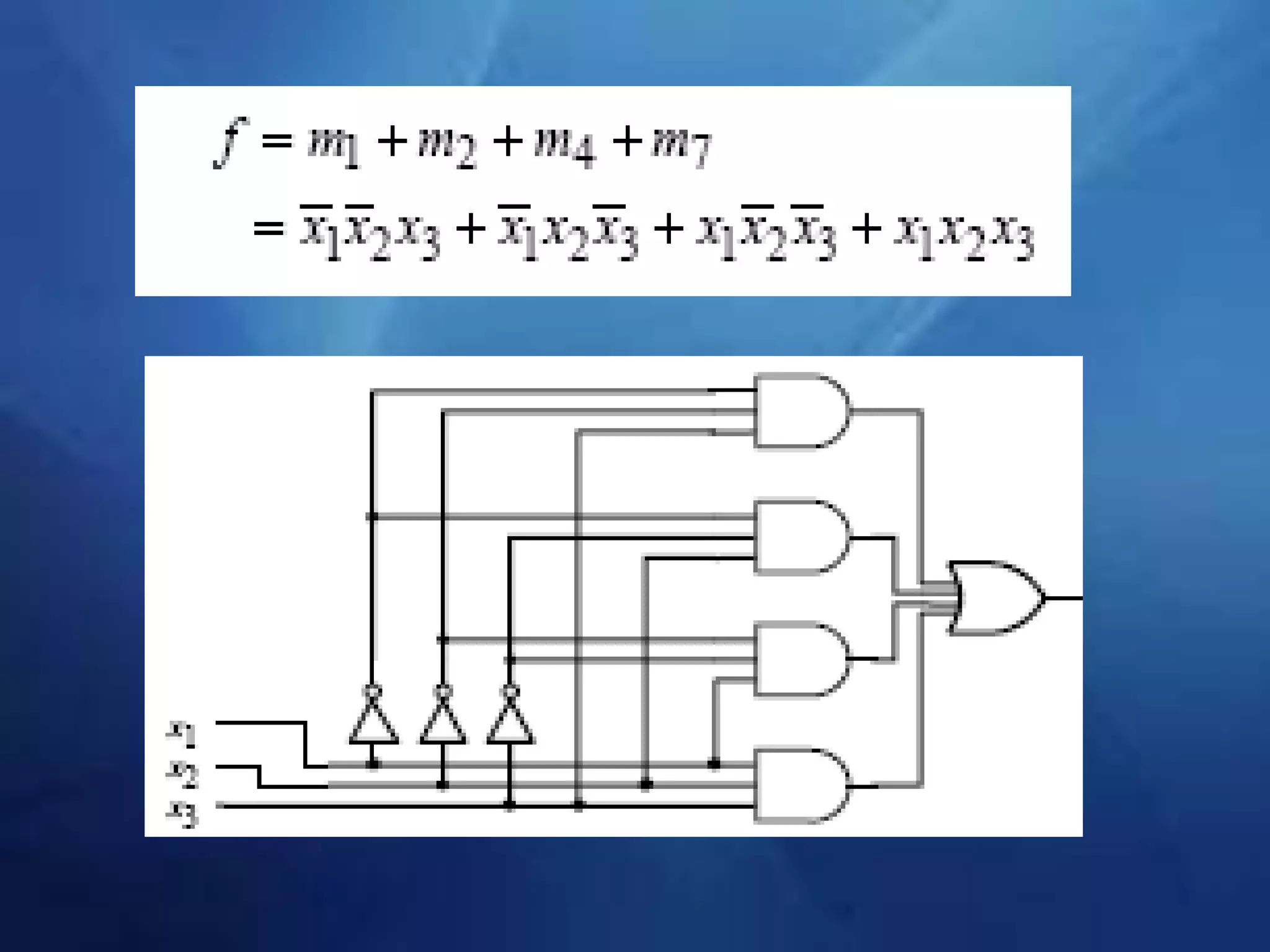
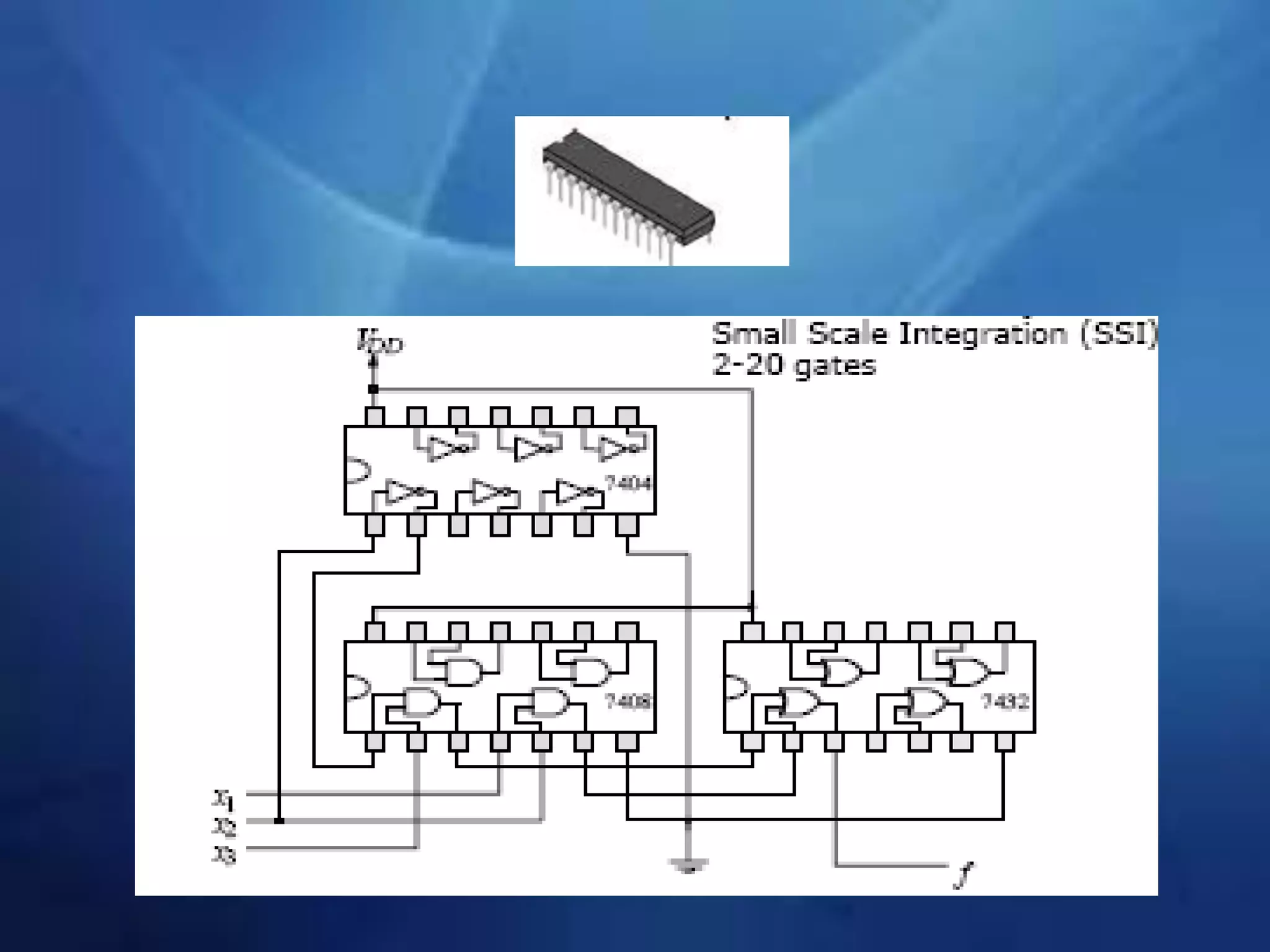
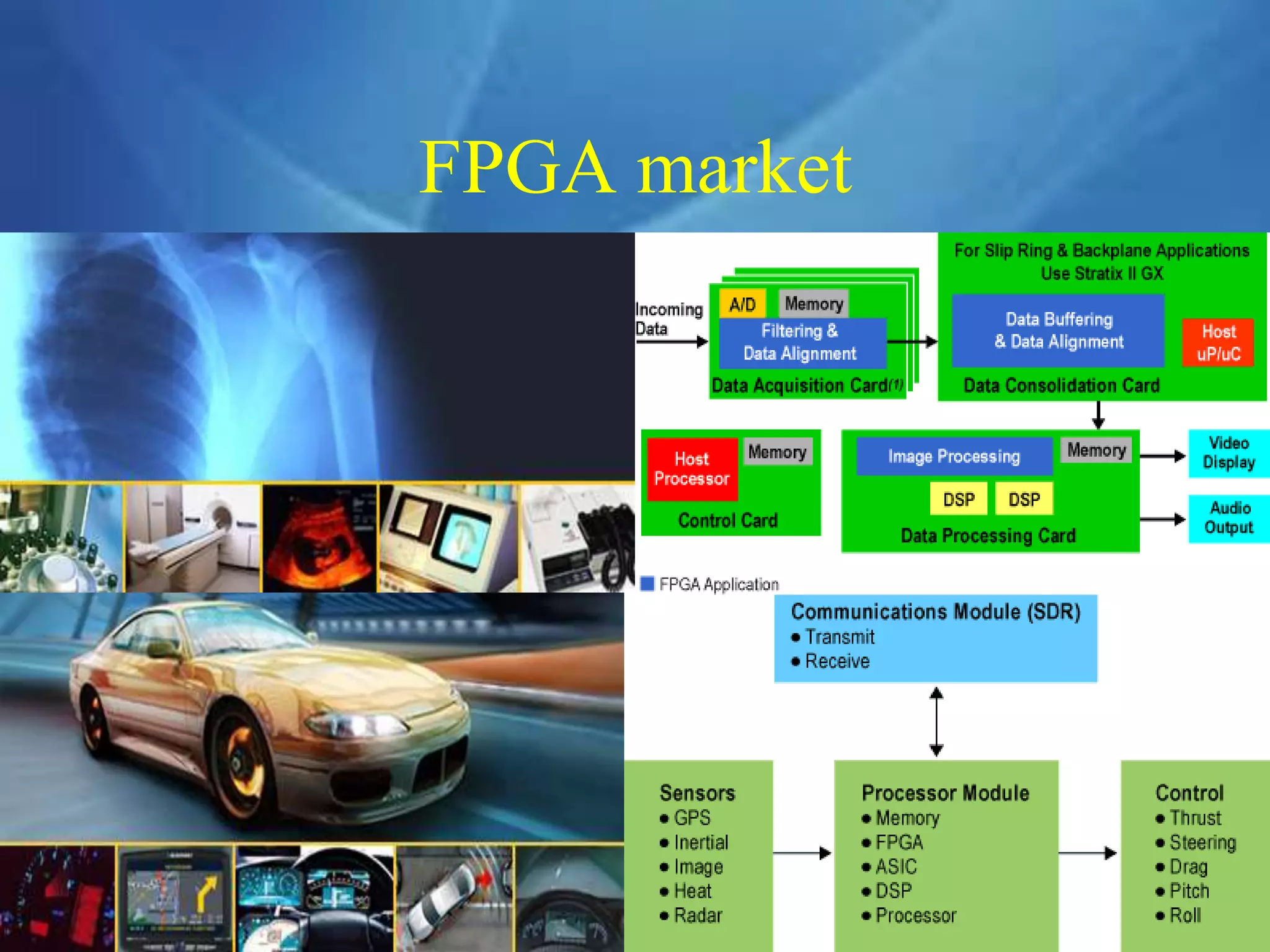
