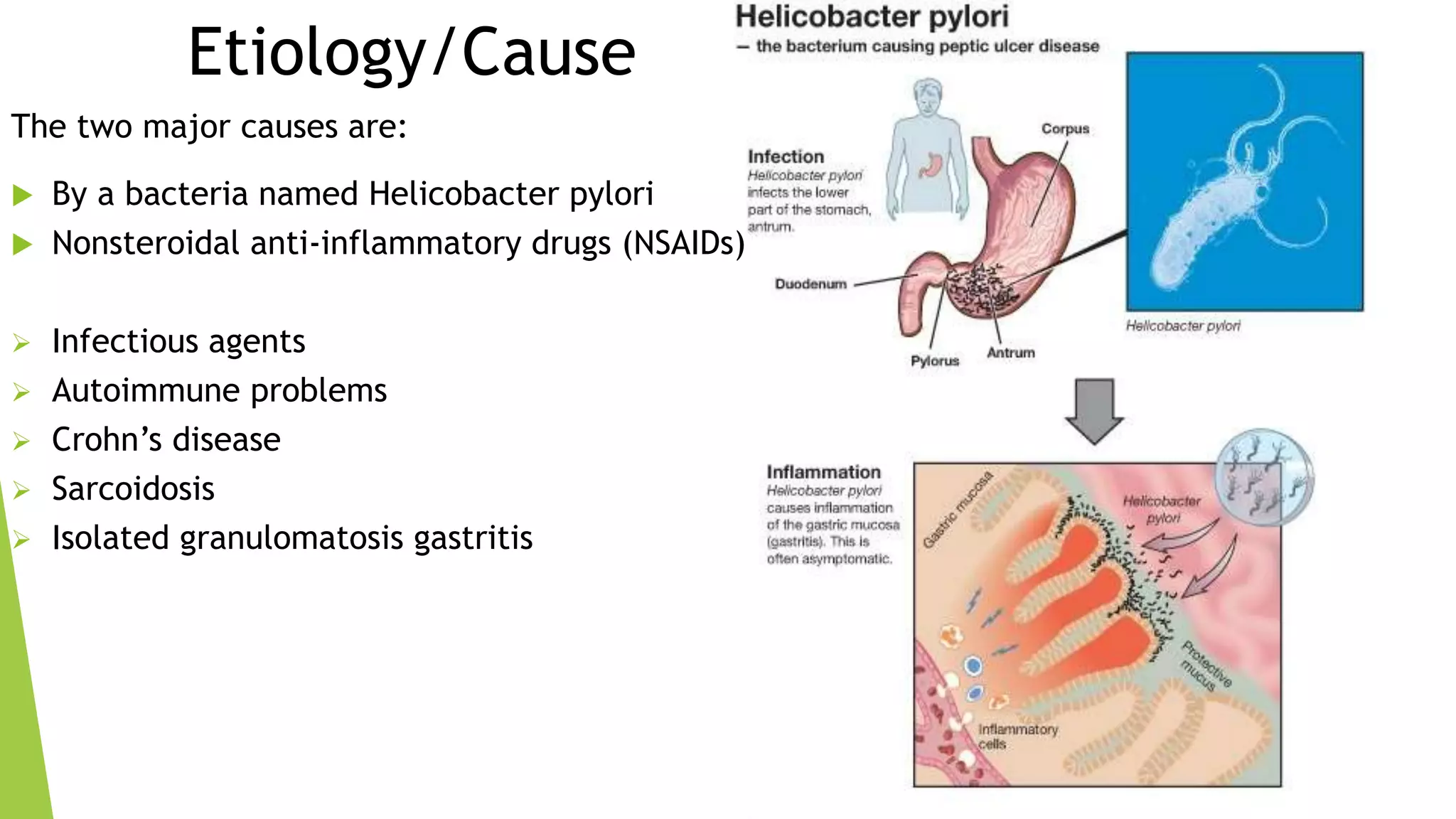
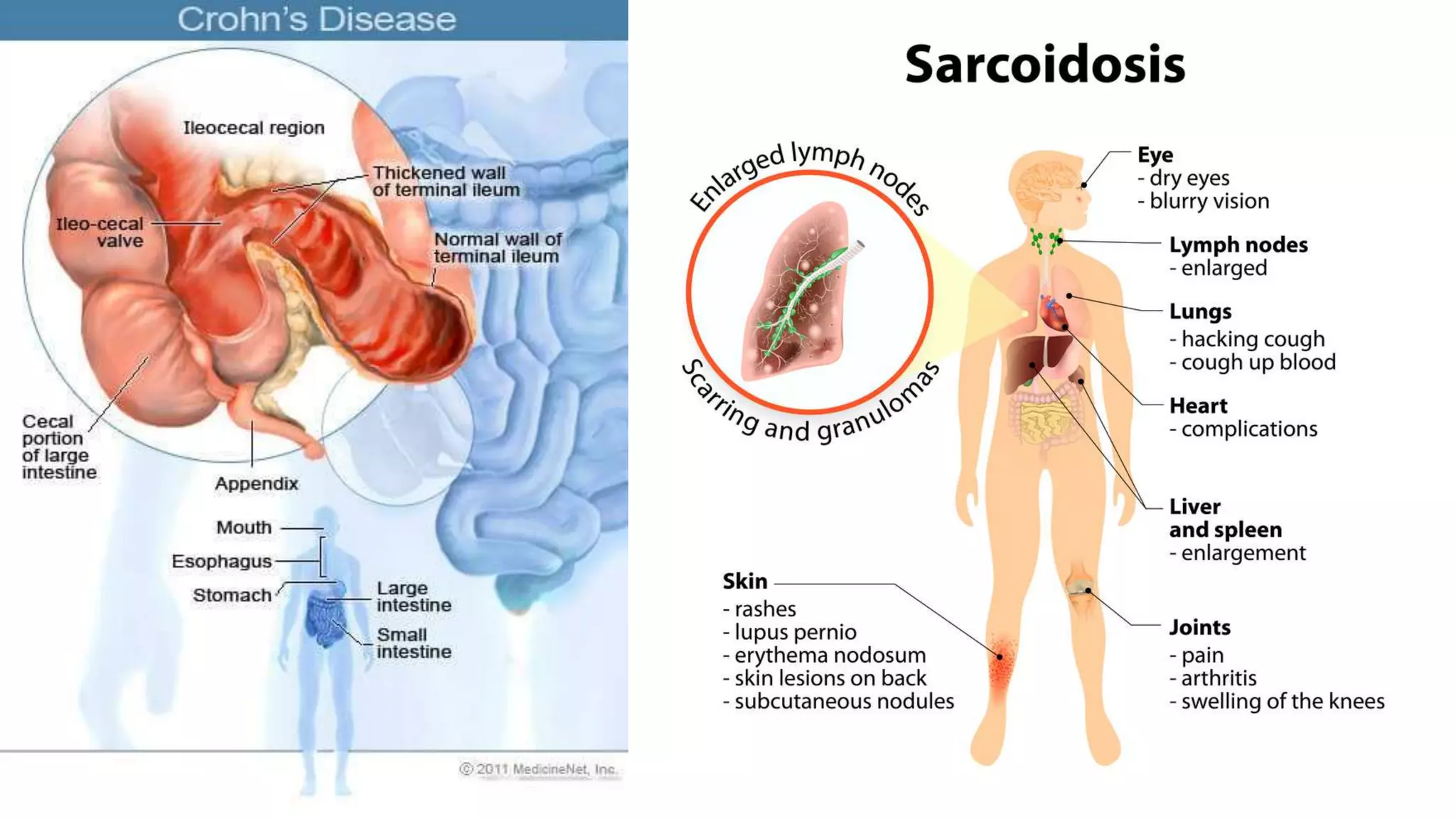
This document discusses gastritis, an inflammation of the stomach lining. It defines gastritis and lists common signs and symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. The major causes are identified as Helicobacter pylori bacteria and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Treatment involves antibiotics to kill H. pylori, medications to reduce acid production, antacids, and lifestyle changes like avoiding smoking and NSAIDs. Nursing care includes giving antiemetics if vomiting, administering IV fluids, providing a bland diet, and educating patients about the disorder. The document also notes that the elderly are more susceptible due to thinning stomach lining with age.