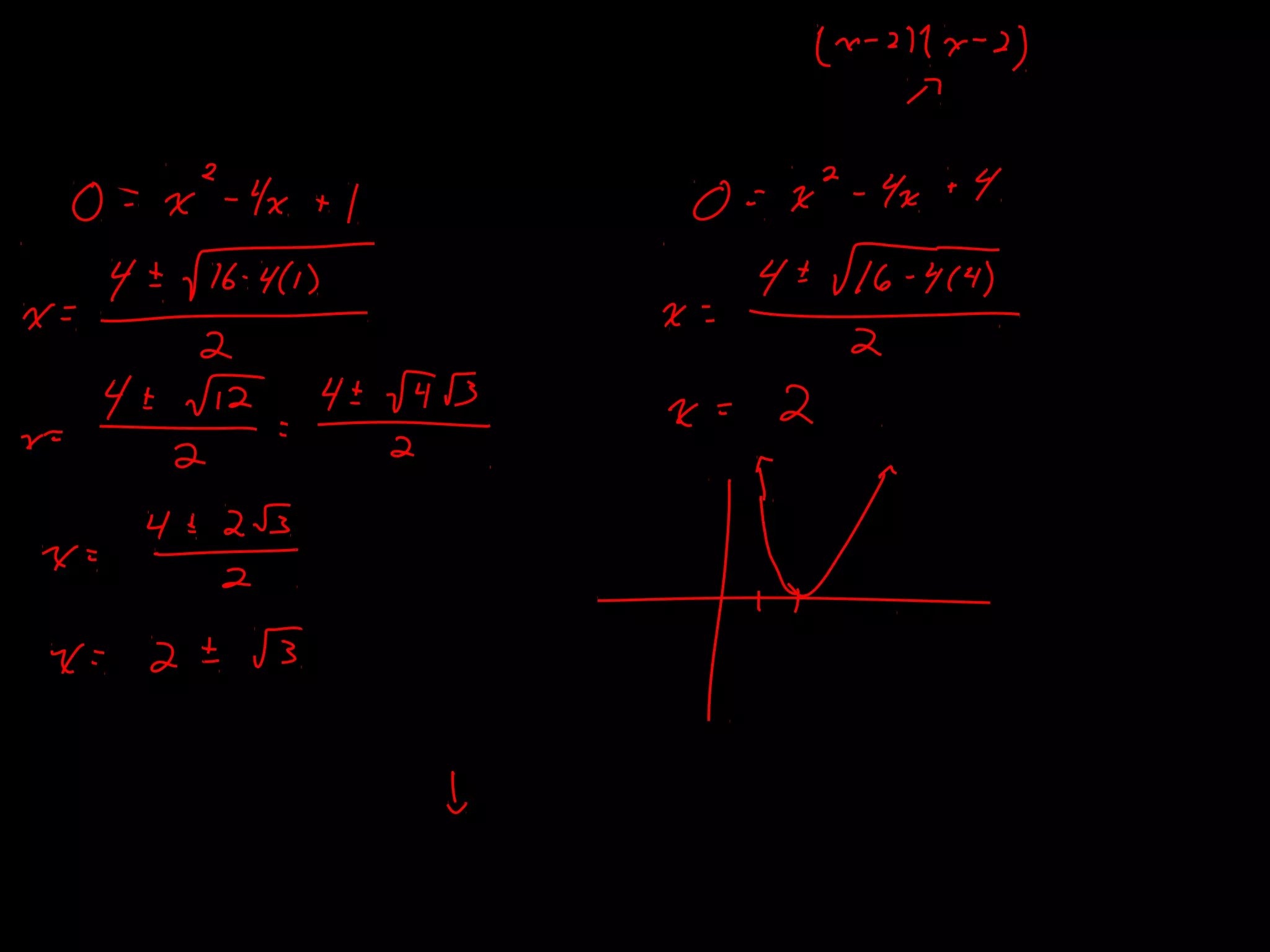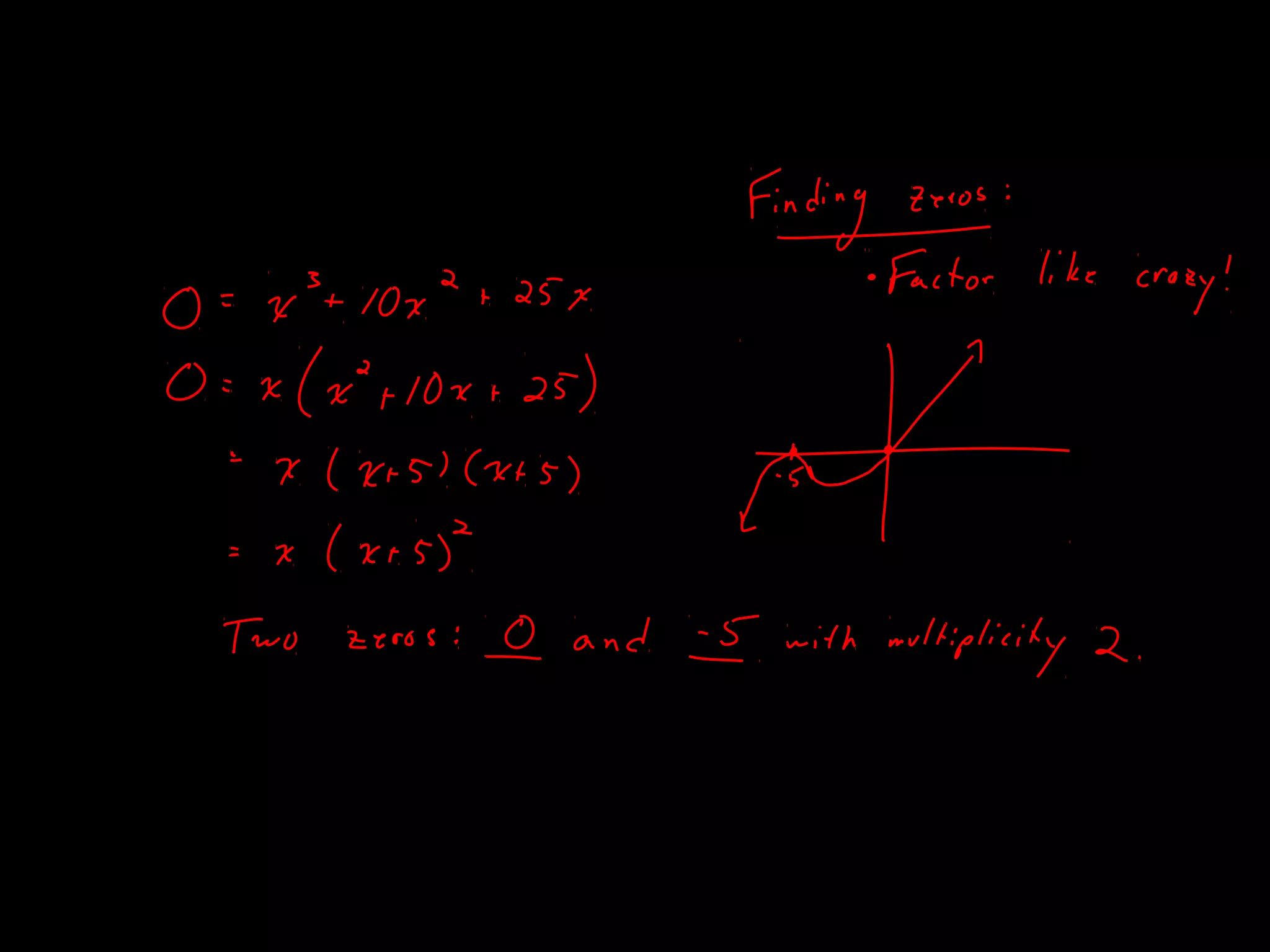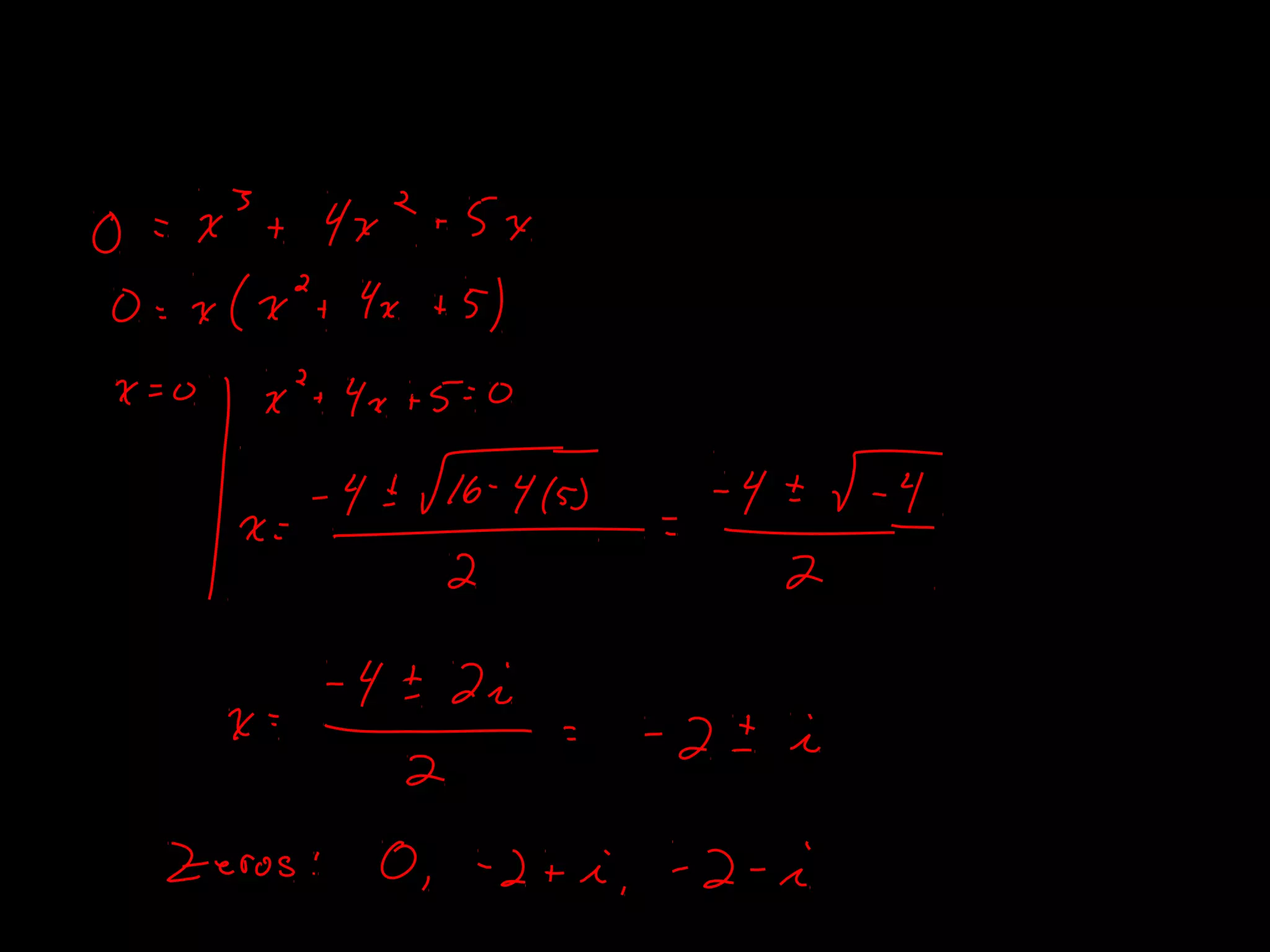