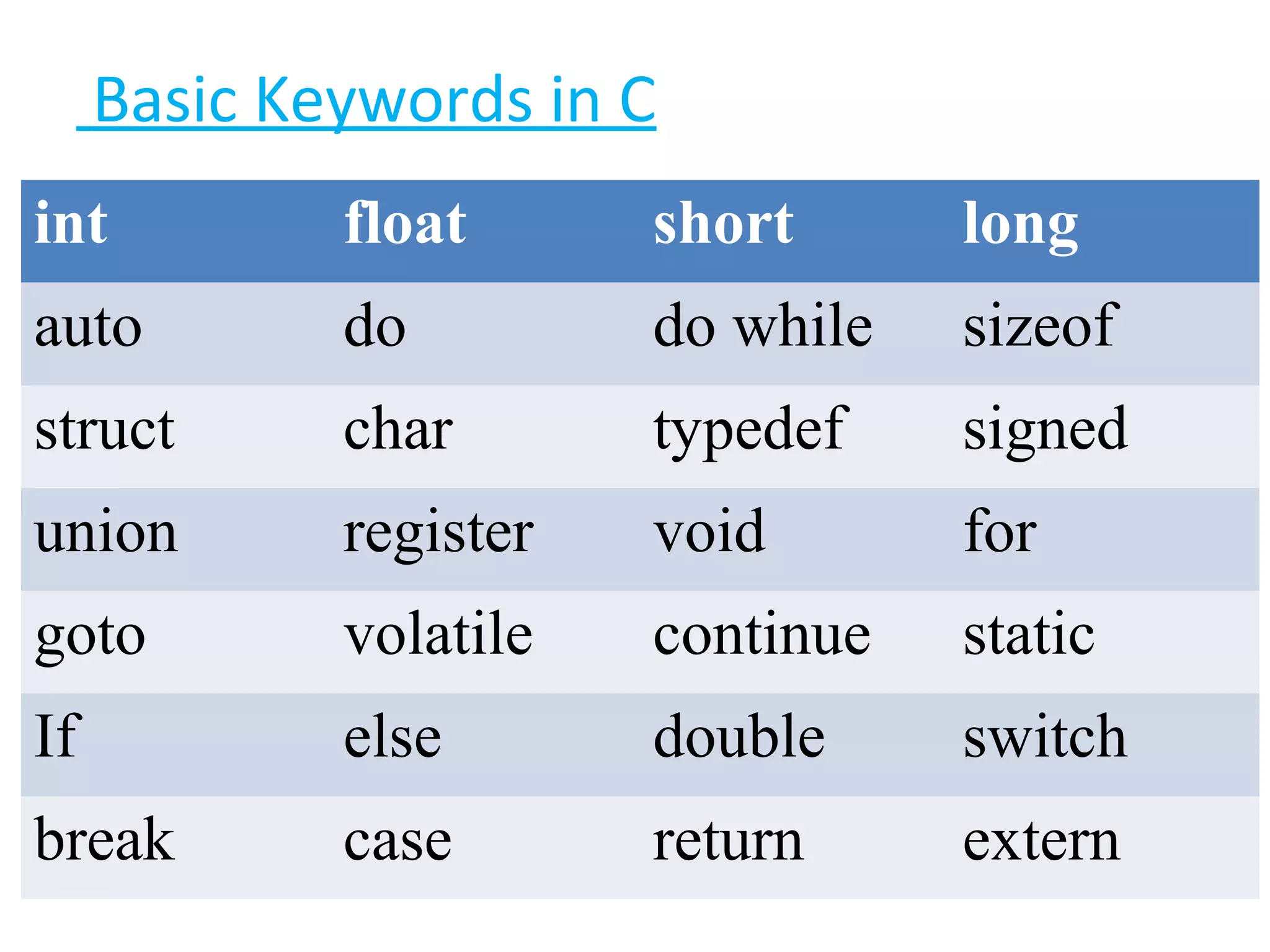
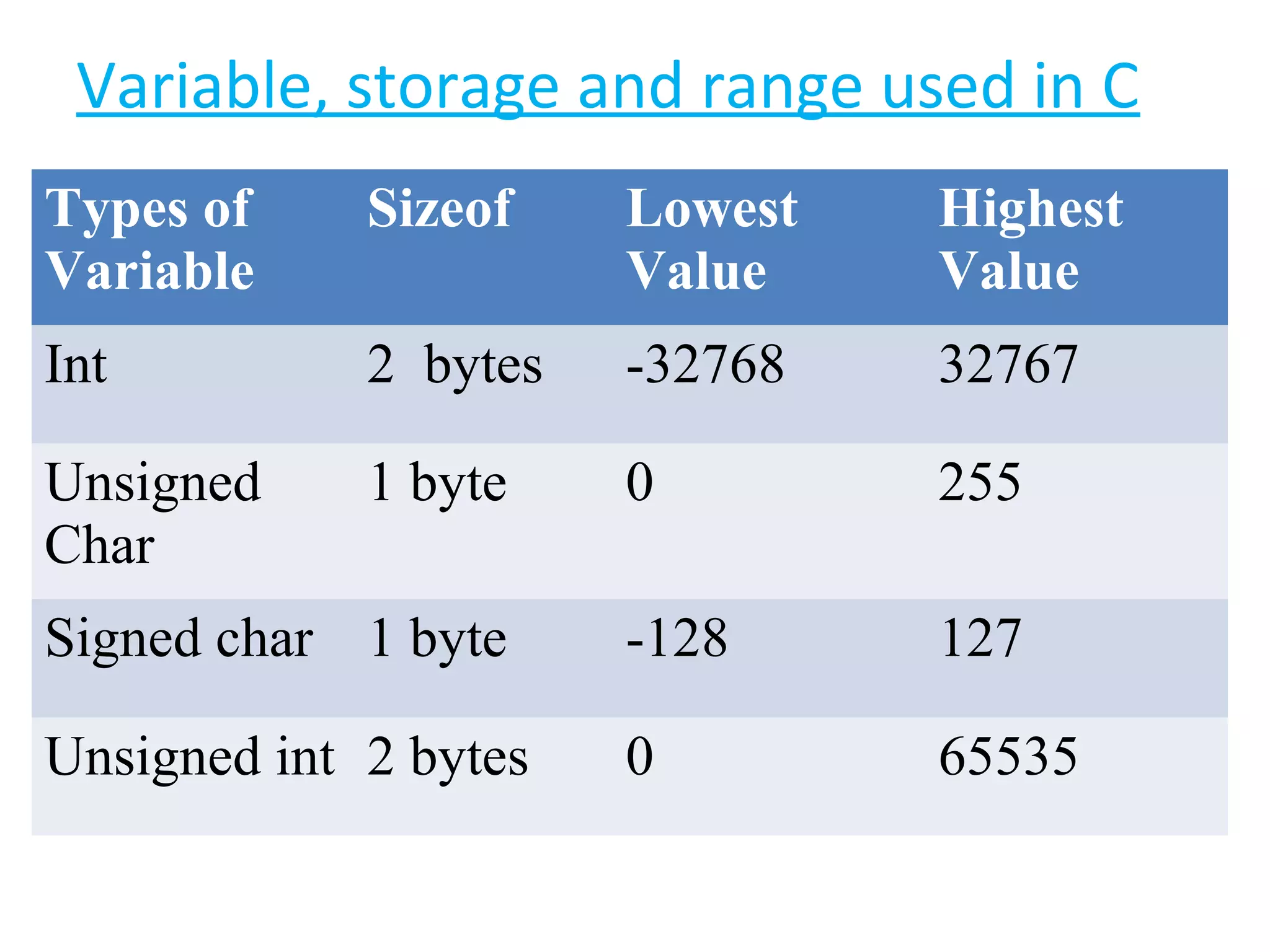