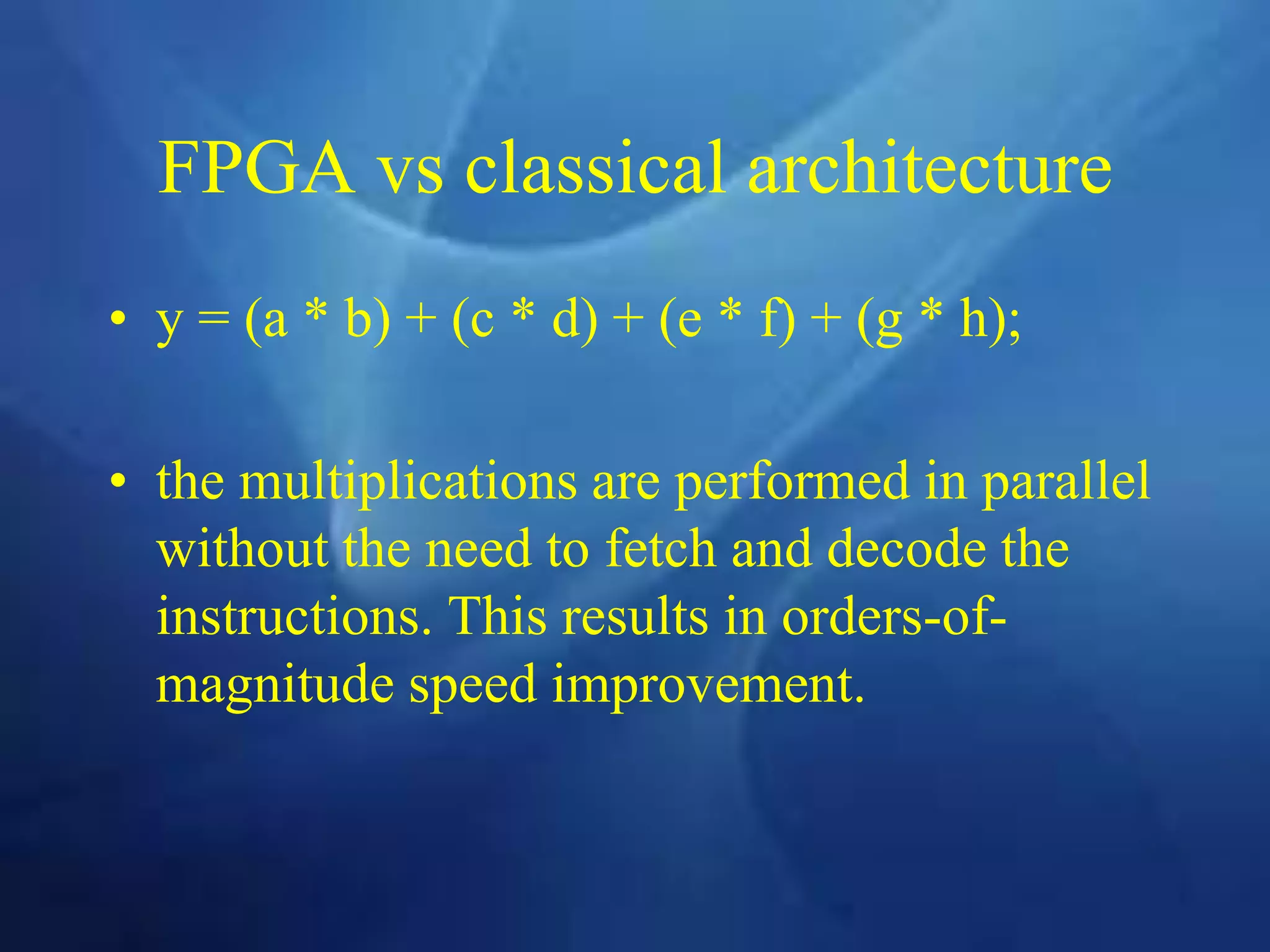
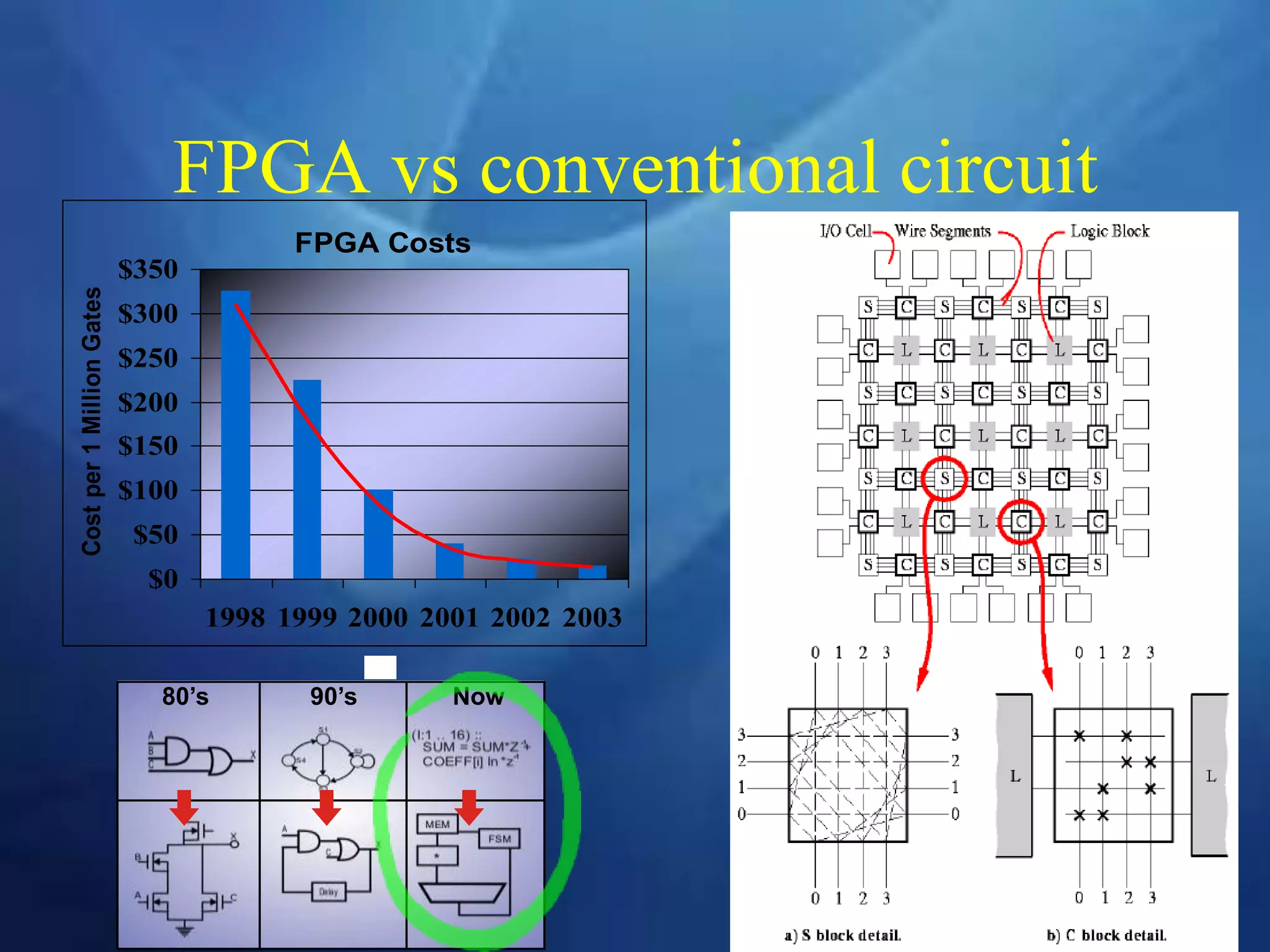
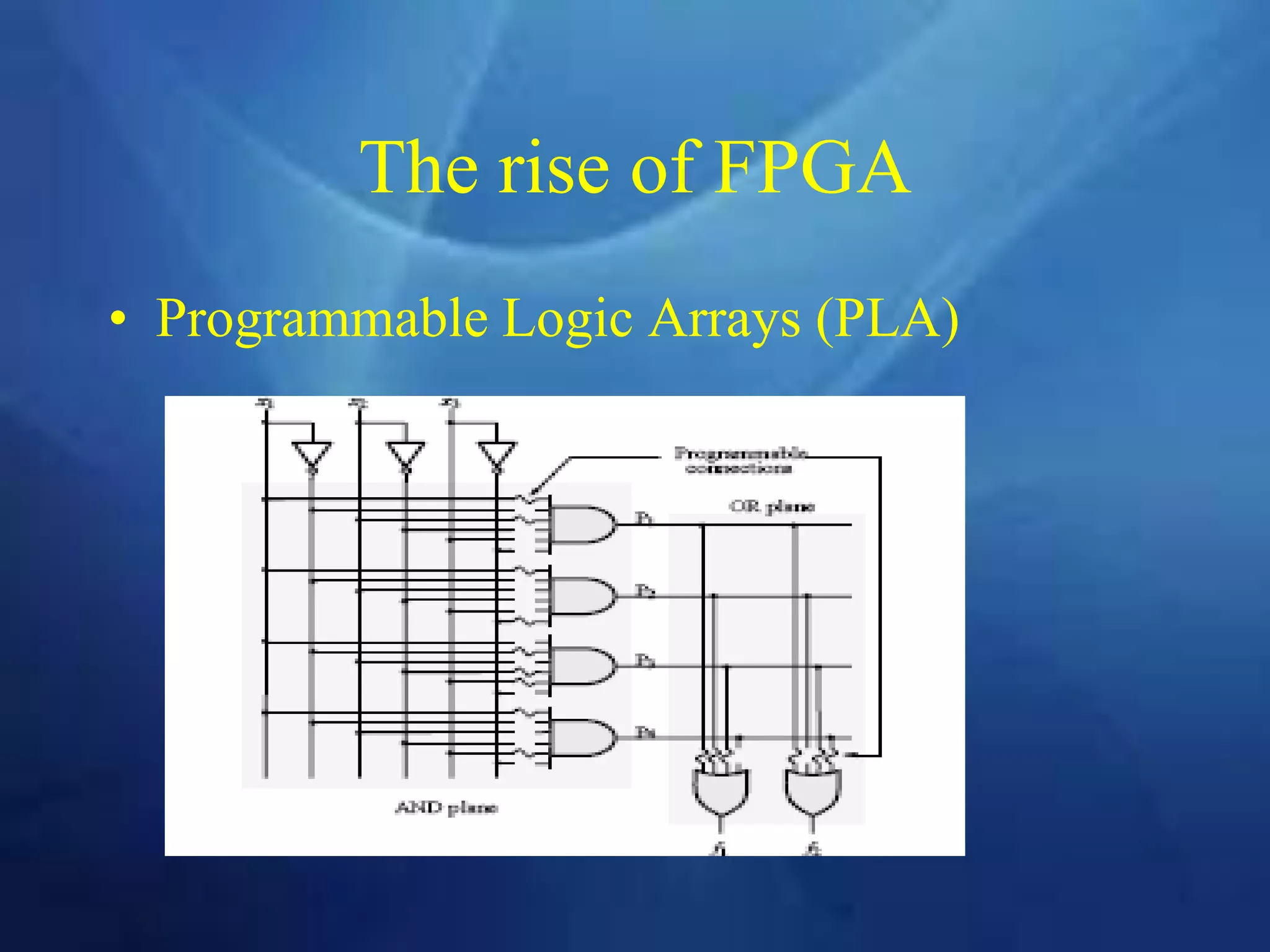
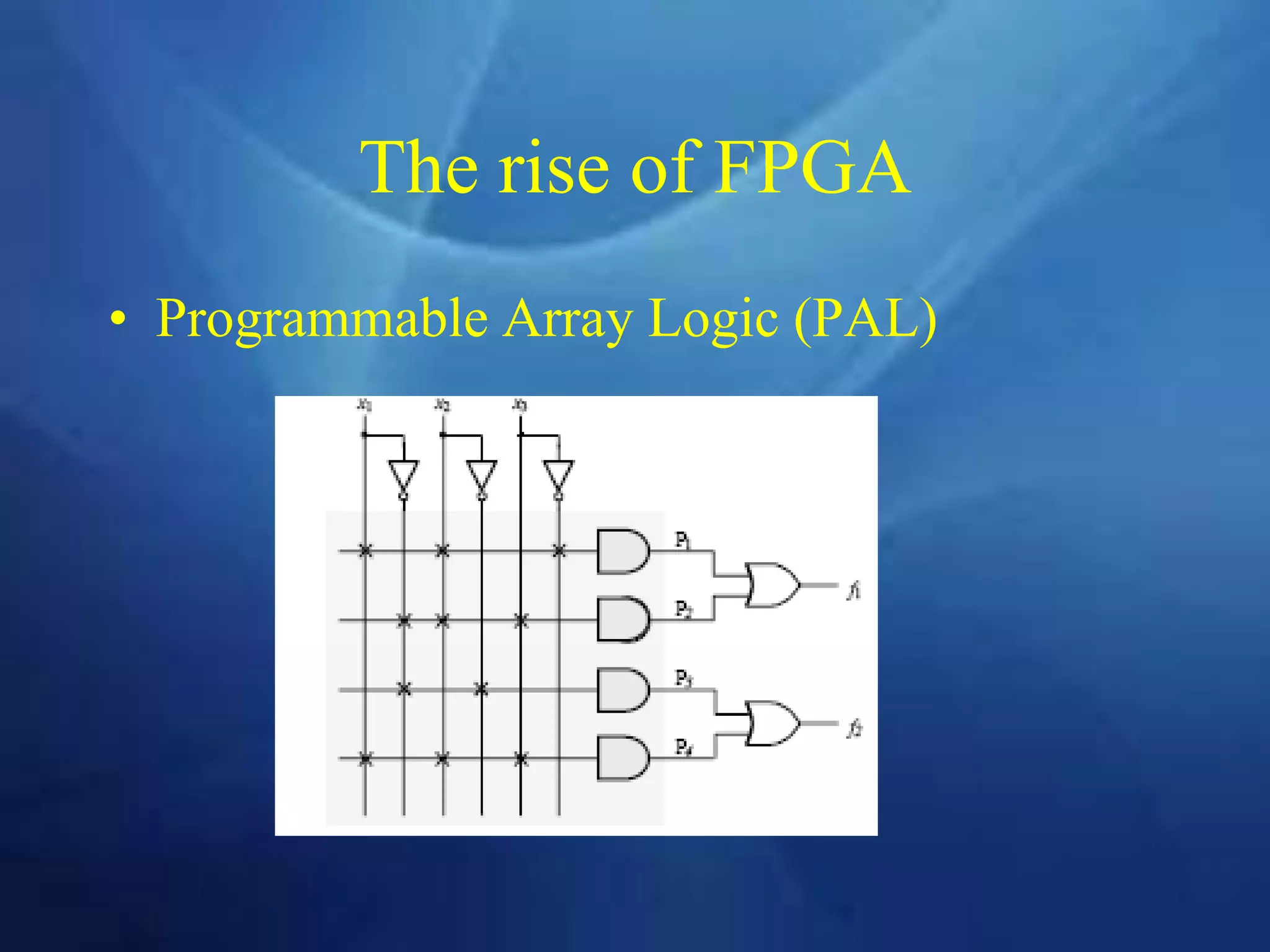