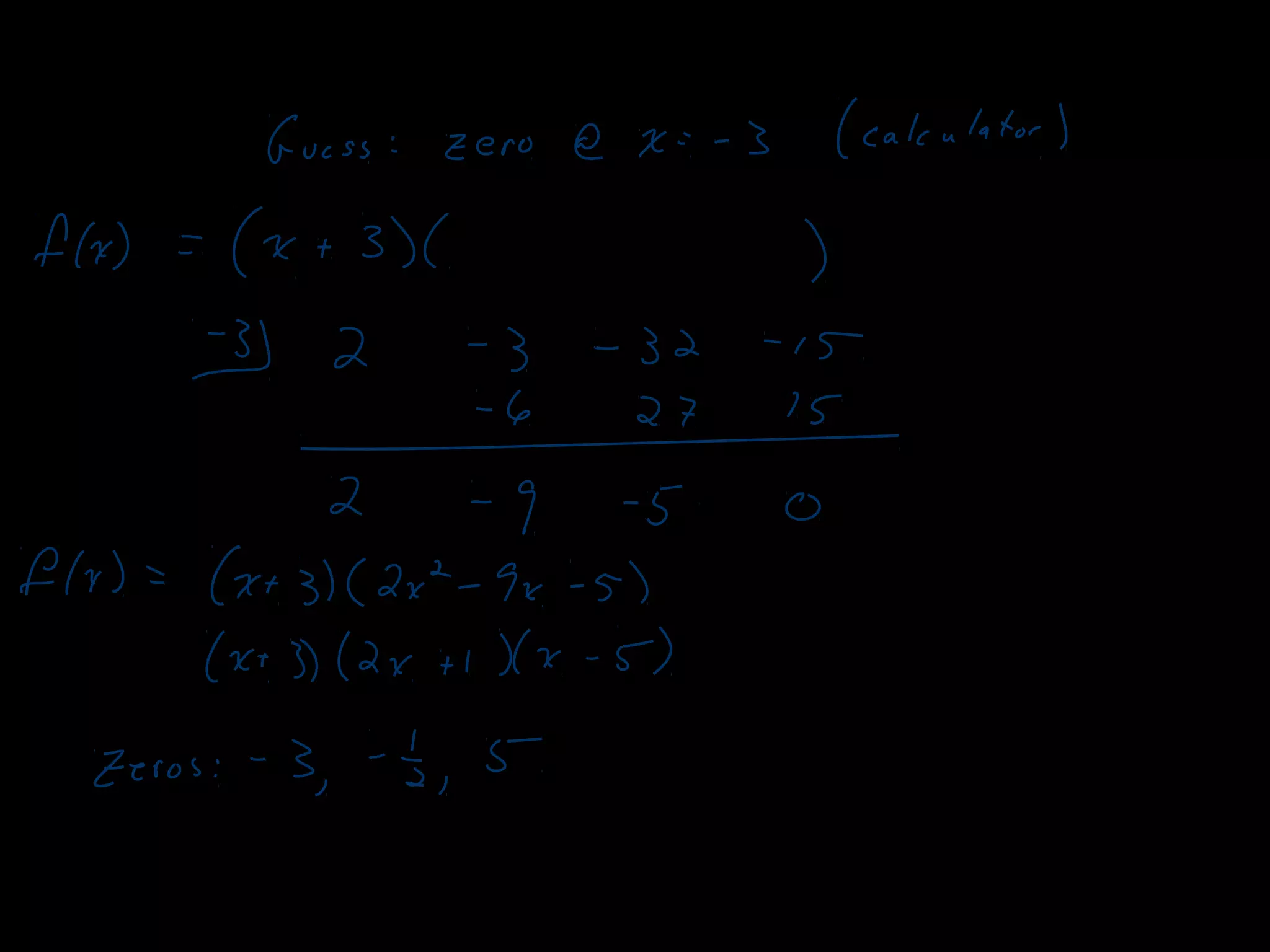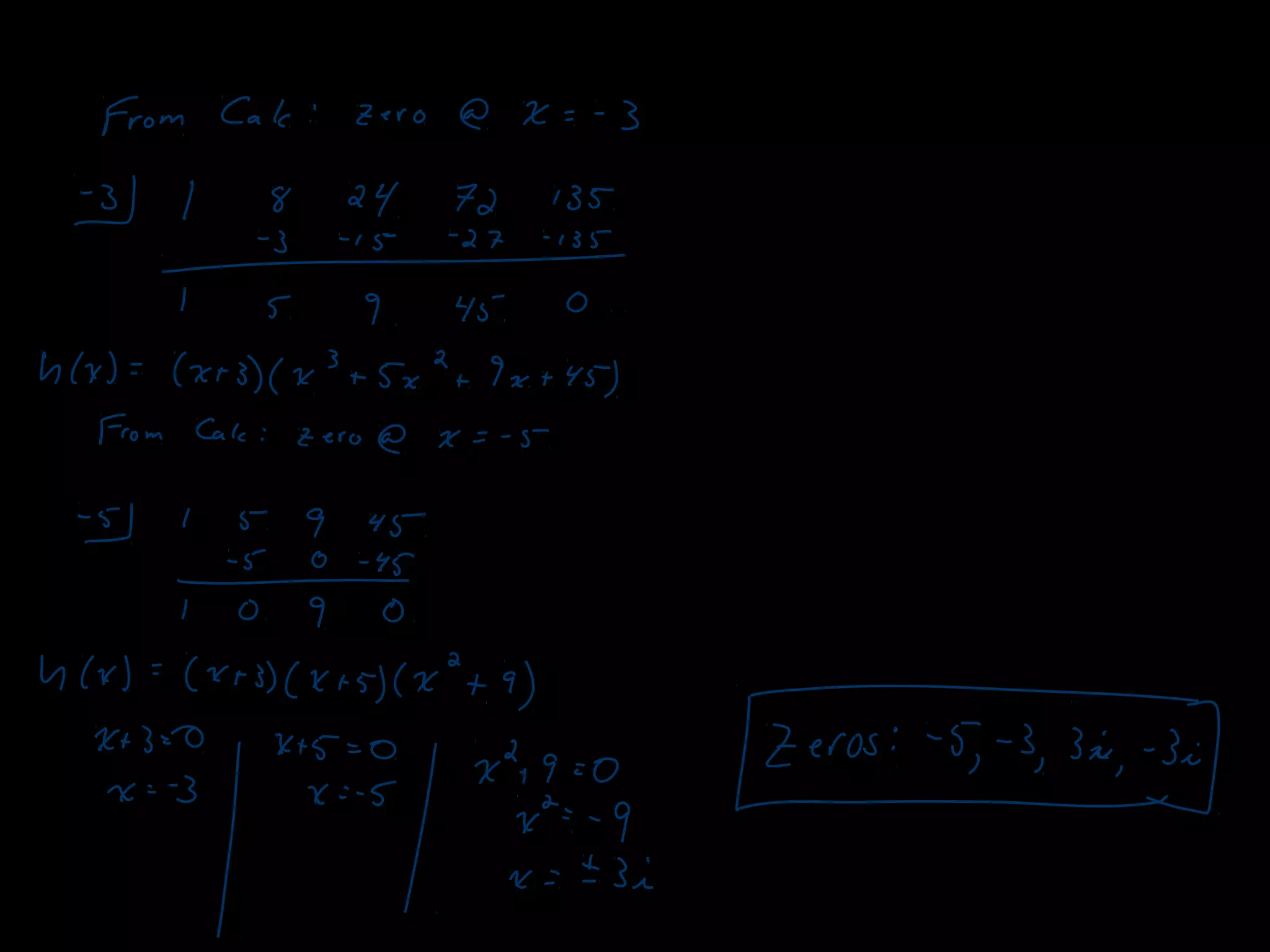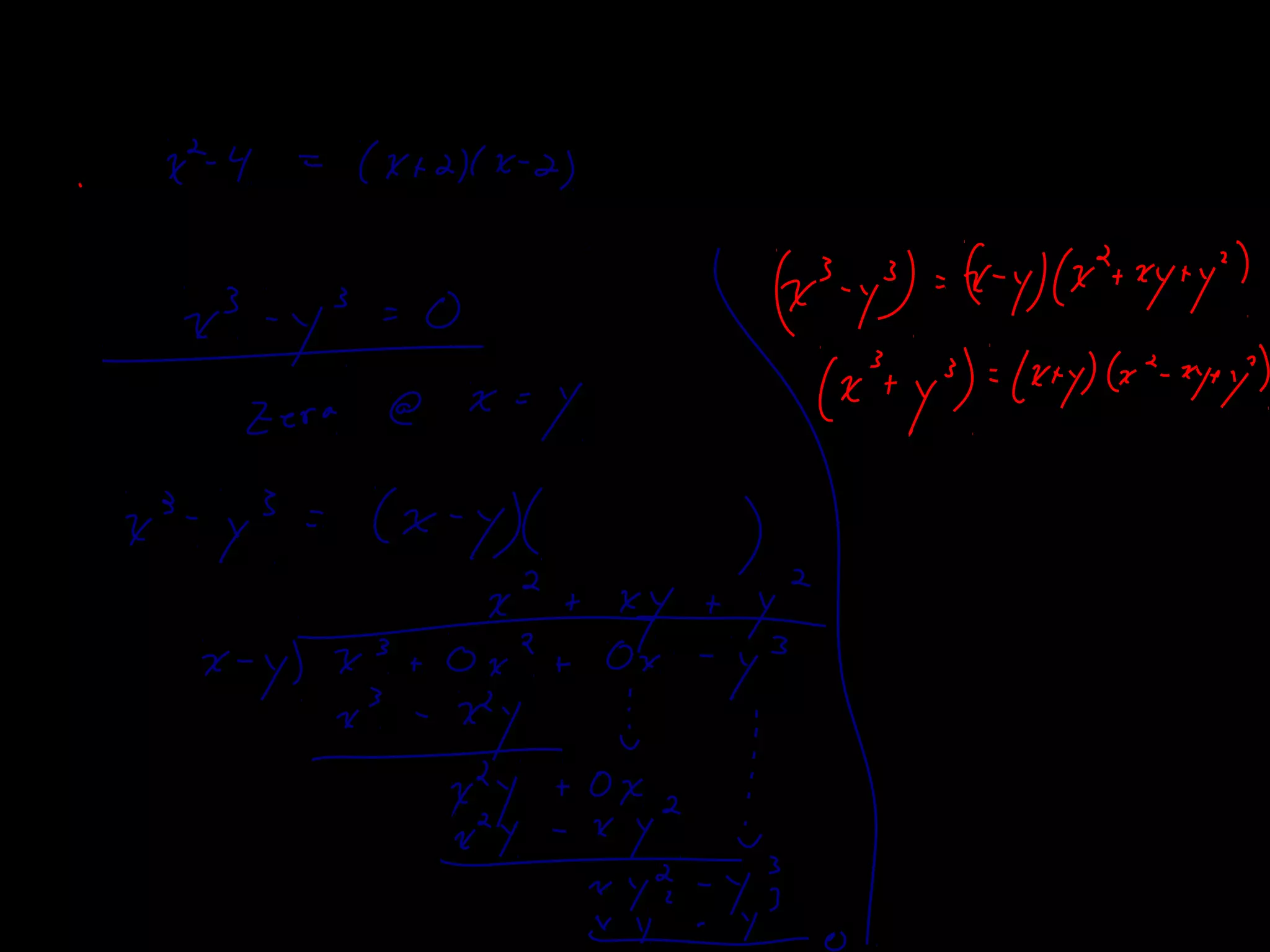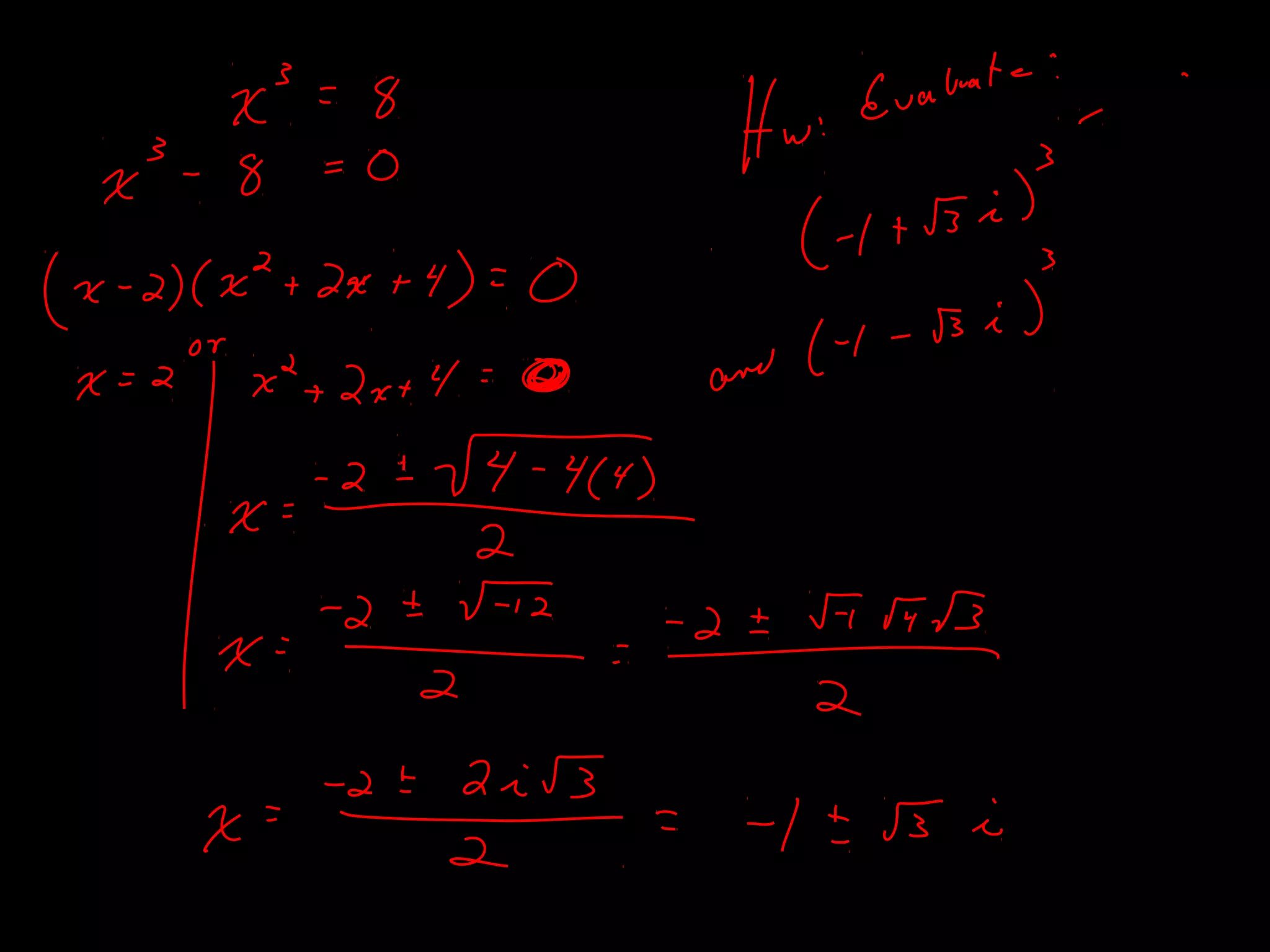Embed