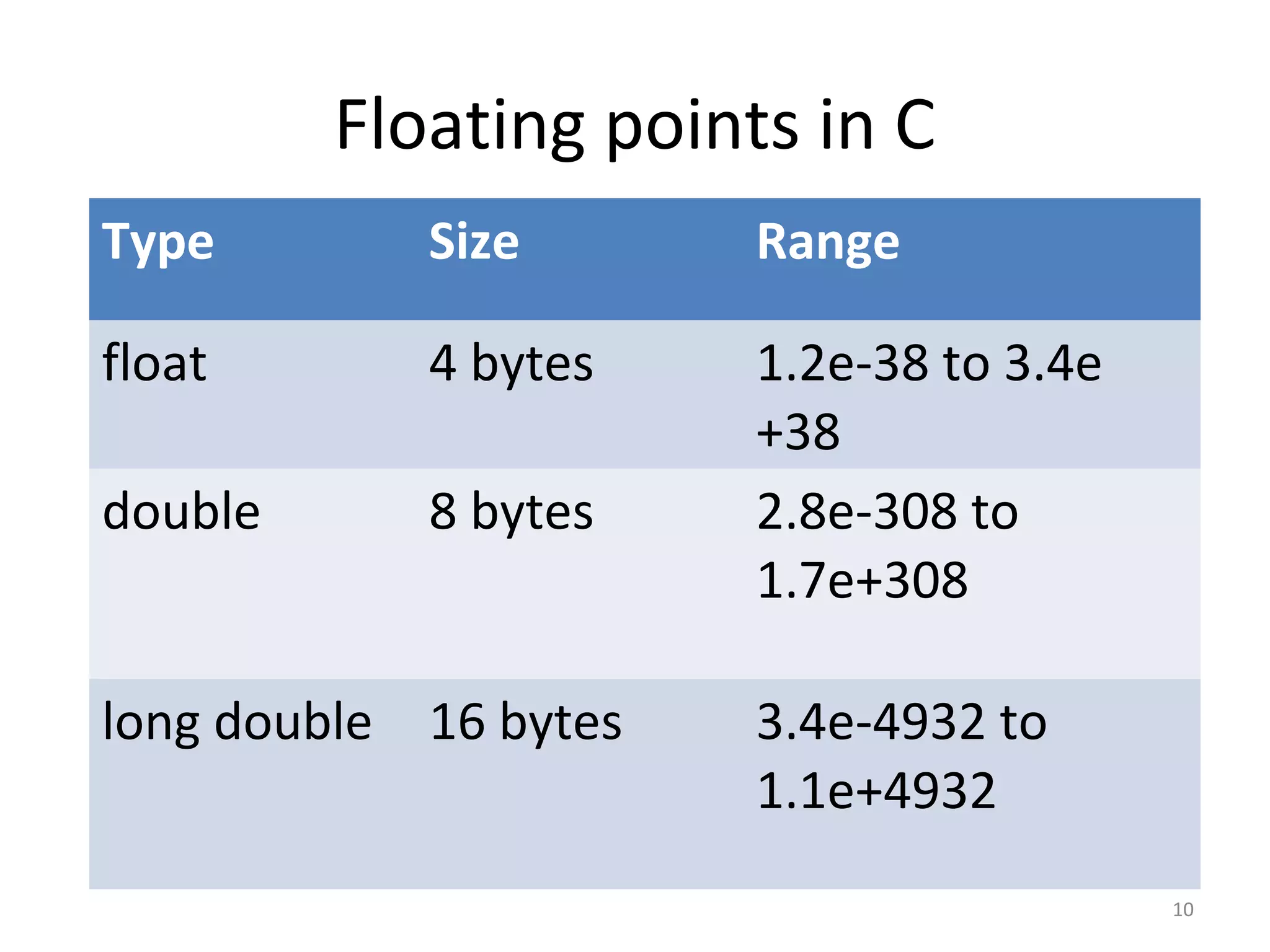
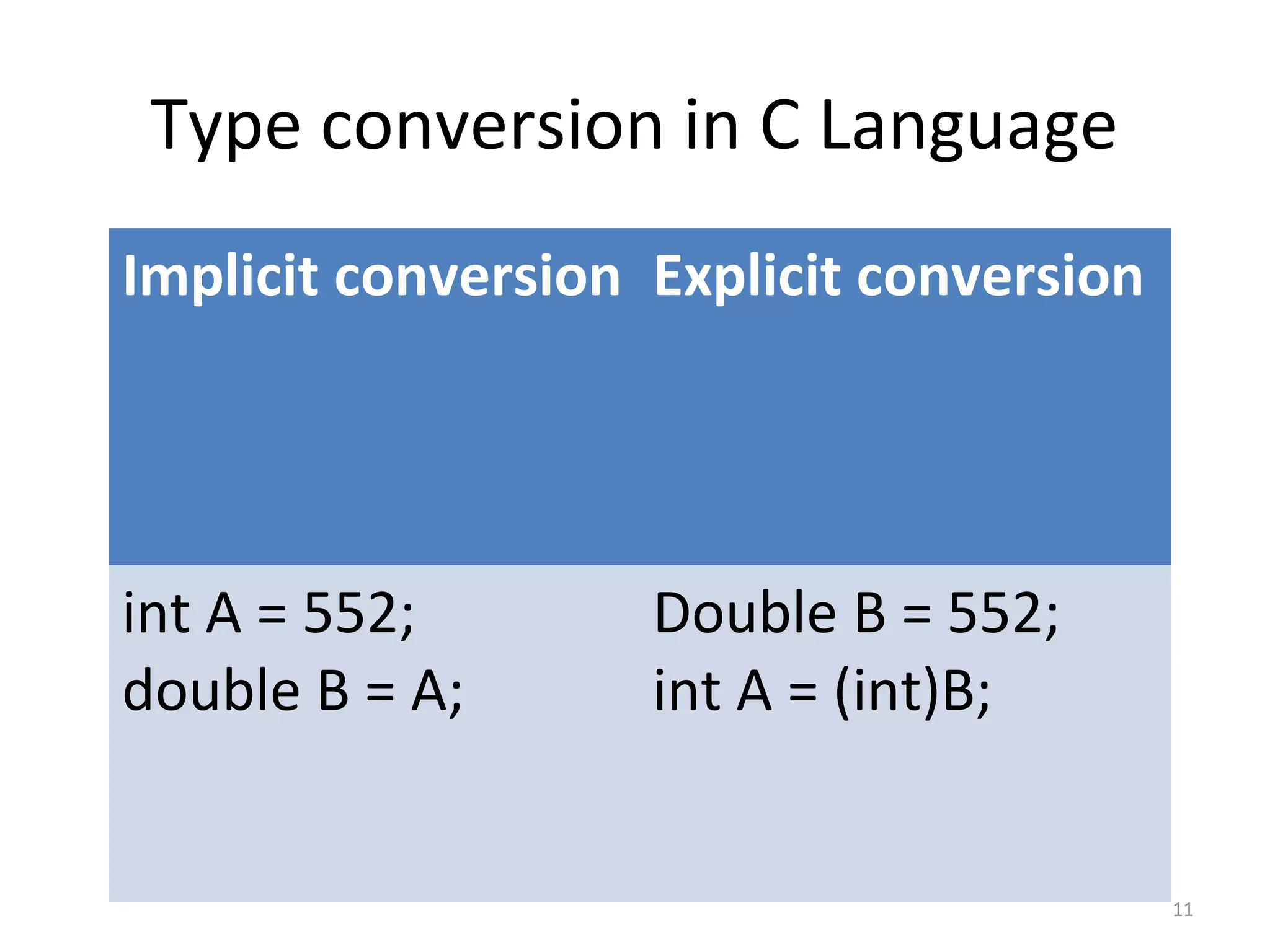
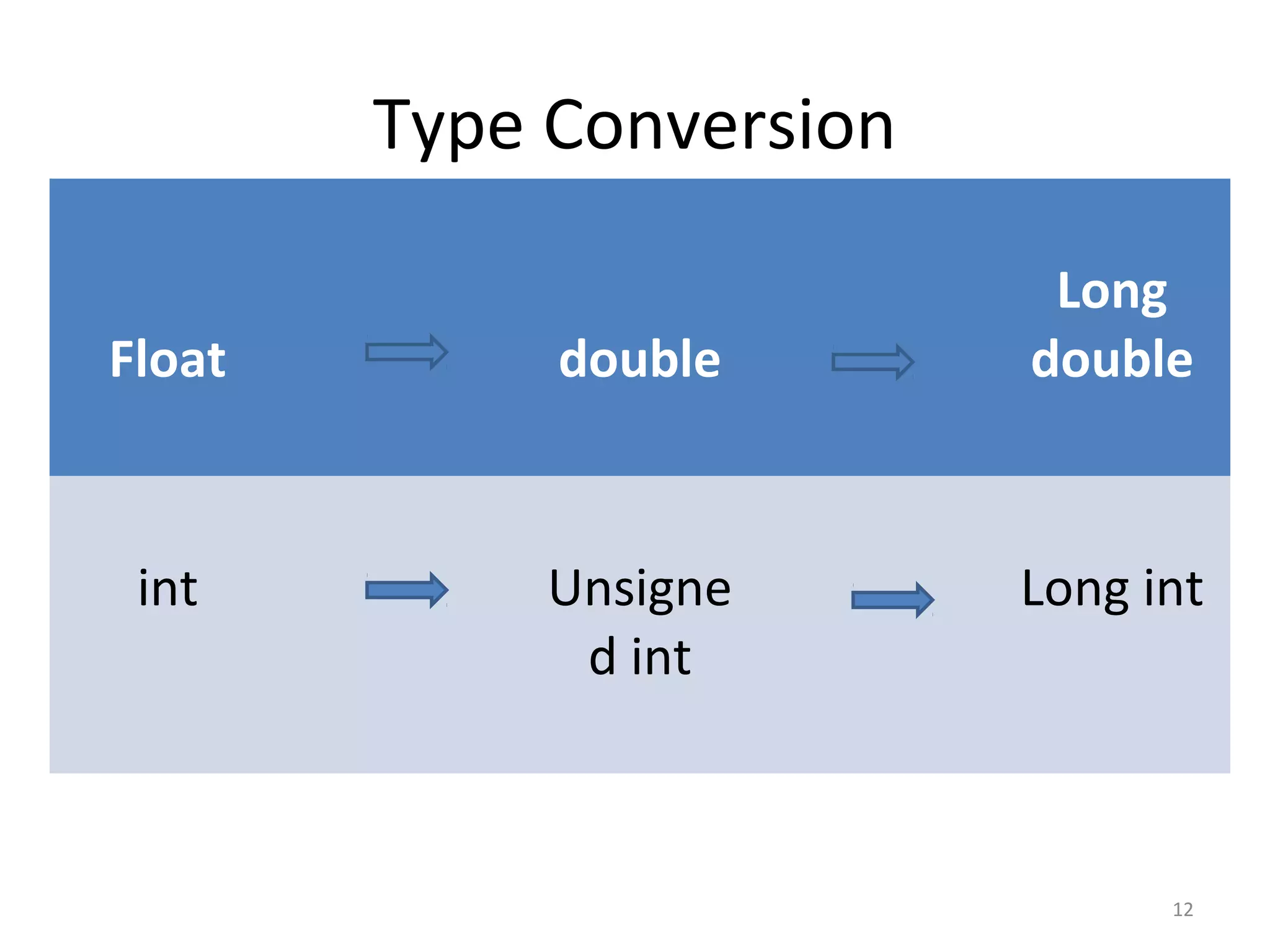
