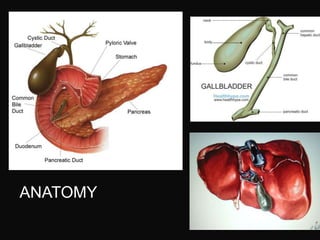
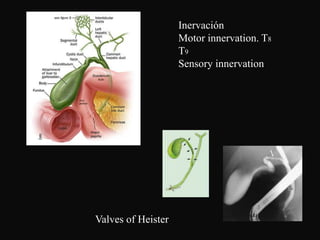
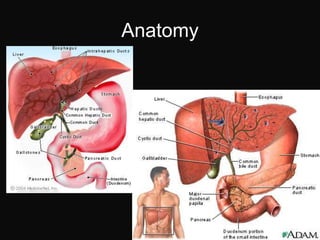
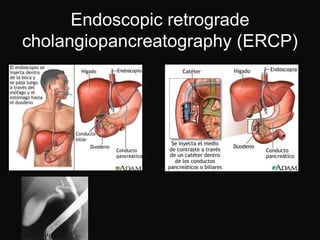
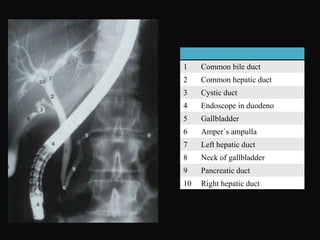
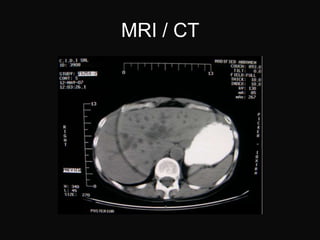
The document summarizes information about the gallbladder and extrahepatic biliary tree. It discusses the embryology, anatomy, physiology, composition of bile, functions of the gallbladder, and radiologic diagnosis of biliary tract disease. Key points include that the liver and biliary structures develop during the fourth week of fetal life, bile is produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder, and techniques for radiologic diagnosis include plain abdominal films, ultrasonography, HIDA scans, ERCP, and MRI/CT.