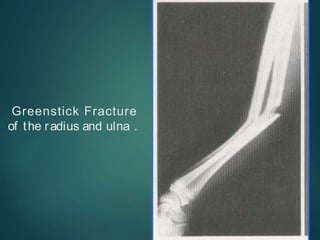
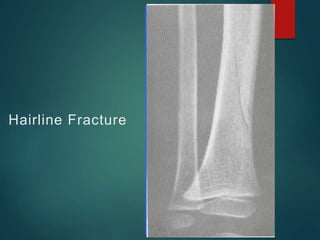
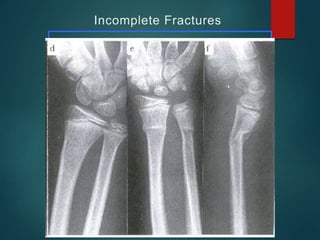
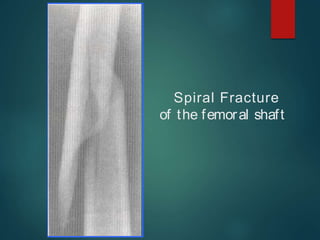
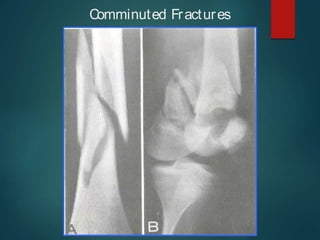
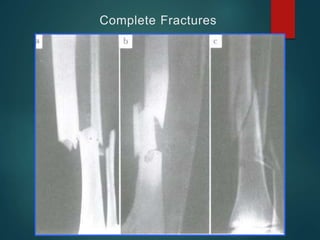
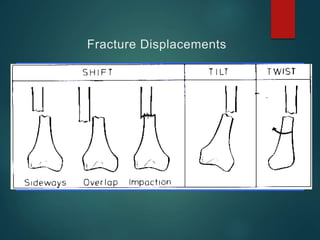
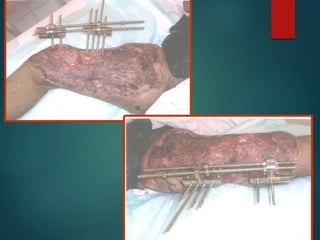
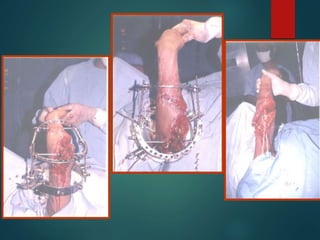
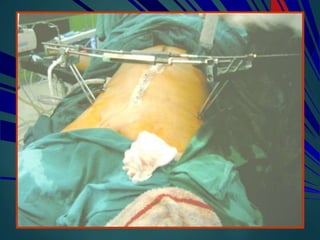
This document provides an overview of orthopaedic trauma and fracture classification. It defines a fracture as a break in bone continuity and classifies fractures based on the fracture line (complete vs incomplete), appearance on radiology, mechanism of injury (direct vs indirect), bone fragment displacement (displaced vs undisplaced), communication with the external environment (closed vs open), and severity of soft tissue damage (Gustillo-Anderson classification for open fractures). The diagnosis involves a history, exam findings like pain, swelling and deformity, and investigations like x-rays, CT scans and MRIs. Management depends on whether the fracture is closed or open, with closed fractures often treated with closed reduction and casting while open fractures require debridement and may