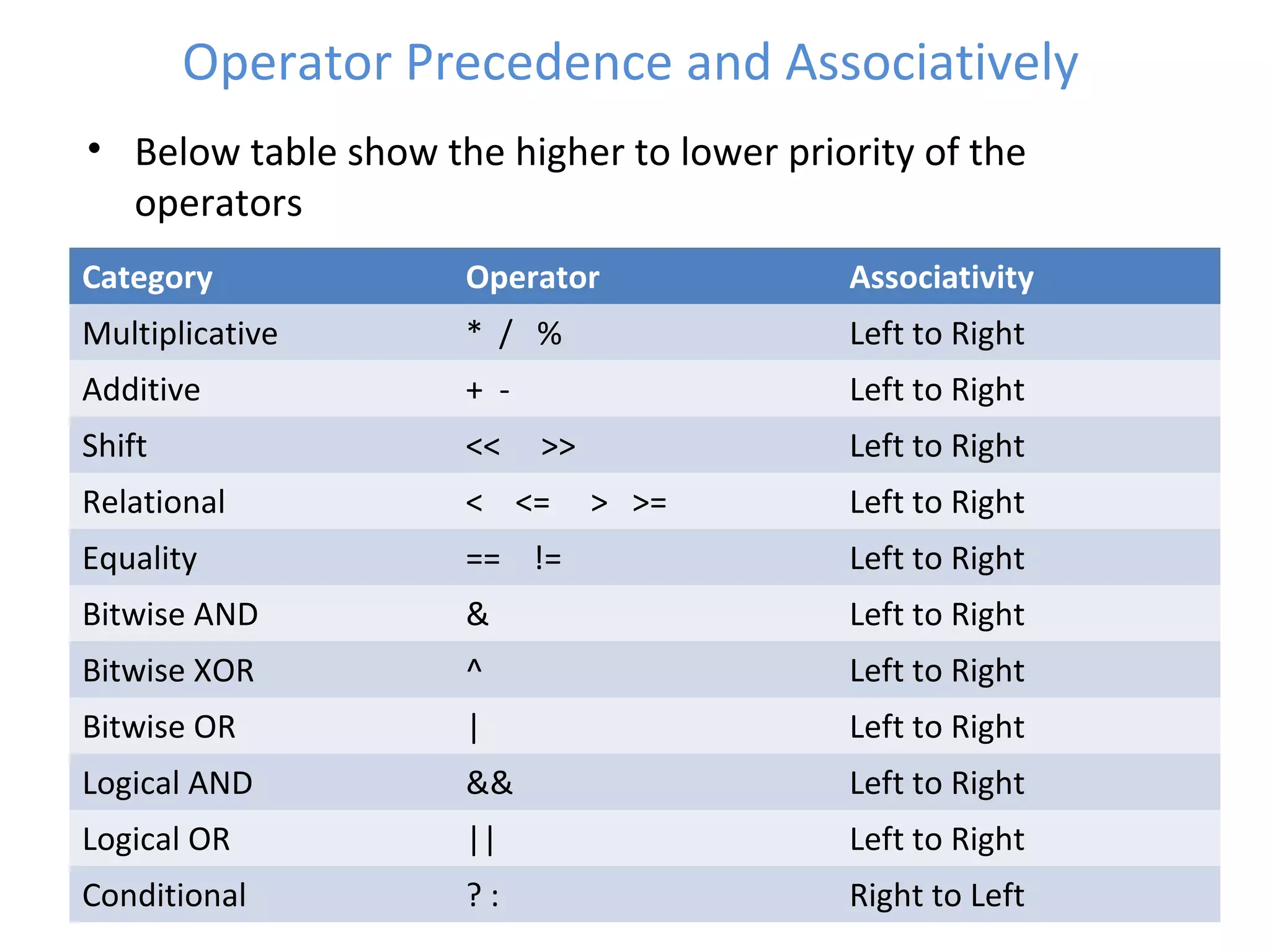
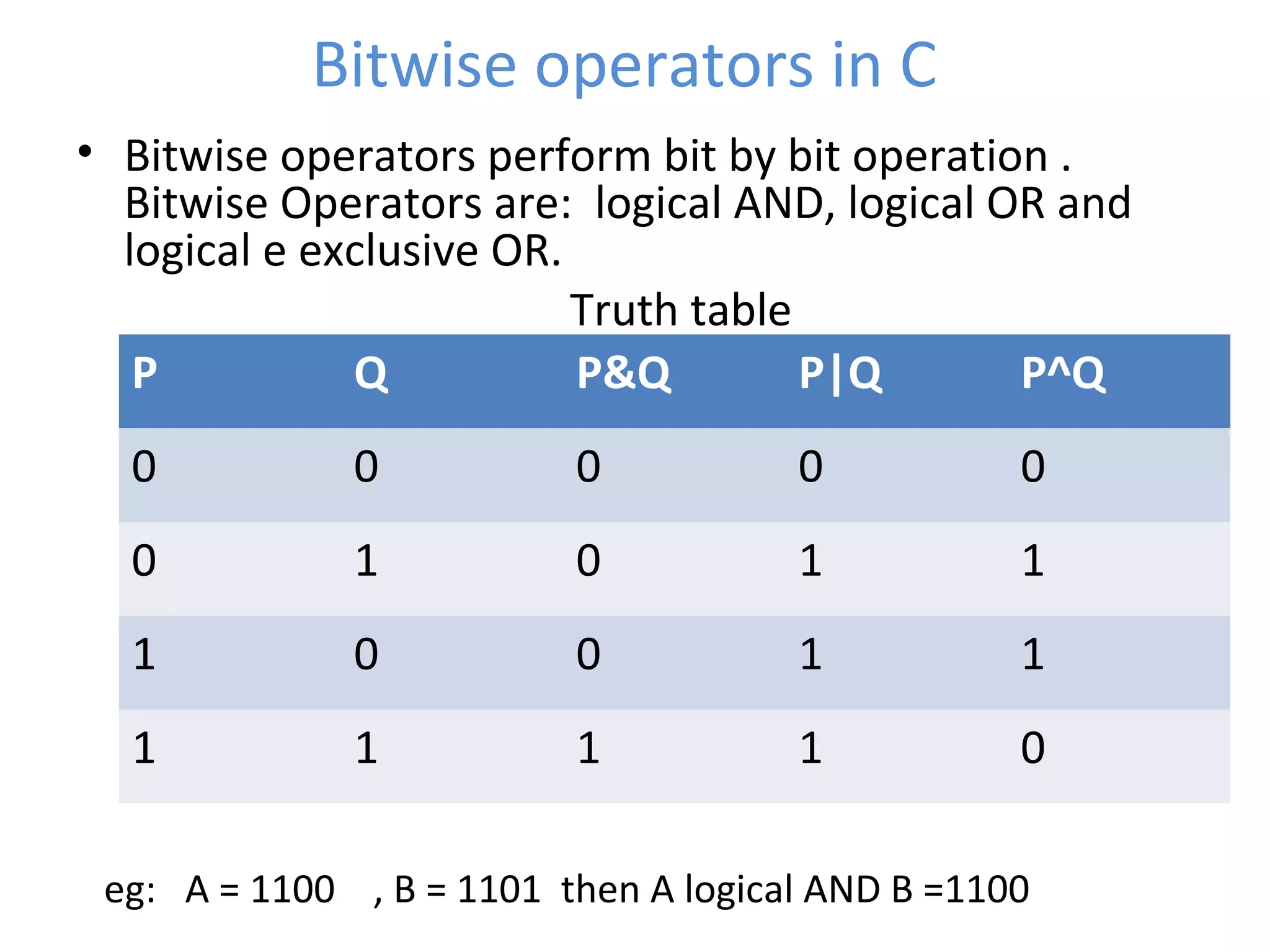
