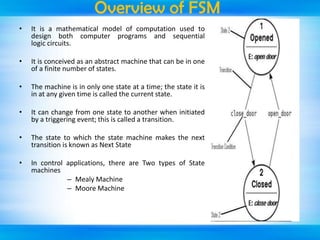
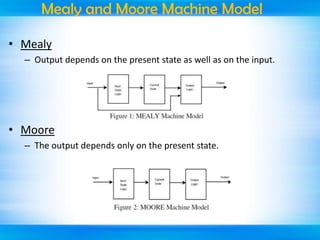
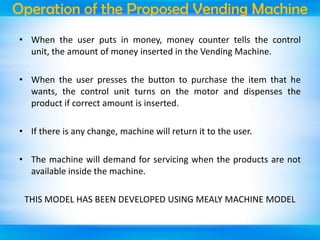
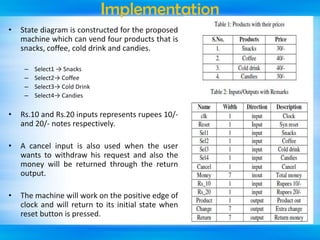
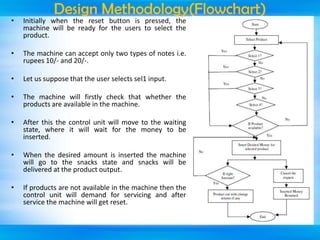
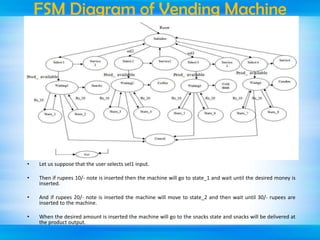
The document outlines a mini-project seminar on a finite state machine (FSM) based vending machine controller featuring automatic billing. It discusses the operation and implementation of the vending machine using Mealy and Moore models, detailing its design methodology, advantages, and disadvantages. Additionally, the document covers the history of vending machines and includes references for further reading.