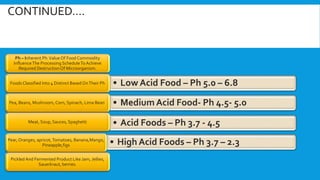
Canning involves preserving food in hermetically sealed containers through the application of heat, which eliminates microorganisms. Canned foods can last 2 years at room temperature. In India, only 2.1% of fruits and vegetables are processed, compared to 40-60% in developed countries. Advances like mobile canning and aseptic packaging help reduce food waste by processing foods on site. The canned food market is growing due to demand for convenient and longer-lasting foods.



















![CANNING[1].pptx](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/canning1-230503074238-532da9a8/85/CANNING-1-pptx-21-320.jpg)