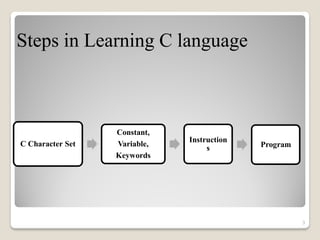
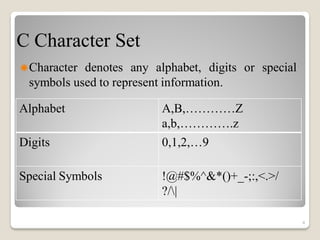
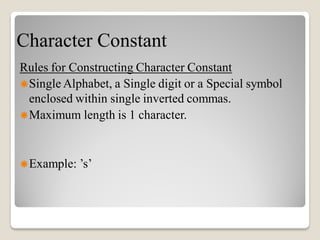
This document provides an overview of the C programming language. It discusses that C was developed in 1972 and its advantages include being simple, reliable, and easy to use. It outlines the steps to learning C, including understanding the character set, constants like integers and characters, variables, and keywords. The document provides examples of integer and character constants and rules for constructing them. It also defines variables and lists rules for constructing them. Finally, it provides a simple "Hello World" example C program to demonstrate basic syntax like functions, arithmetic operators, and output statements.