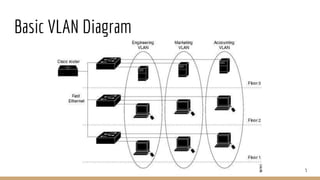
This document provides an overview of VLANs, trunk ports, and related protocols. It discusses the basics of VLANs including their purpose of logically segmenting networks. It describes trunk ports and the protocols used to carry traffic from multiple VLANs over trunk links, such as ISL and 802.1Q tagging. The document also covers the Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) used to share information between Cisco devices, as well as the Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) used to negotiate trunking. Finally, it lists some mitigation techniques like disabling trunking and securing ports to prevent VLAN hopping attacks.