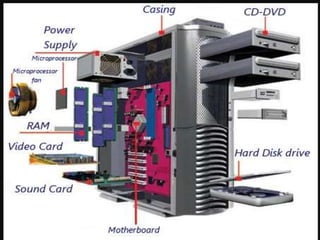
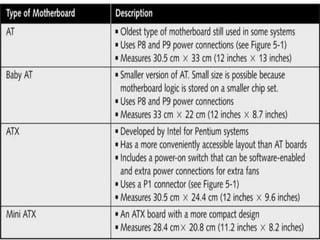
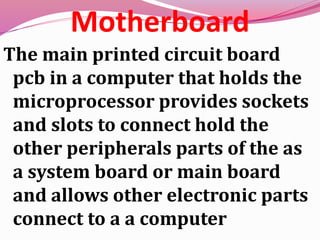
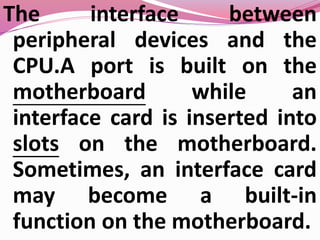
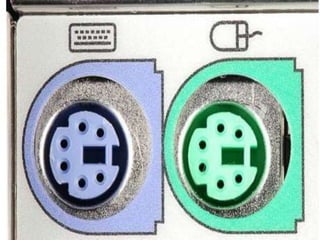
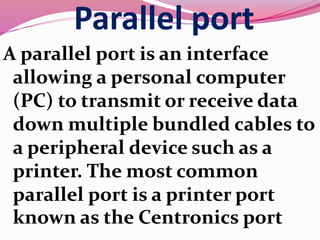
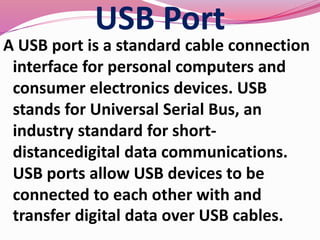
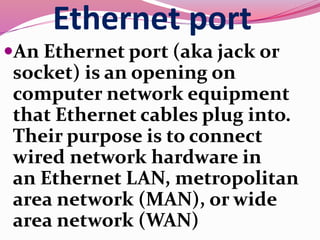
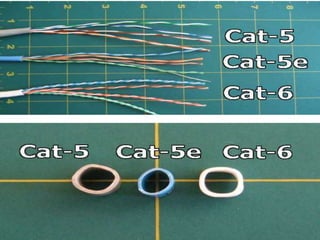
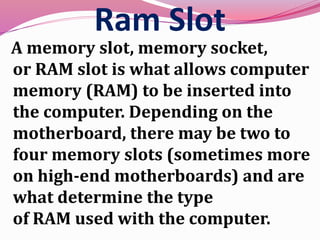
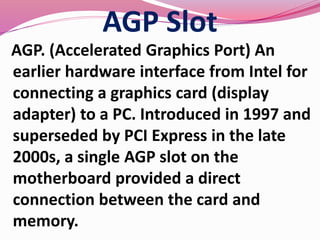
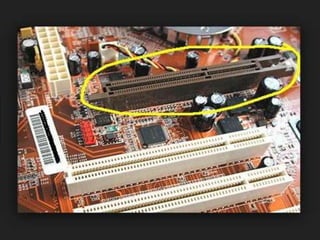
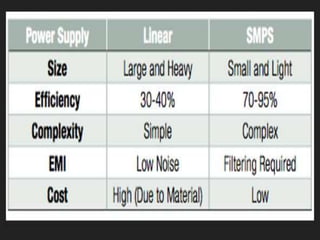
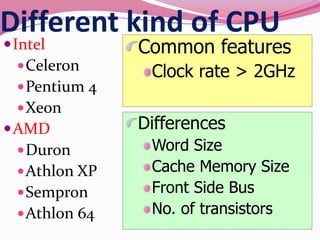
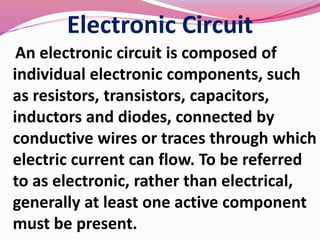
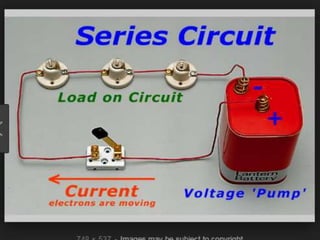
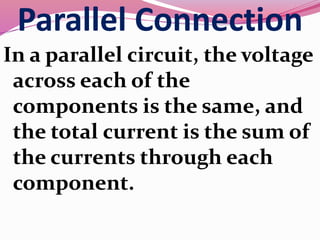
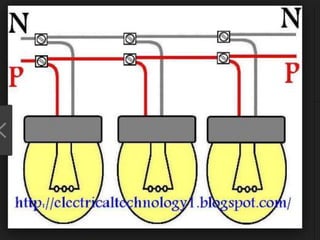
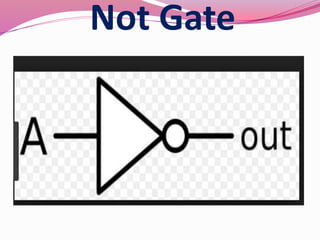
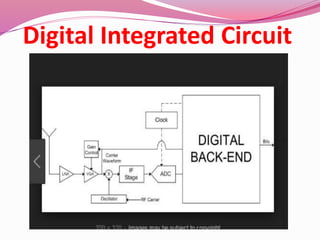
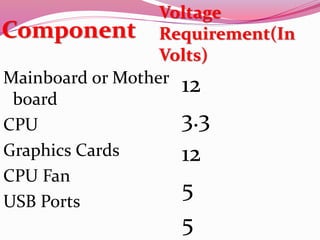
