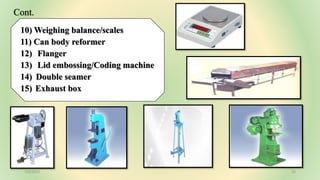
The document is an assignment on the processing of horticultural produce, specifically focusing on freezing fruits and vegetables, canning containers, and associated technologies. It details the freezing process, types of freezers, various types of containers including glass, metal, and plastic, along with their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it addresses quality assurance defects in cans and spoilage causes in canned and bottled products.