presentation
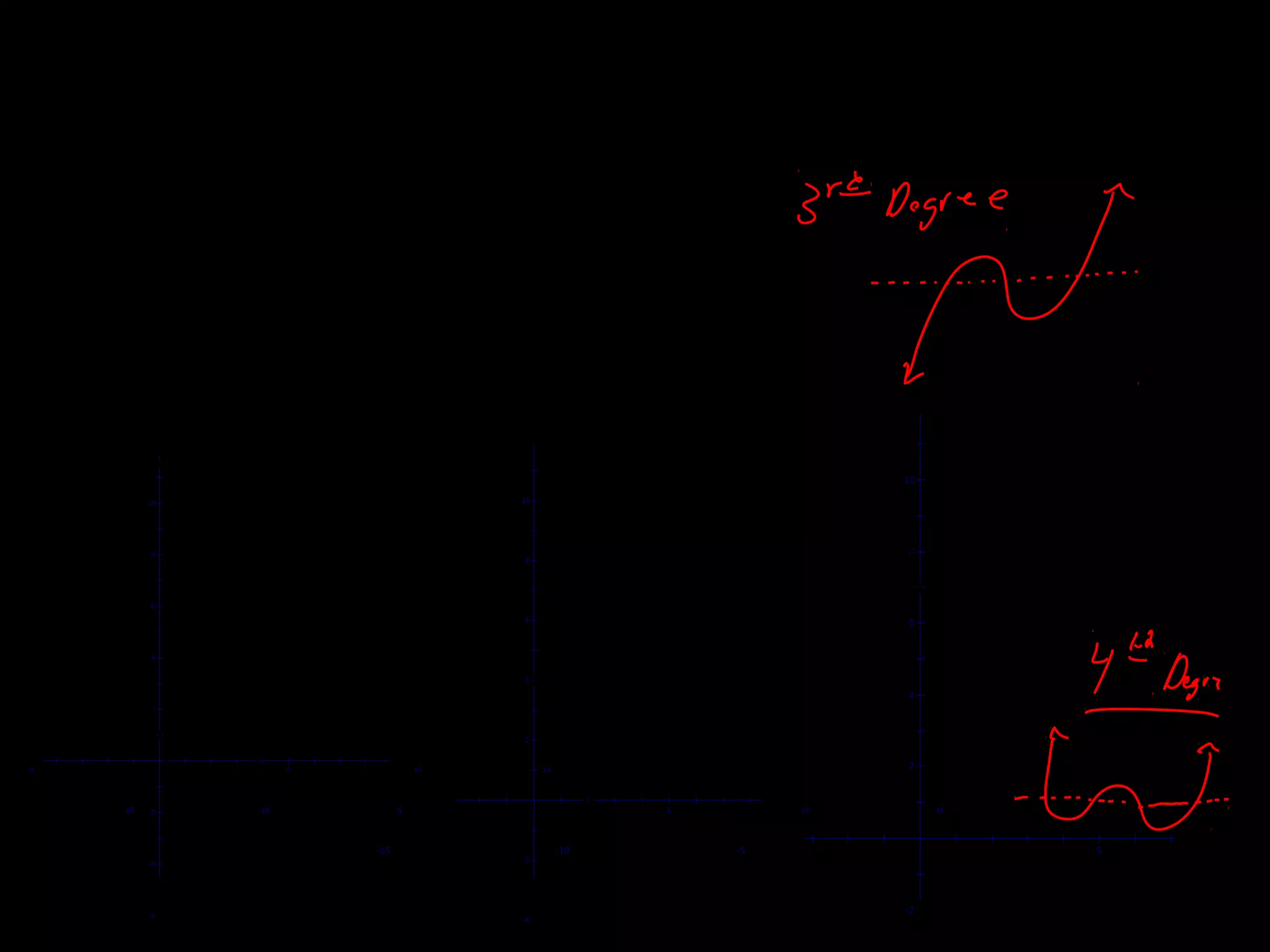
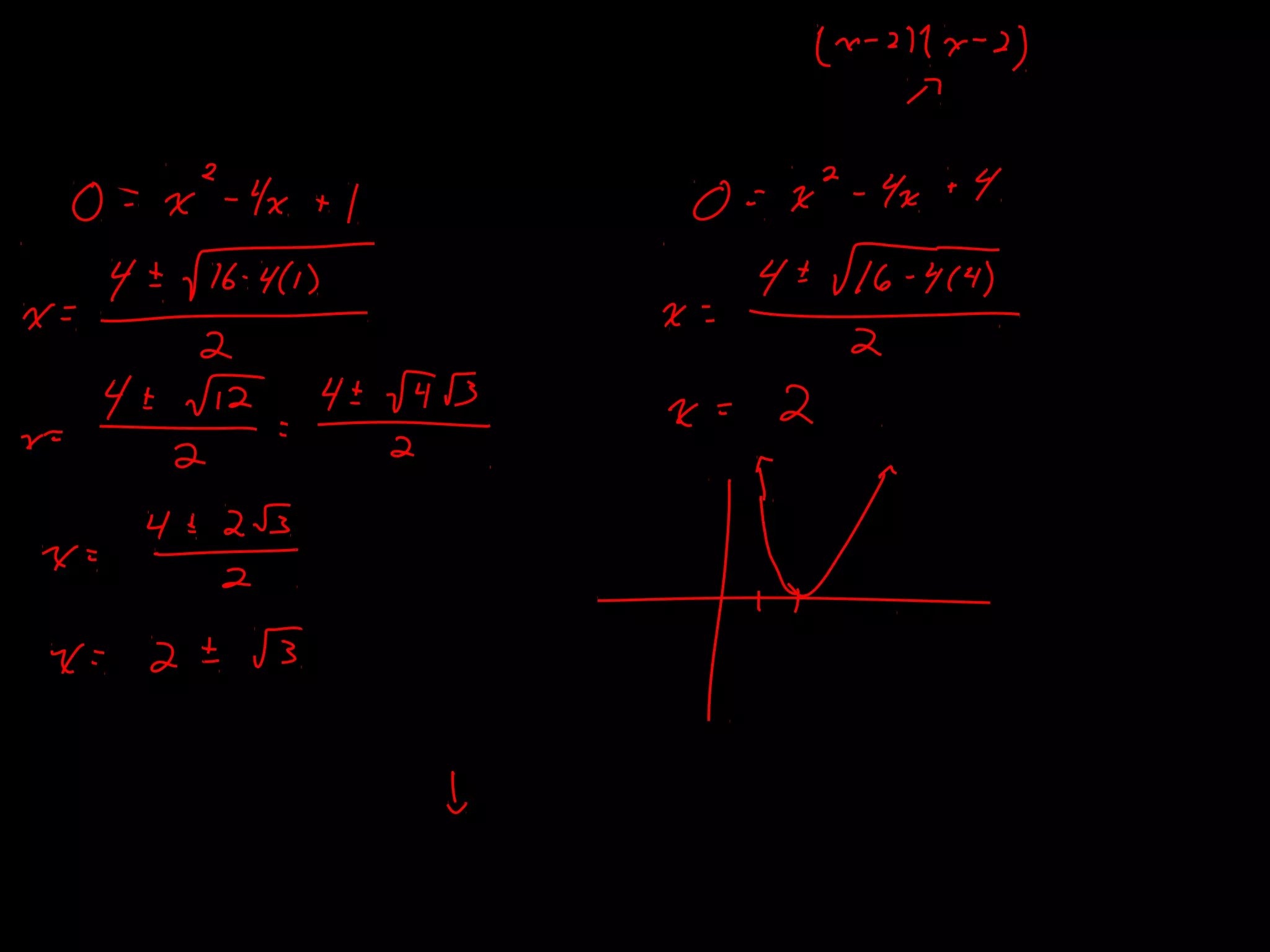
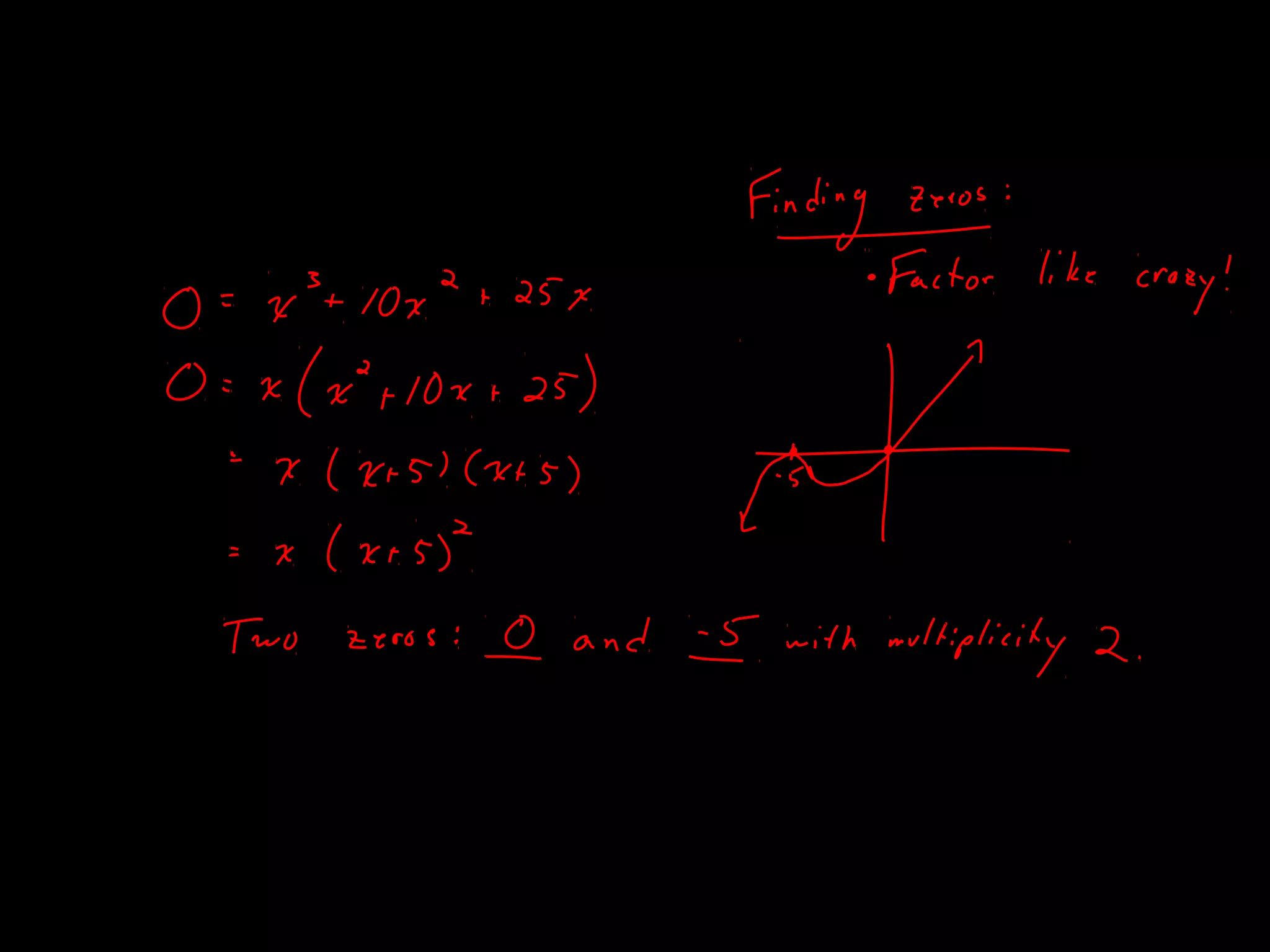
