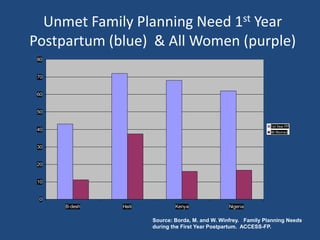
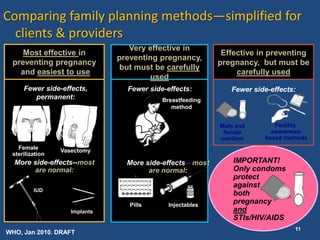
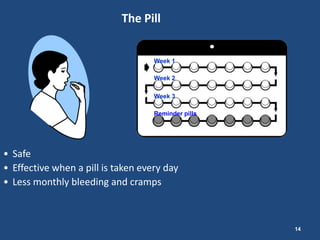
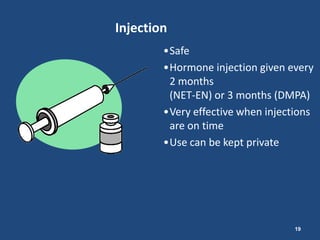
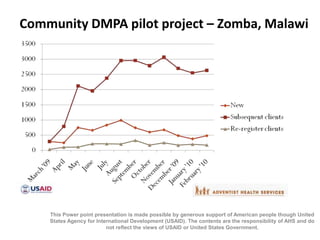
The document outlines strategies and tools for effective family planning within Christian health programs, emphasizing the importance of family planning in achieving various Millennium Development Goals, particularly in relation to maternal health. It provides information on different contraceptive methods, addressing common misconceptions and promoting the use of effective family planning for healthy timing and spacing of pregnancies. The document advocates for overcoming barriers to contraceptive use and ensuring universal access to family planning services.