The document discusses the potential of serious games and immersive technologies like virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) in enhancing the understanding of cultural heritage. It highlights the challenges in effectively using these tools, such as the lack of user engagement, preservation issues, and interaction design problems. The conclusion calls for better collaboration between the gaming and cultural heritage sectors to create more meaningful and reusable digital experiences.


























![ALIA
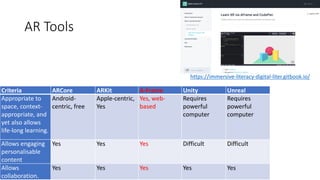
• Include suitable content in an appropriate, accessible space.
• Feature engaging personalisable content that can be examined in
stages or detail.
• Affords opportunities for reflection, and, [adding media literacy]
affords guides and learners the ability to construct meaning, think
creatively and solve problems.
• Provides multiple learning modes, media and material and, [adding
digital dexterity]: critical engagement with media and lifelong
learning.
• Allows collaboration.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20211006-jyv-graz-211006084657/85/Games-XR-DH-Graz-talk-06-10-2021-33-320.jpg)