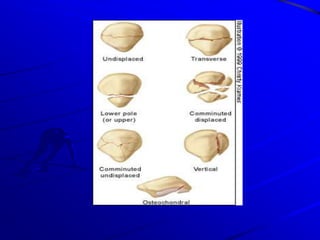
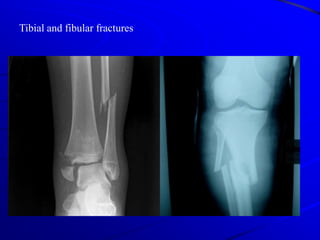
Fractures of the lower limb can result from high-energy trauma or osteoporosis in the elderly. Common fractures include the femur, patella, tibia, fibula, ankle, and bones of the foot. Treatment depends on the type and location of the fracture, ranging from closed reduction and casting to open reduction with internal fixation using plates, screws, or intramedullary nails. Pelvic fractures may also require surgical fixation depending on the forces involved and stability of the injury.

















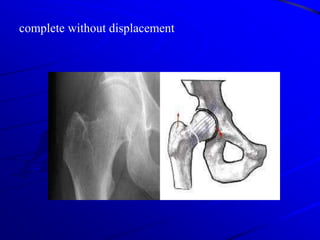



















![Types 1.direct [stellate] 2.indirect [transverse]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/72554-offracturesofllff-110813002010-phpapp01/85/FRACTURES-0F-LOWER-LIMB-38-320.jpg)