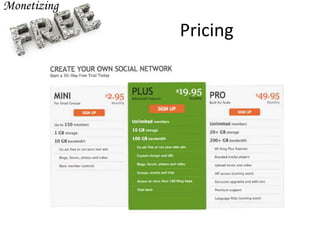
Ning, founded in 2004, evolved from a social app platform to a provider of social networks, reaching 2 million networks by 2010. Despite its rapid growth and significant funding, Ning struggled with monetization and faced challenges related to customer expectations and market competition. Key lessons learned include the importance of early monetization planning, managing customer segments, and the difficulties of scaling and pivoting in a shifting market landscape.