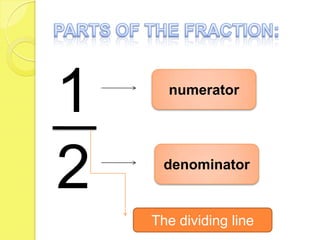
This document discusses different types of fractions including proper fractions, improper fractions, and mixed fractions. It explains how to convert between improper fractions and mixed numbers, and how to reduce fractions to their lowest terms. The document also covers factoring numbers to find common factors and greatest common factors, finding multiples and common multiples, and operations involving fractions such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and complex fractions.