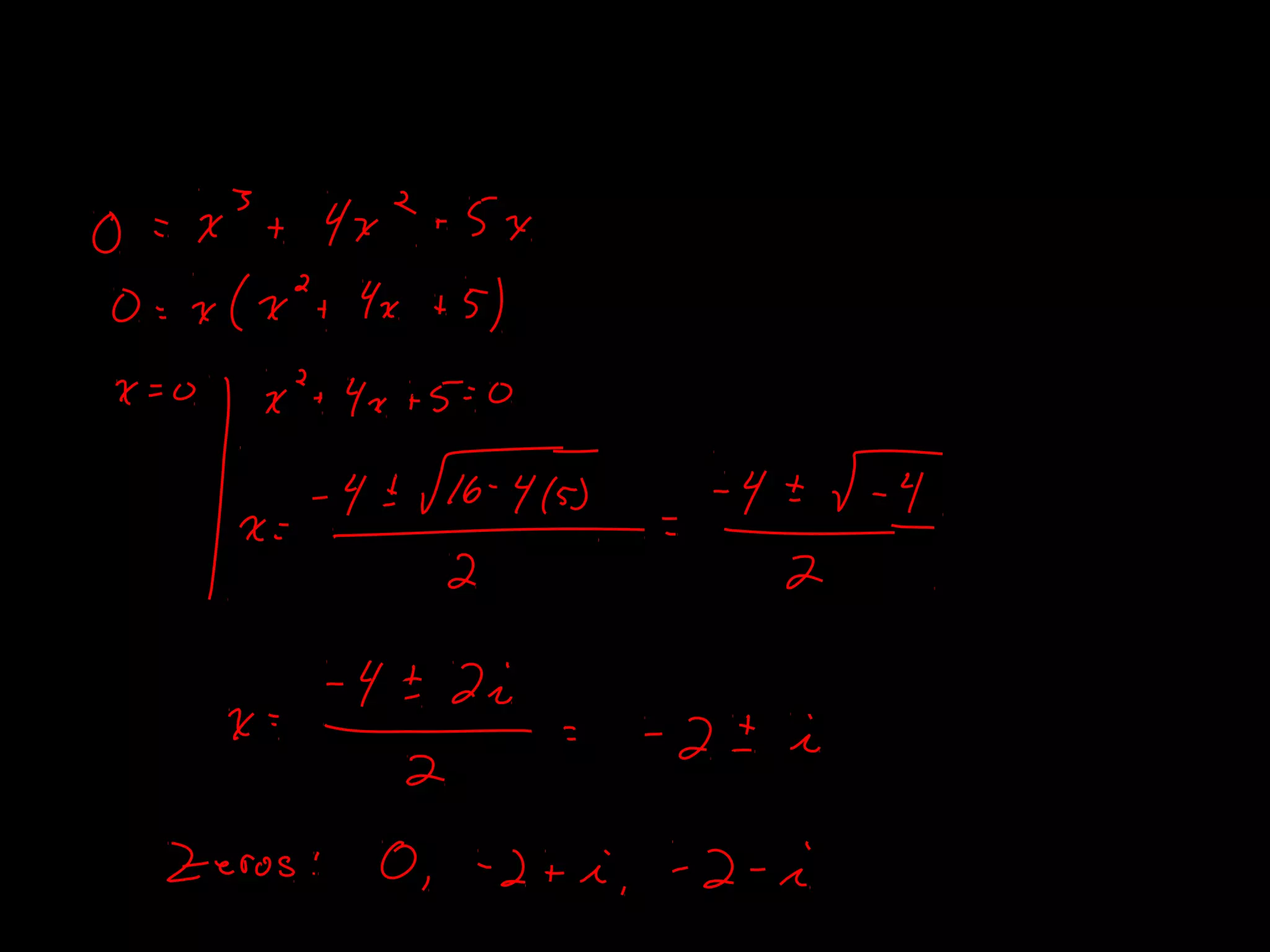
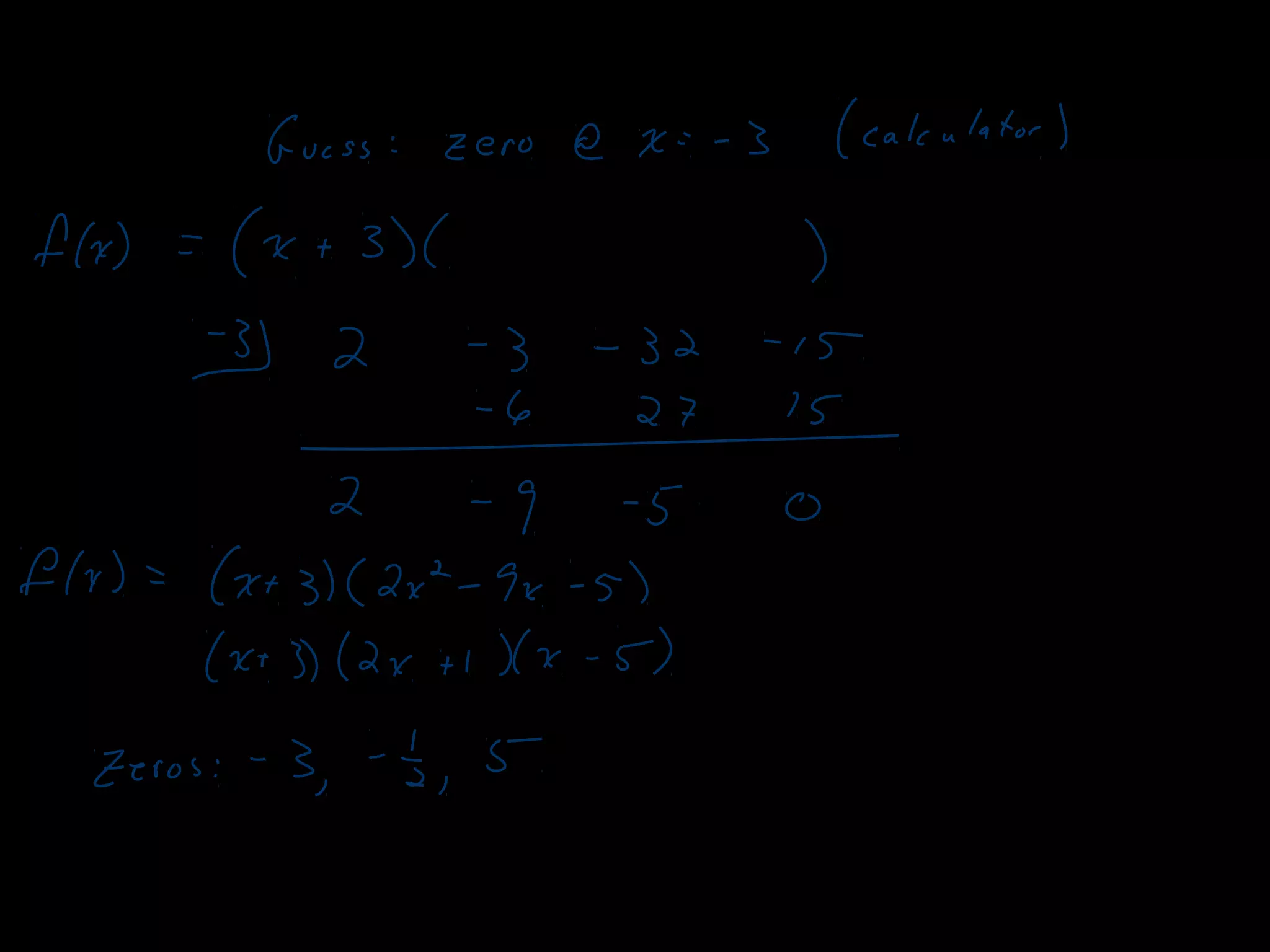

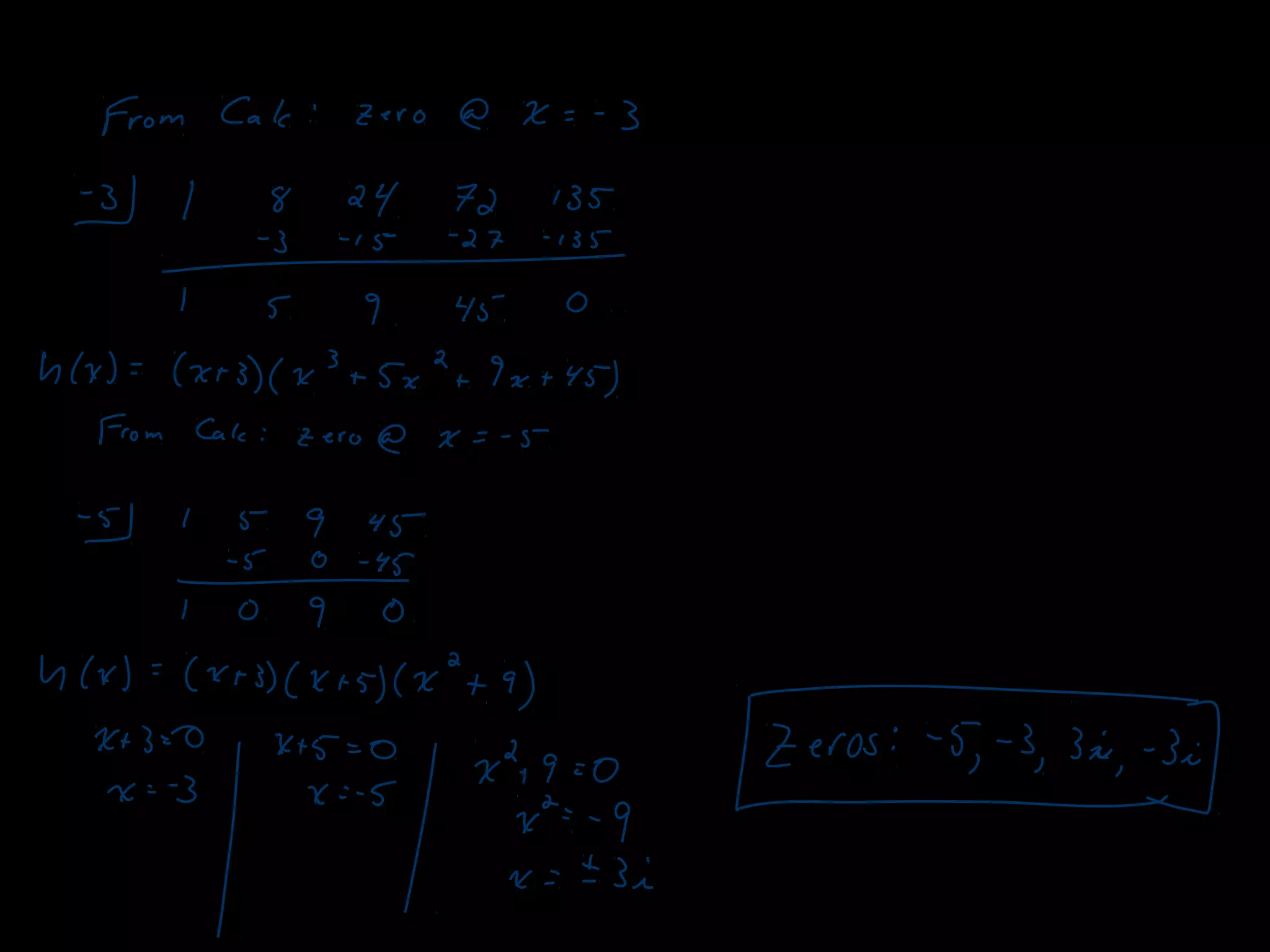
