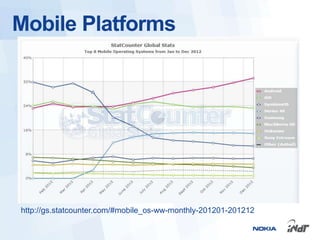
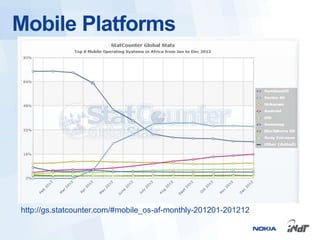
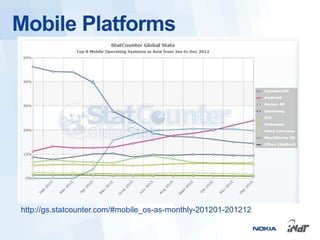
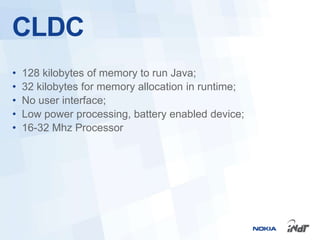
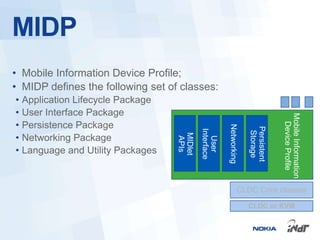
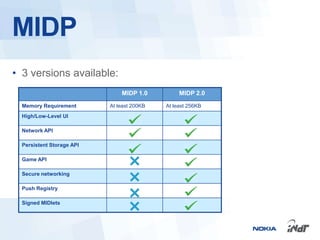
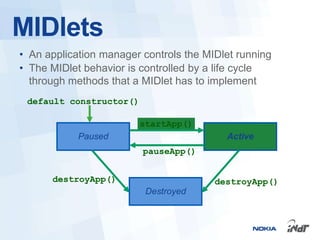
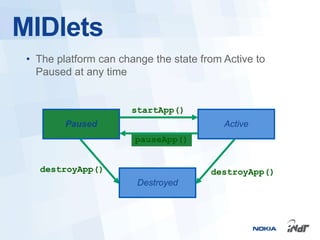
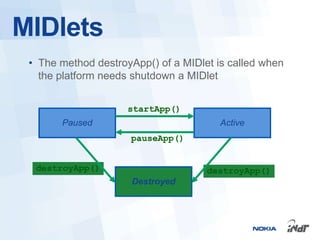
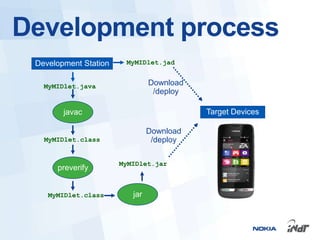
The document outlines the development of mobile games for Nokia Asha devices using Java ME, highlighting the significance of Nokia's app store and the platform's architecture. It discusses Java ME configurations, profiles, and key components like MIDP and CLDC, detailing the lifecycle and management of MIDlets. Furthermore, the document provides insights into IDE integration and the development process for creating Java applications tailored for resource-limited devices.