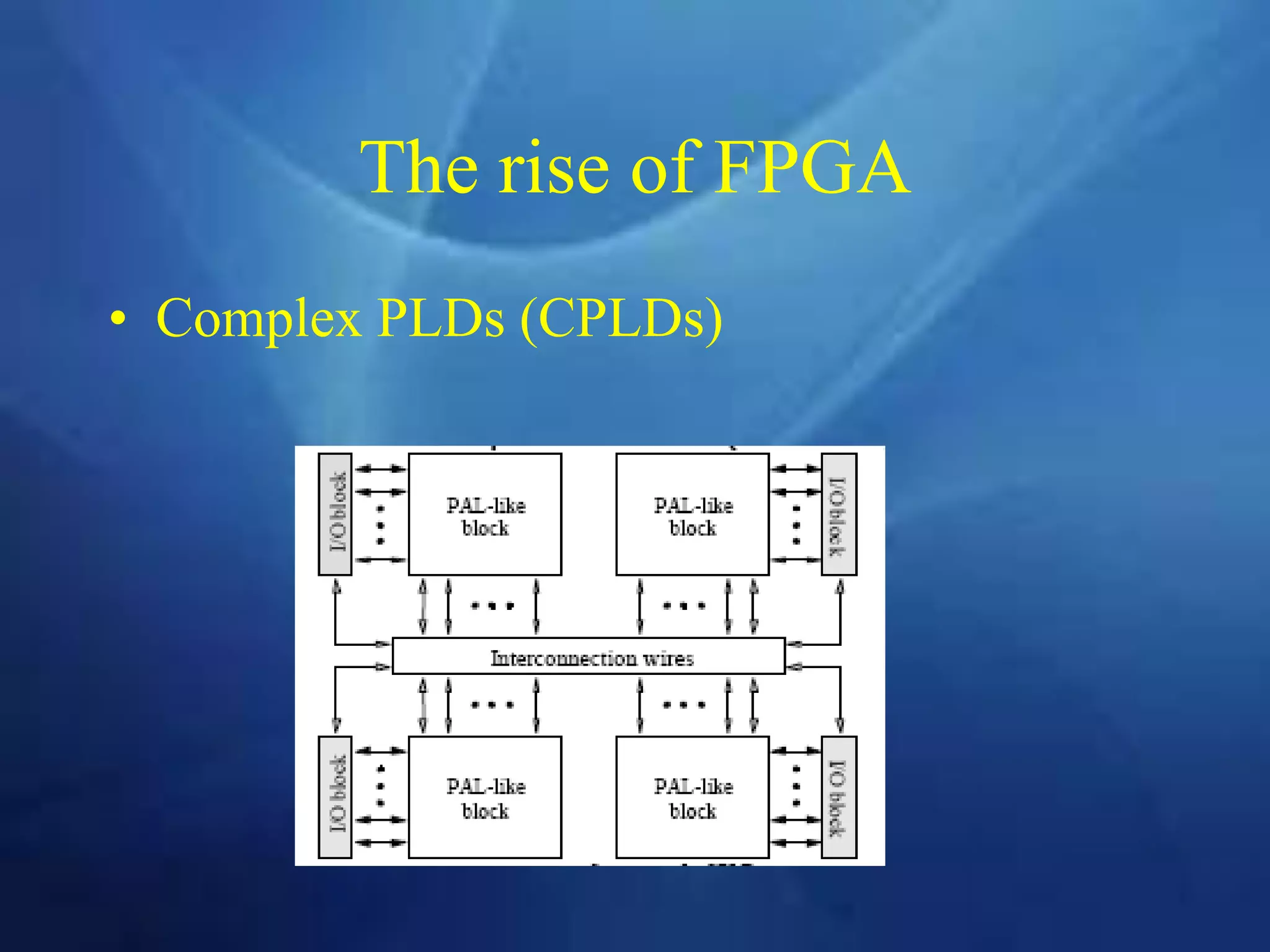
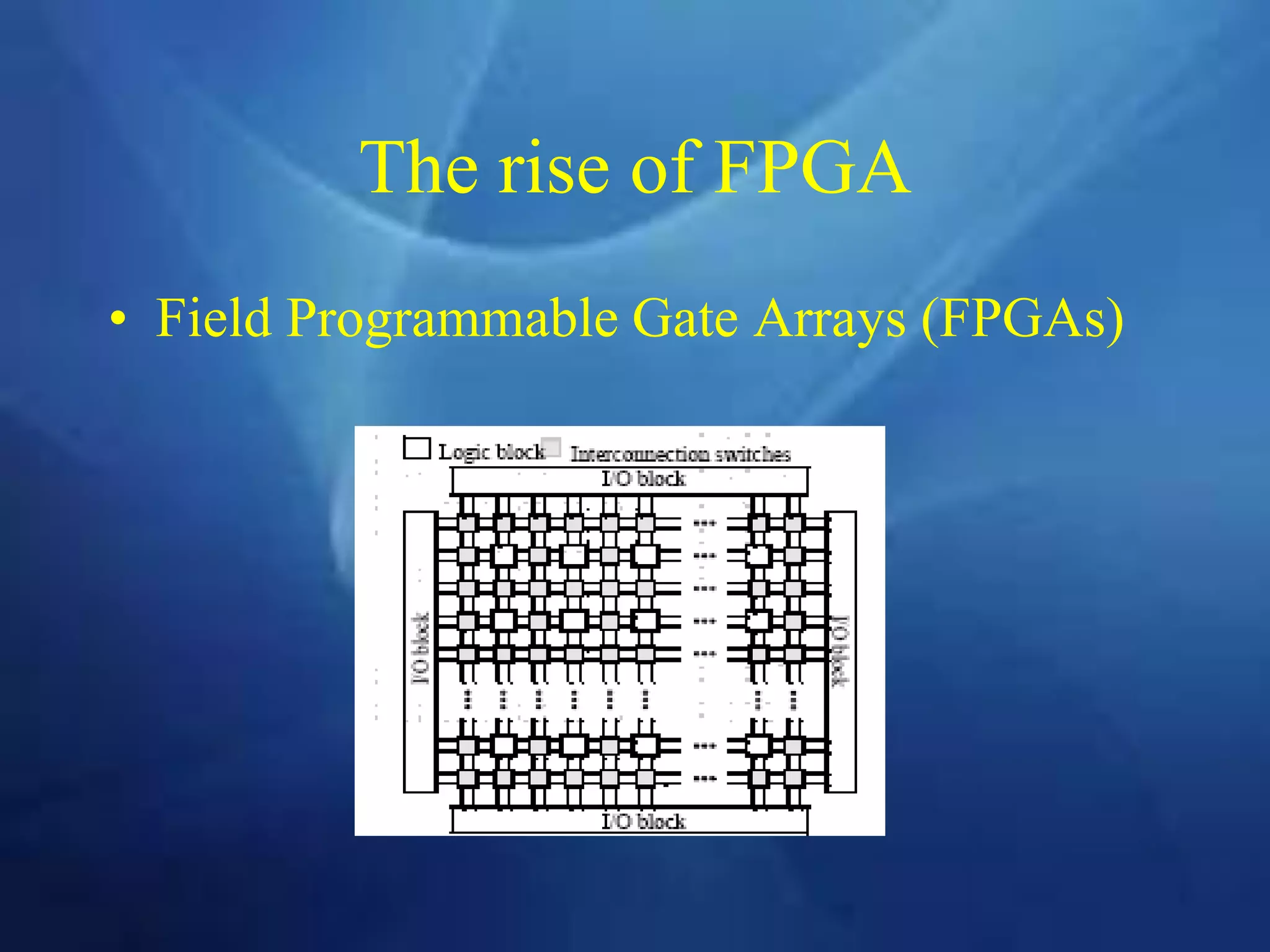
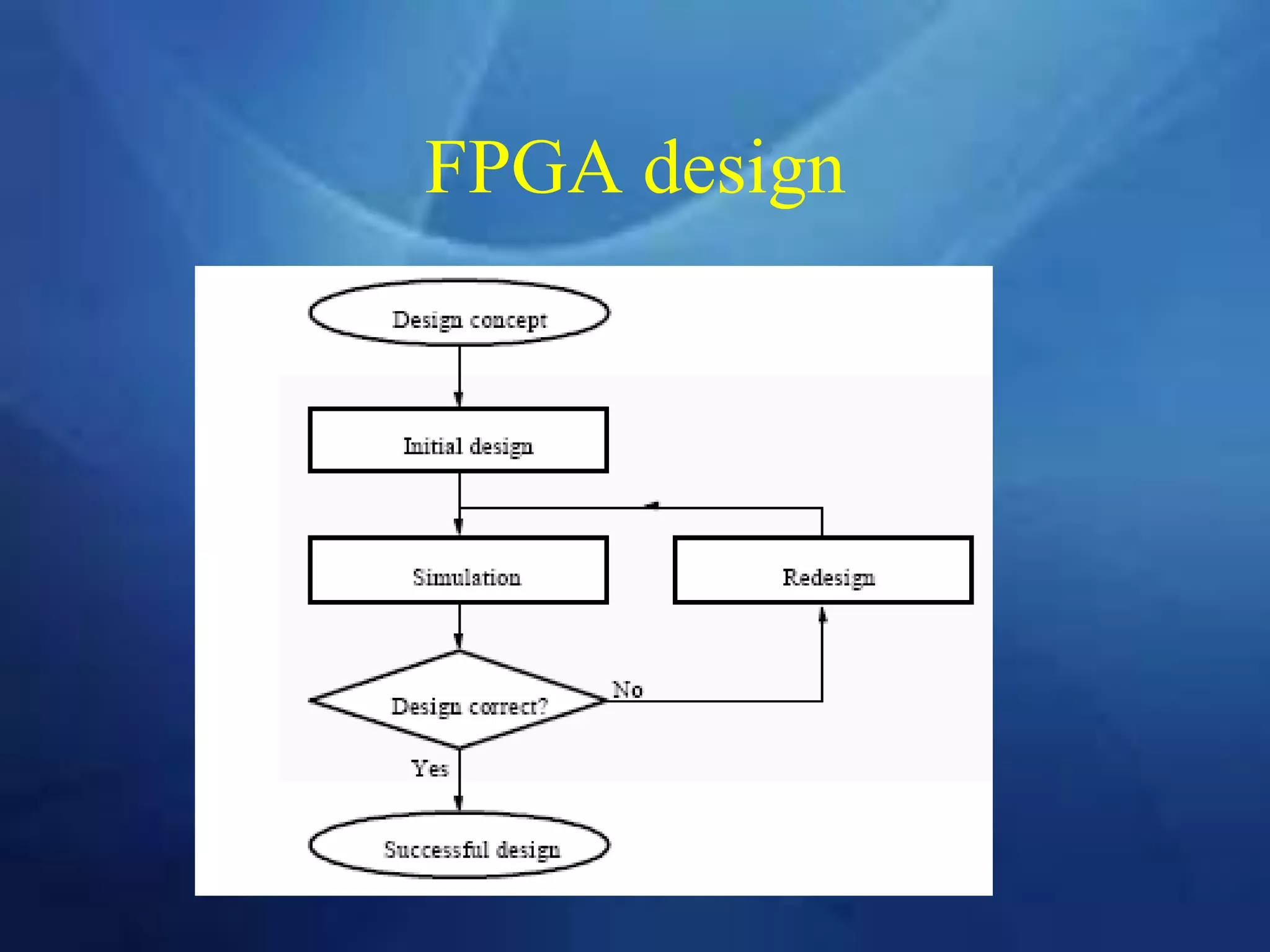