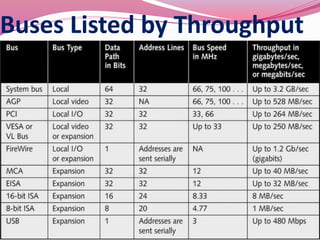
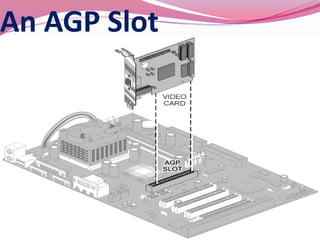
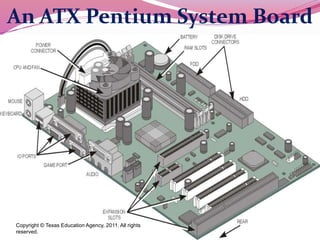
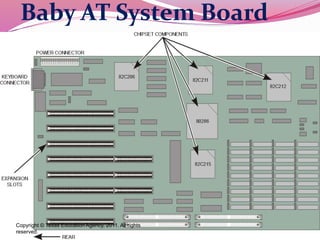
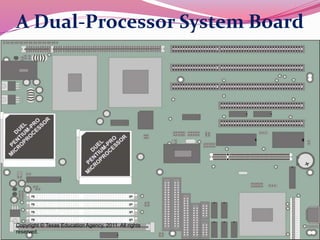
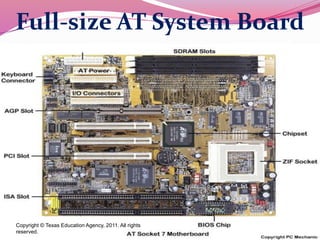
Computer hardware refers to the physical components of a computer system, both internal and external. Internal components include the motherboard, CPU, memory, and other peripherals. External components, called peripherals, include input devices like keyboards and mice, and output devices like monitors, printers, and speakers. Motherboards are the main circuit boards that hold these internal components together and allow them to communicate with each other and external peripherals. Common ports and slots on motherboards include RAM slots, expansion slots, CPU sockets, and ports for connecting peripherals.