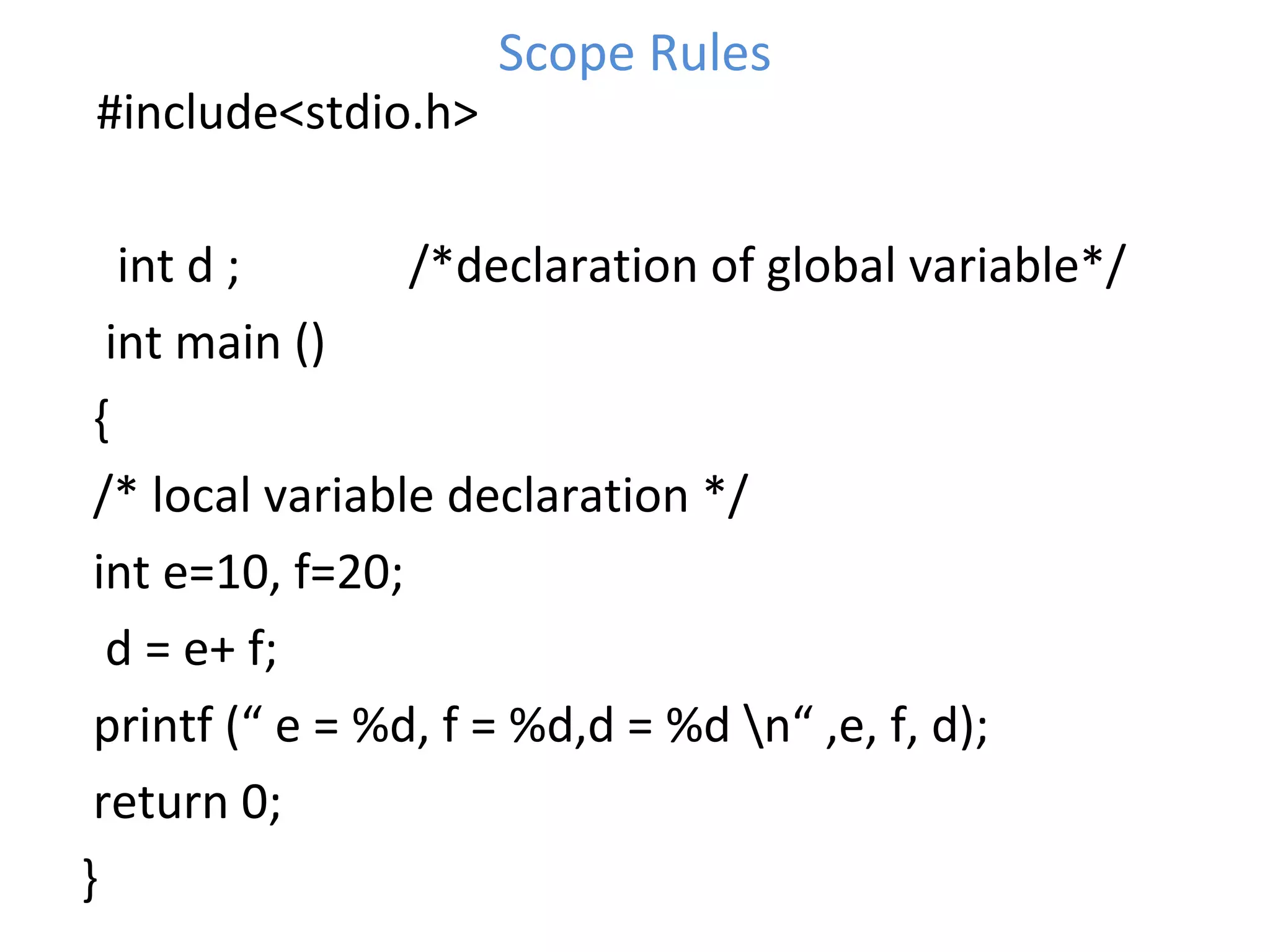
This document provides an introduction to fundamentals of the C programming language. It covers topics such as compiling and linking C code, basic keywords, variable types and ranges, data types, floating point variables, type conversion, expressions, operators precedence and associativity, bitwise operators, conditional statements, and scope rules. The document is presented over multiple slides by three authors, with each author covering several related topics in the C language.