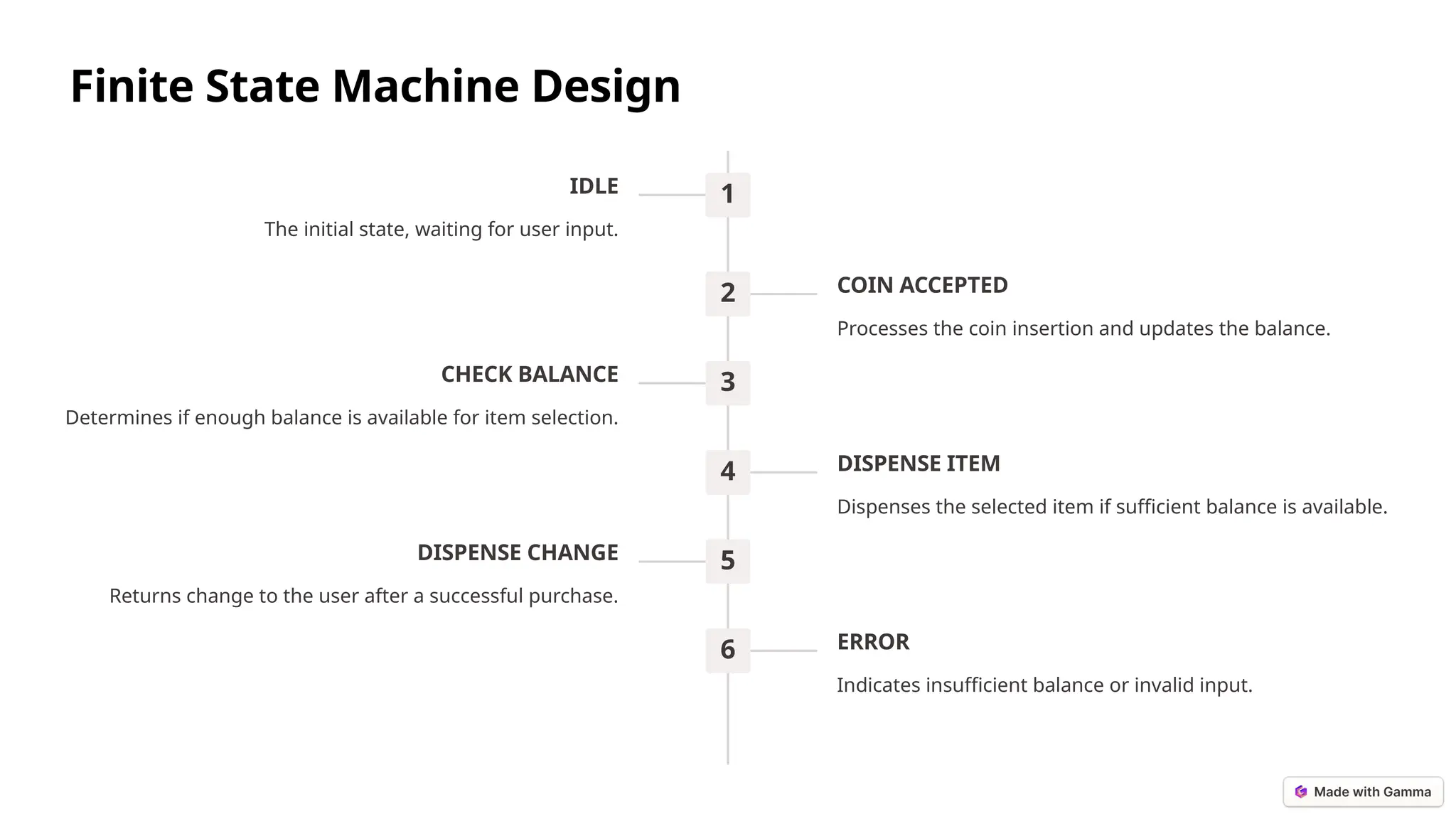
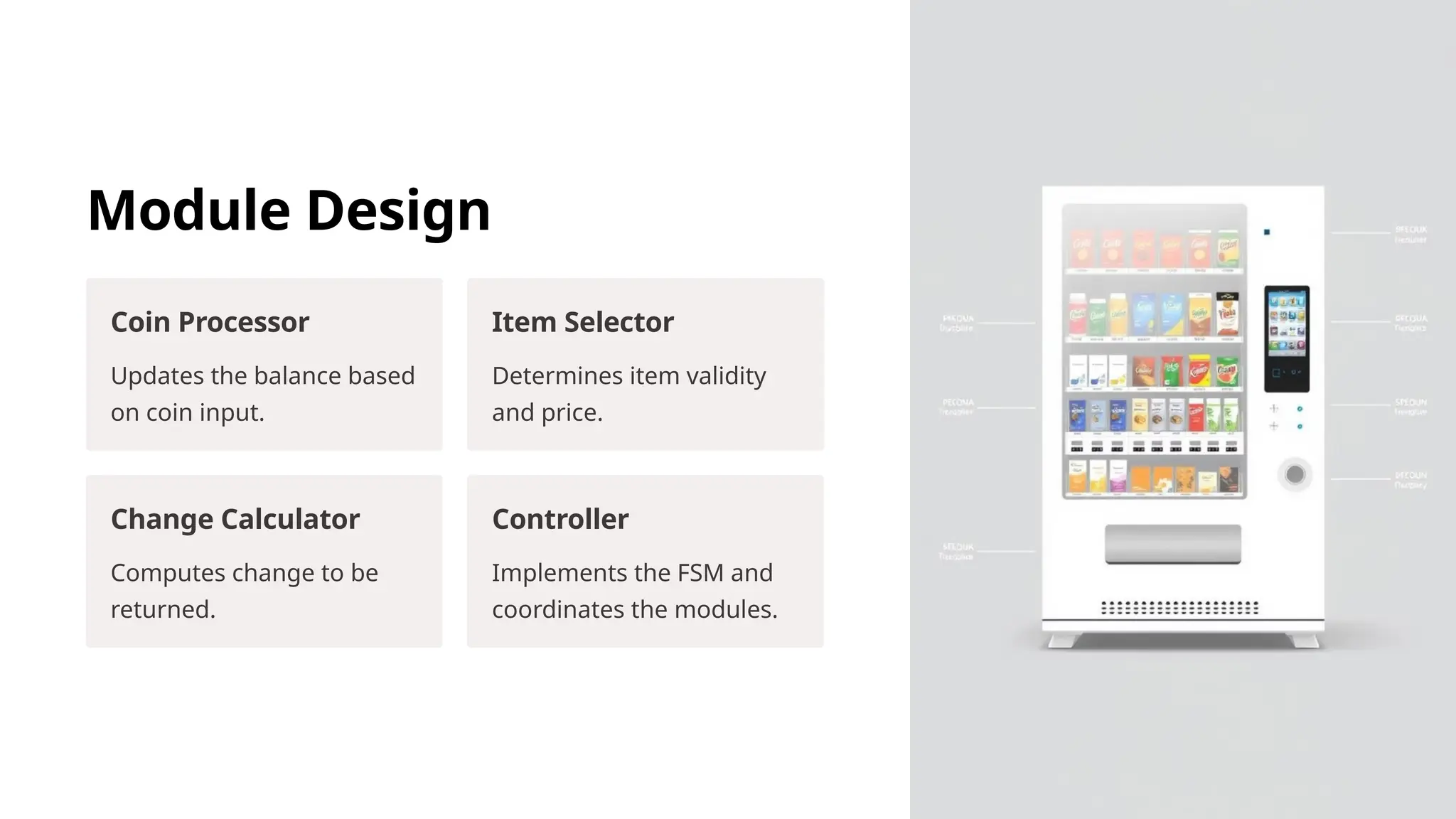
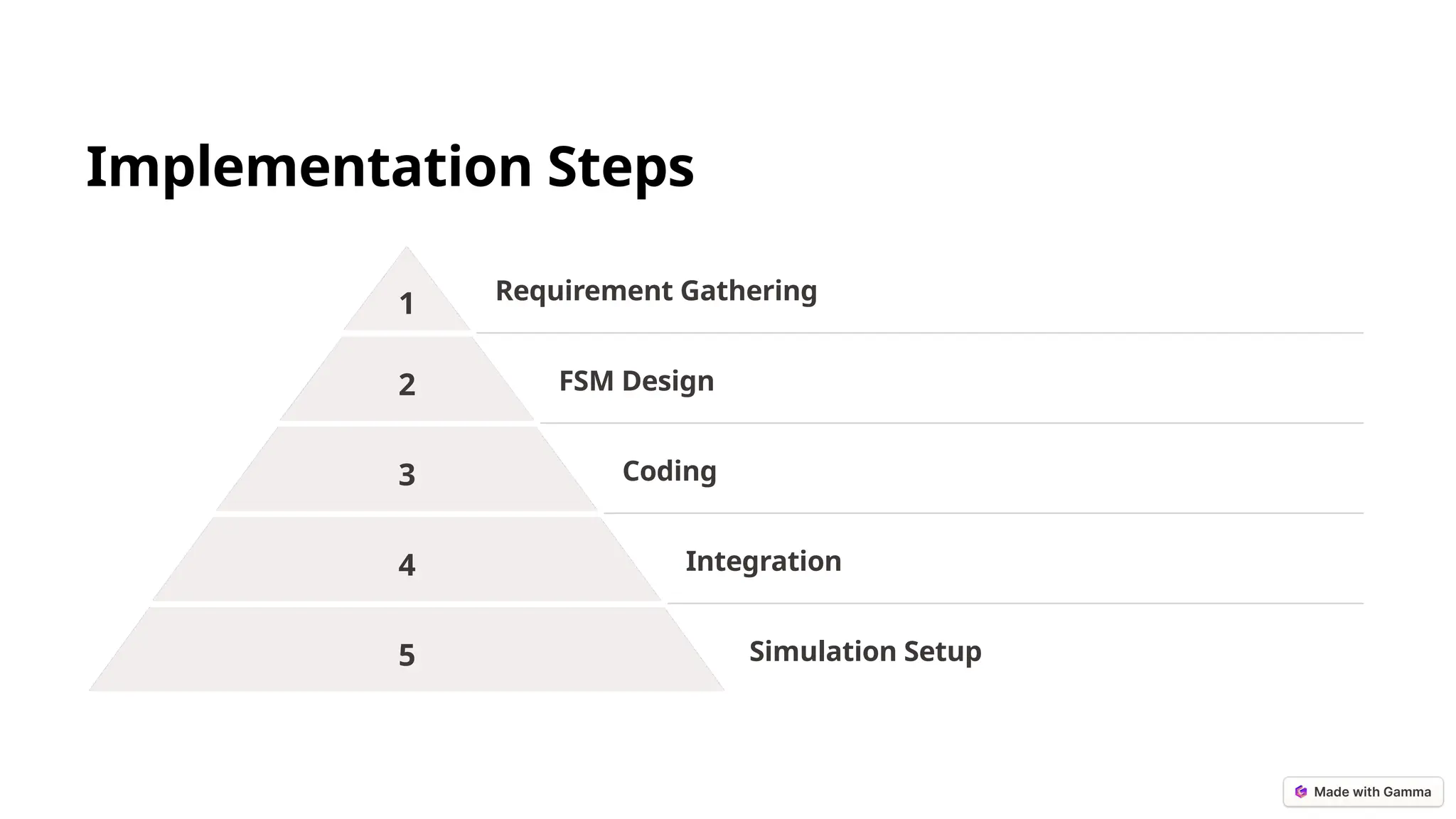
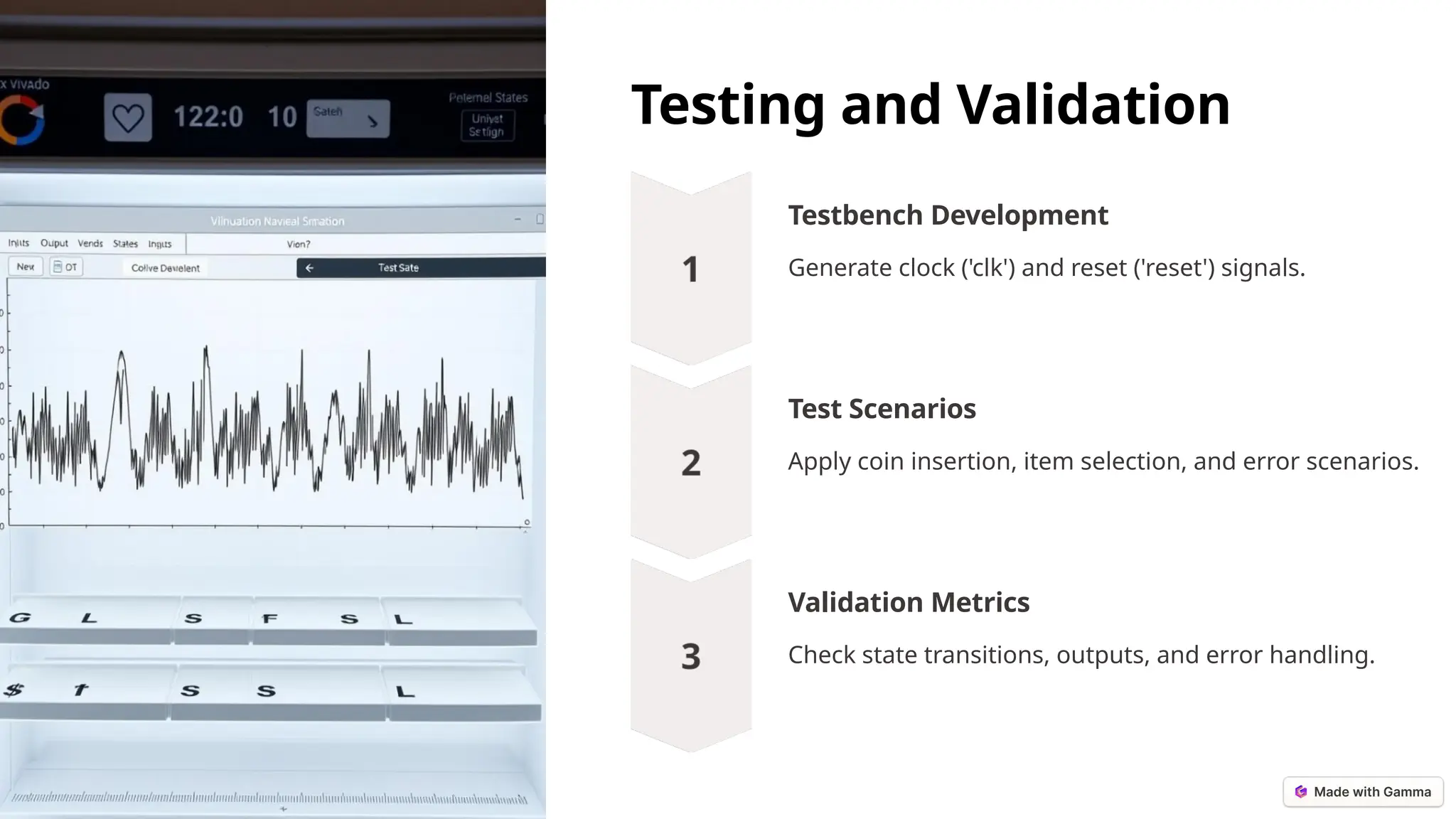
The document outlines the design and simulation of a finite state machine-based vending machine using Verilog HDL in Xilinx Vivado. It details the functional and non-functional requirements, modular design, implementation steps, and validation metrics in order to ensure accurate operations such as coin processing, item selection, and change dispensing. The project aims to validate its objectives through comprehensive simulations and provides insights for future enhancements.