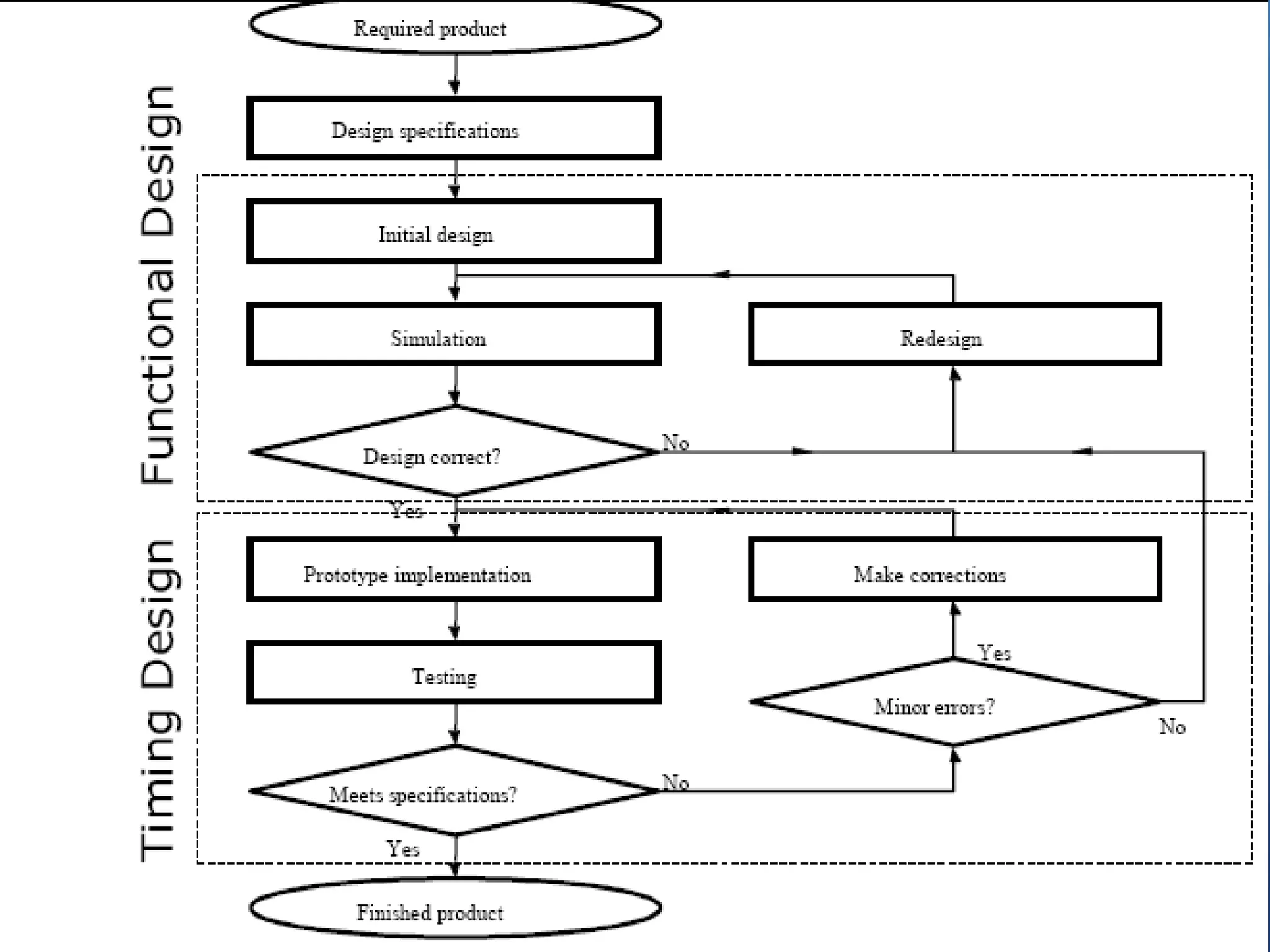
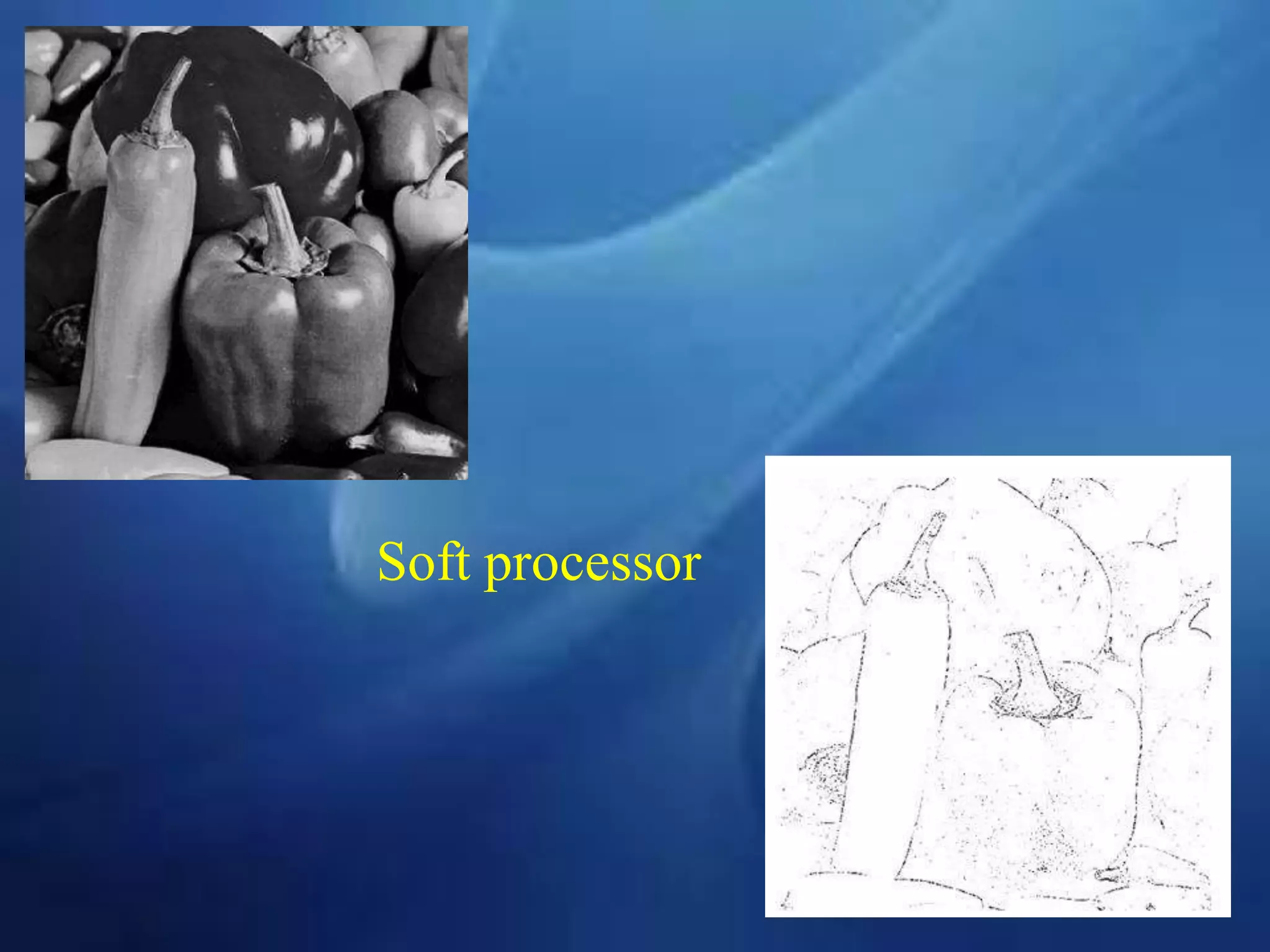
This document provides an overview of field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs). It discusses the differences between hardware engineers and software developers. It covers the history of FPGAs, including the development of VHDL as a hardware description language. The document also discusses FPGA architecture, programming languages, markets, vendors, and design flow. It compares FPGAs to traditional hardware in terms of parallelism and reprogrammability. In conclusion, it notes that FPGAs have replaced discrete logic devices and enabled more flexible designs.