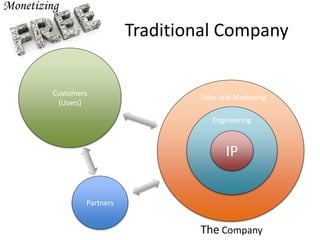
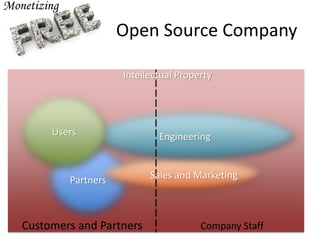
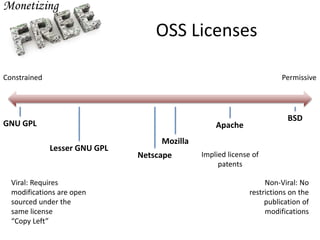
The document discusses open source as a model where intellectual property is shared, allowing users to modify, enhance, and distribute software freely. It includes examples of successful open source projects, their widespread adoption by major companies, and financial strategies for monetizing open source software. It also predicts that within a decade, most widely used software will be either open source or software as a service (SaaS), marking a significant shift in the software landscape.











![Open Source Adoption
Major websites all run on open source
- Facebook
- Twitter
- Linkedin
- Google
- Amazon
- Wikipedia
Virgin America (in-flight entertainment)
KLM – Web services
London stock exchange – trading platform
New York stock exchange – trading applications
Banco do Brasil – biggest bank in Brazil, desktops, ATMs
French Parliament moved to Ubuntu on desktop PCs in 2007
French Gendarmerie Nationale switch to Ubuntu by 2015
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_Linux_adopters
Linux Ecosystem is
around $30B [IDC]
- Red Hat
- Ubuntu
- IBM’s open source
consulting](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/free-open-source-140510000504-phpapp01/85/The-Rise-of-Open-Source-16-320.jpg)