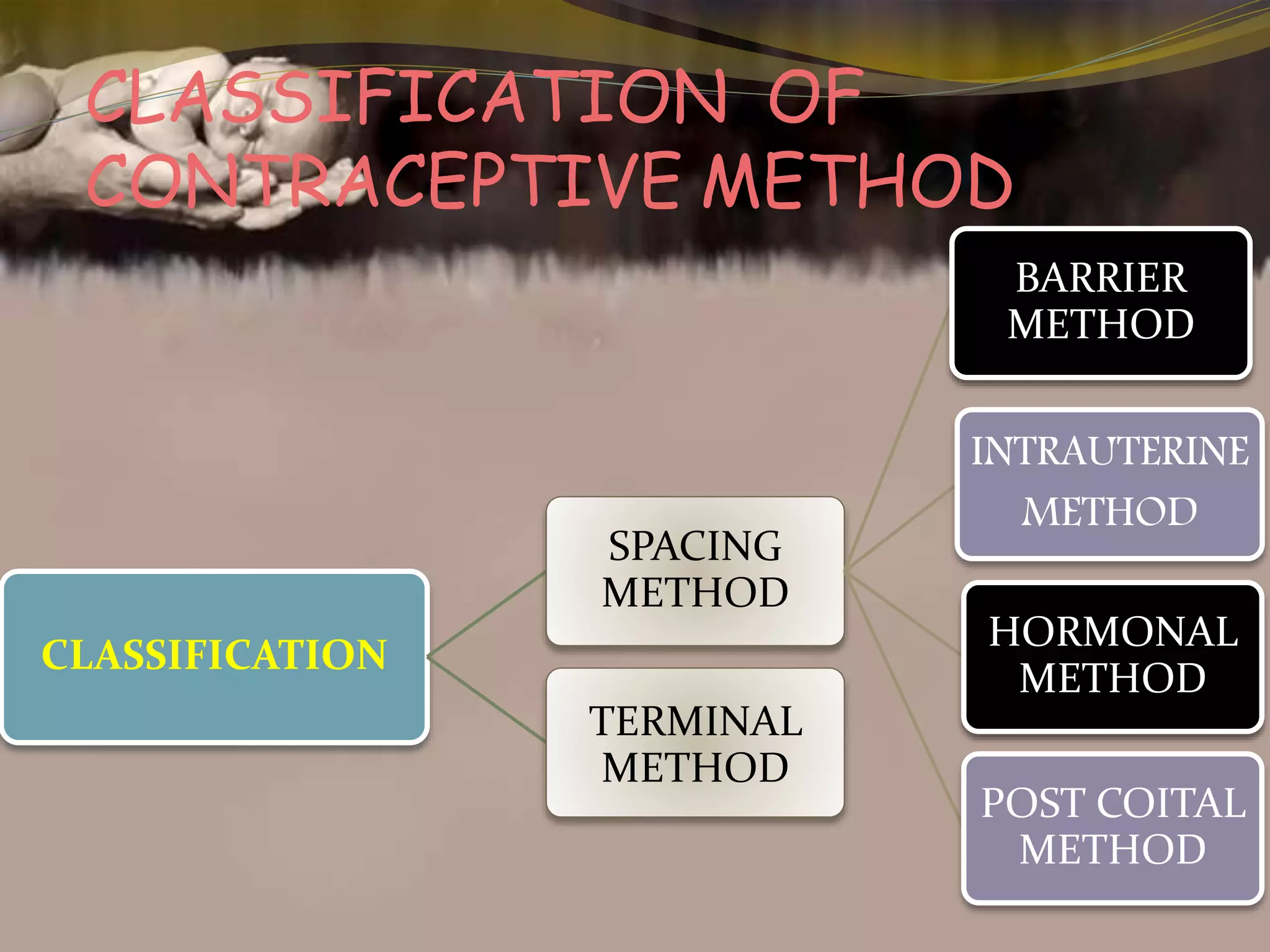
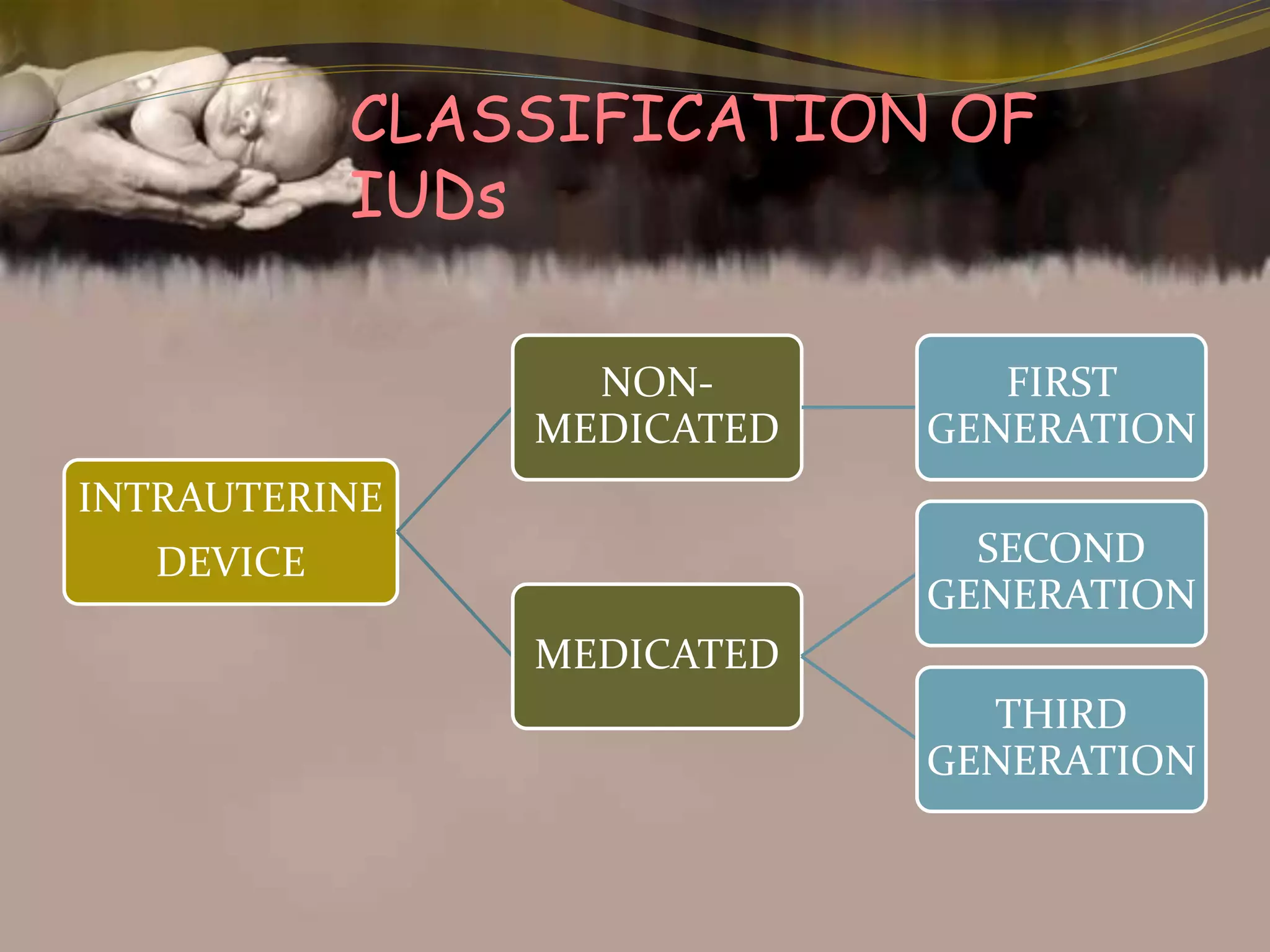
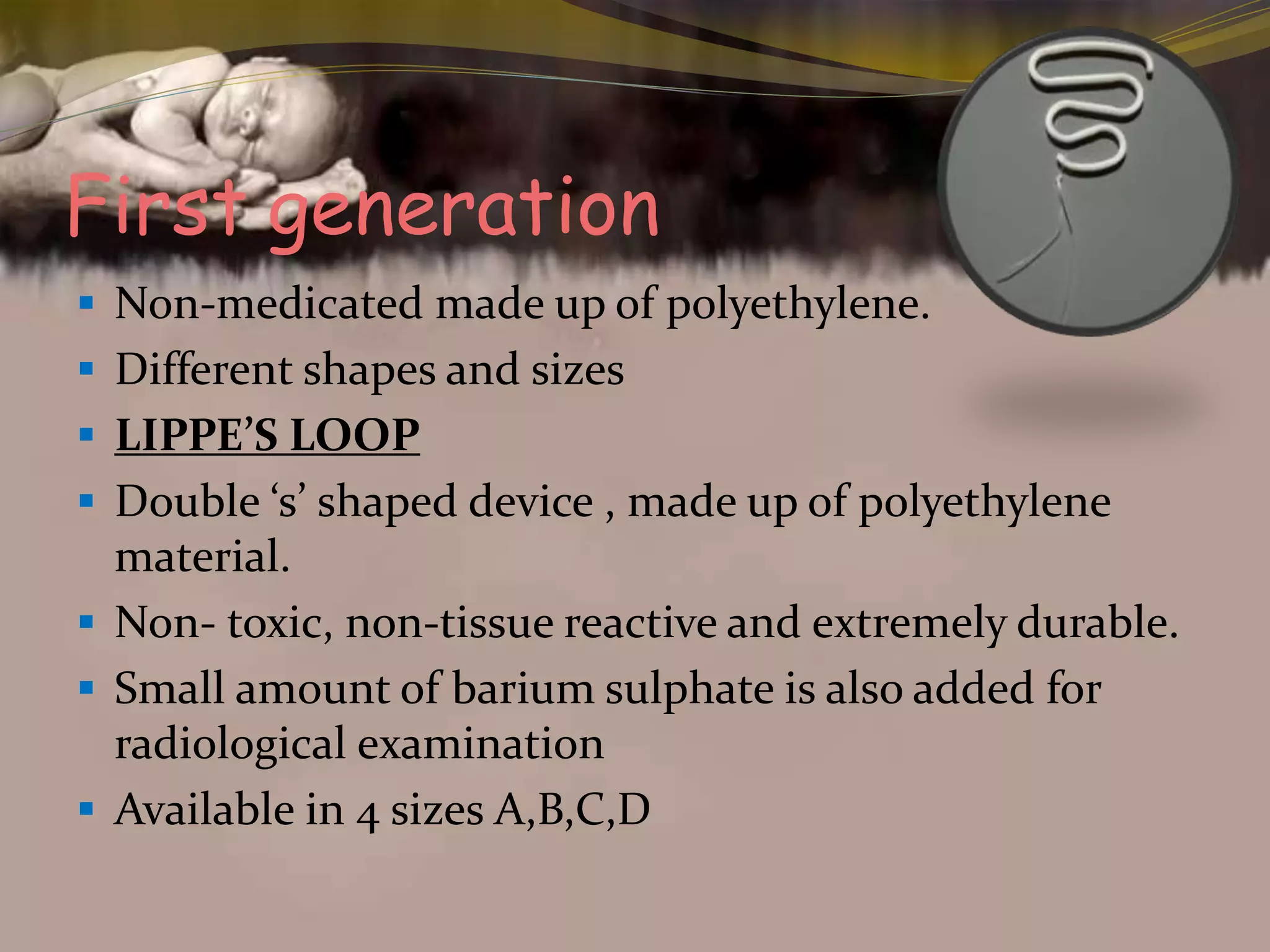
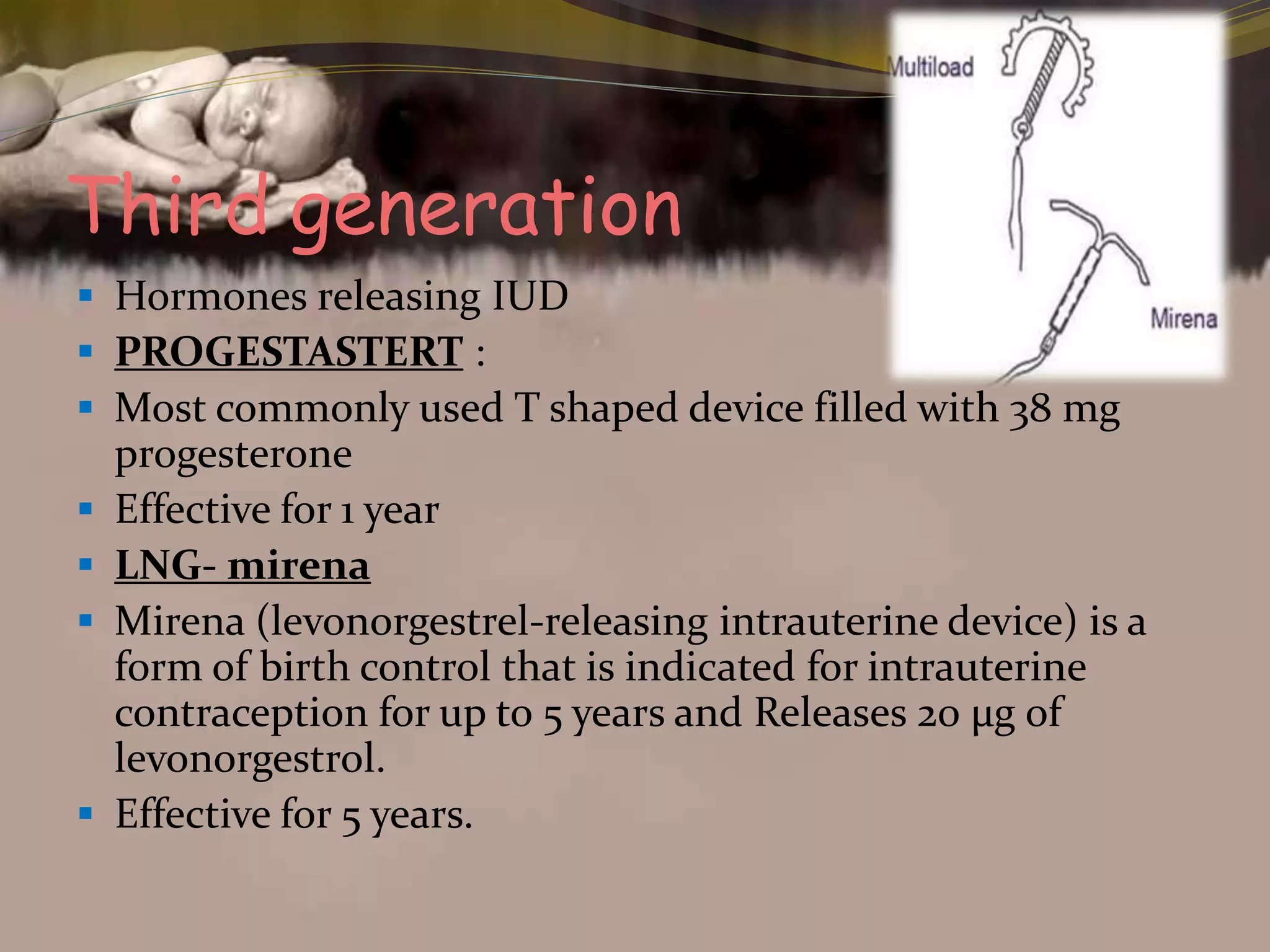
This document provides an overview of family planning methods. It defines family planning and discusses its objectives according to WHO. Natural family planning methods like rhythm method, basal body temperature, and cervical mucus methods are described. Barrier methods like condoms, diaphragms, and spermicides are also summarized. Intrauterine devices including non-medicated, copper, and hormonal IUDs are covered. Oral contraceptives and other hormonal methods like injections and implants are briefly outlined. Benefits, side effects, and contraindications of various family planning methods are highlighted.