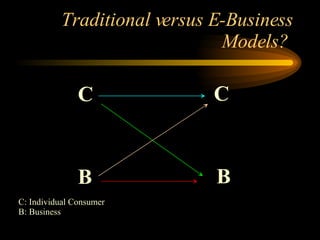
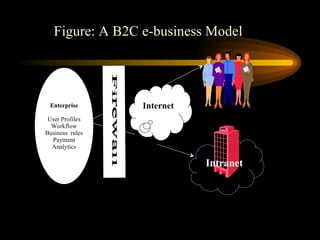
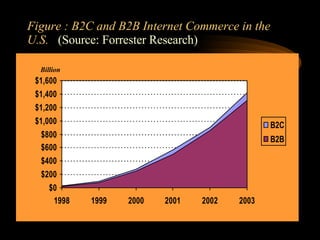
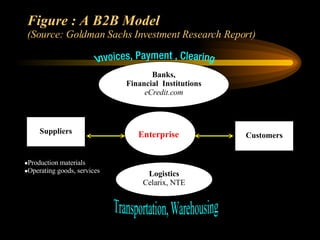
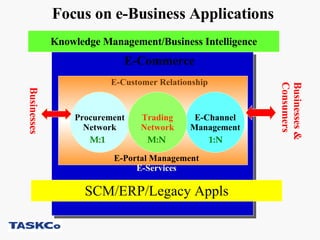
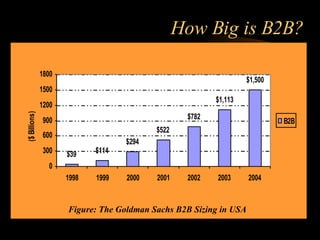
This document discusses e-commerce, including business-to-consumer (B2C) and business-to-business (B2B) models. It provides an overview of key concepts in e-business and e-commerce. The document also analyzes the size and growth of the B2B market, drivers for B2B adoption, and factors for success in B2B e-marketplaces.
![E-Commerce Jason C.H. Chen, Ph.D. School of Business Administration Gonzaga University, Washington, U.S.A. Senior Consultant, Taskco.com [email_address] Nov. 20, 2000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecommerceppt-1216116804705432-9/75/E-Commerce-Ppt-1-2048.jpg)

![E-Commerce: From B2C to B2B and Beyond Jason C.H. Chen, Ph.D. School of Business Administration Gonzaga University, Washington, U.S.A. Senior Consultant, Taskco.com [email_address] Nov. 22, 2000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecommerceppt-1216116804705432-9/85/E-Commerce-Ppt-3-320.jpg)