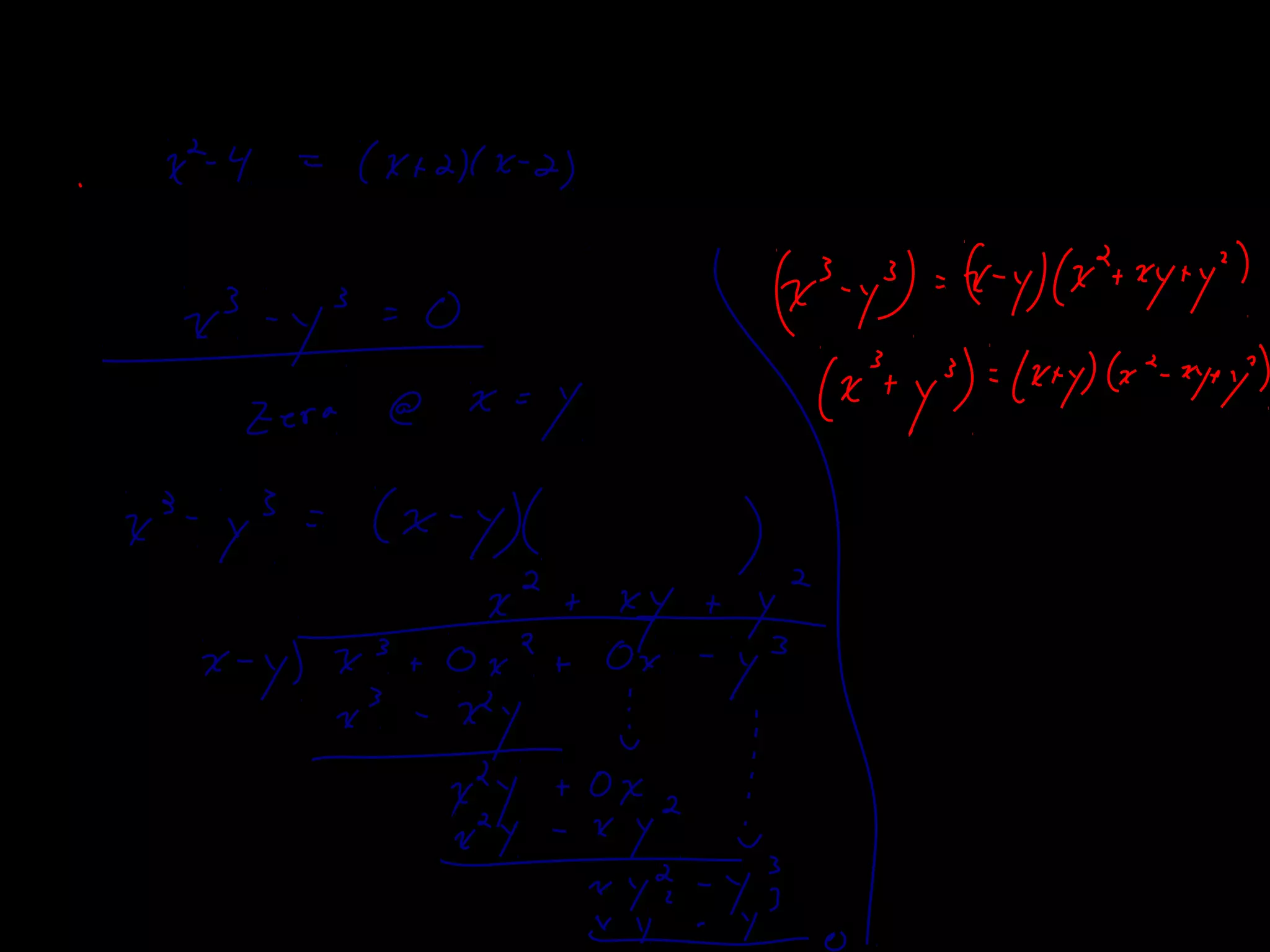
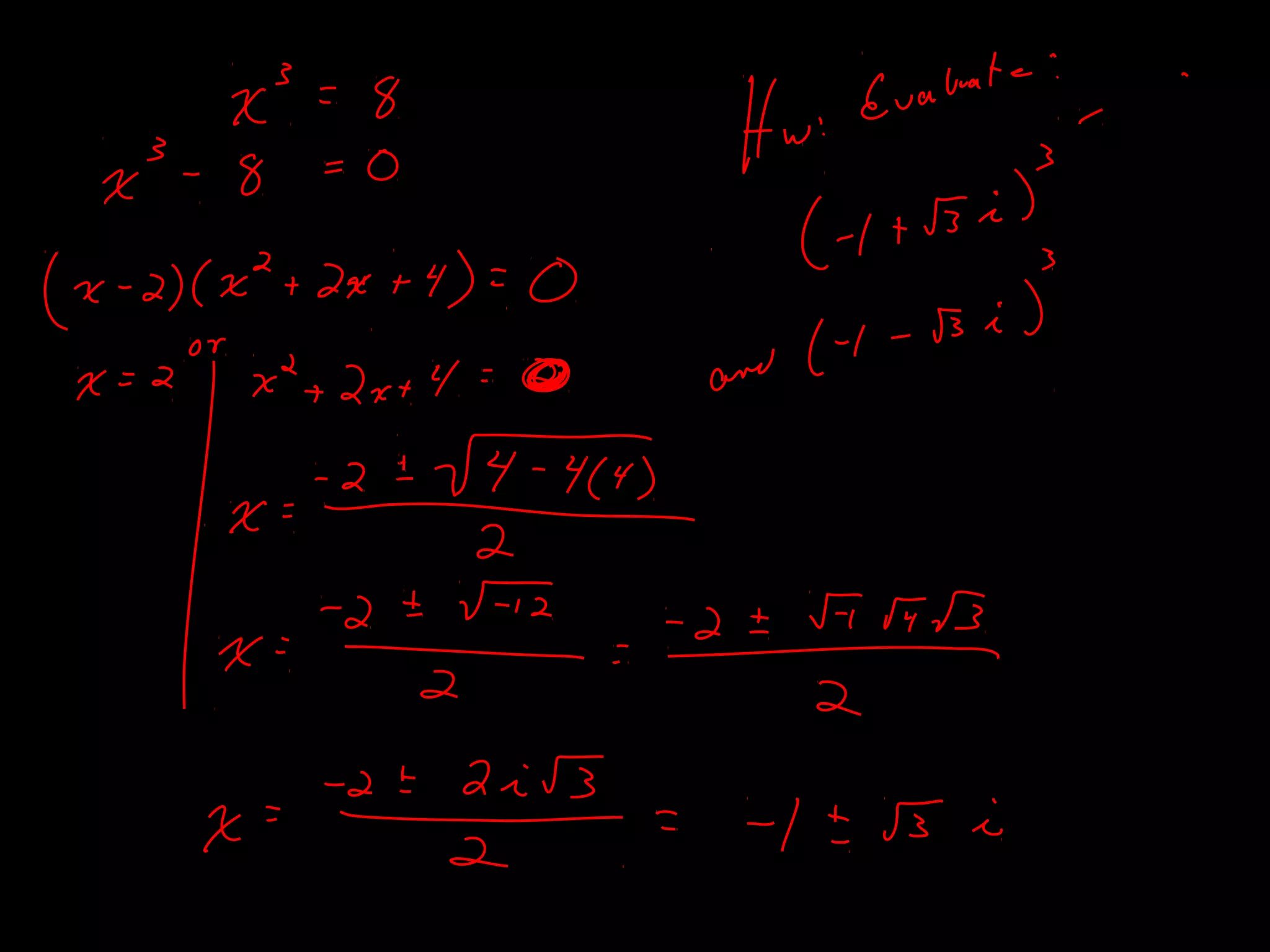
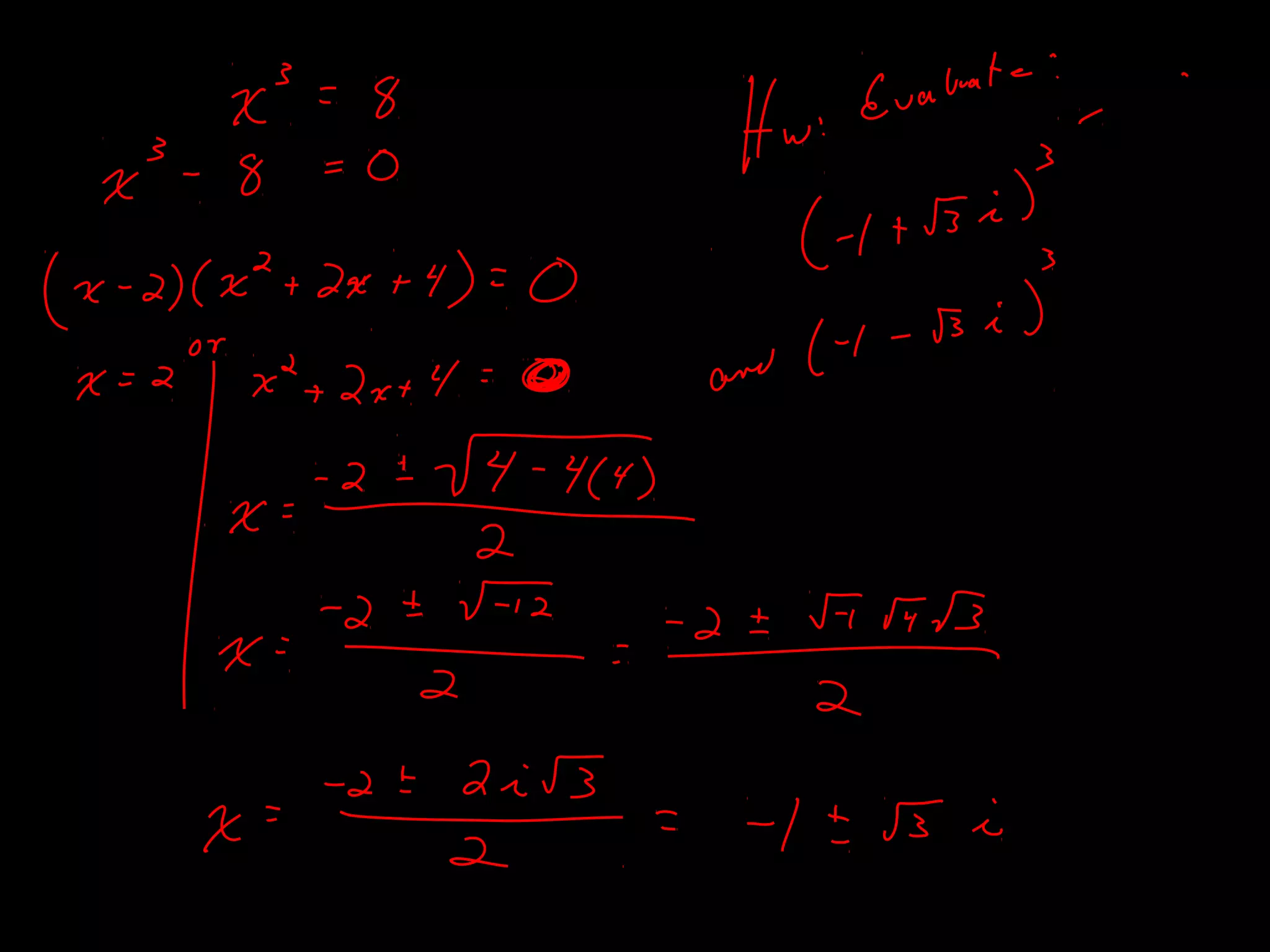

The document discusses several theorems related to polynomials: 1) The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra states that any polynomial of degree greater than 1 with complex coefficients has at least one complex zero. 2) A polynomial of degree n has at most n zeros. 3) A polynomial of degree n greater than 1 with complex coefficients has exactly n complex zeros, if multiplicities are counted.