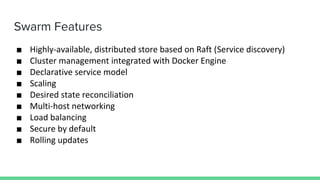
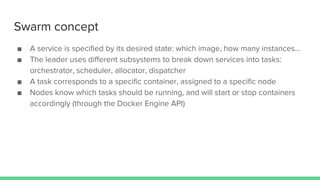
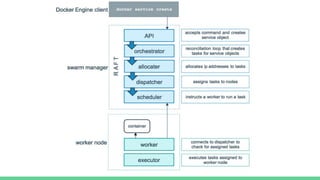
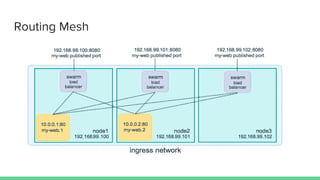
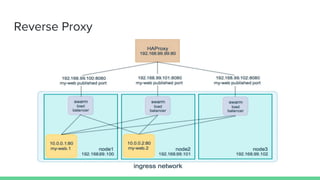
This document discusses Microservices and Docker Swarm. It begins by introducing the presenter and their background. It then defines what a microservice is and introduces Docker. Key concepts about Docker Swarm are explained such as swarm features, service discovery without an external database, and the swarm concept of managers, workers, services and tasks. It demonstrates how to build a swarm cluster and add nodes, and discusses security, routing mesh, scaling, reverse proxy, rolling updates and secrets. Finally it briefly mentions logging, metrics and dashboard tools to monitor Docker systems.