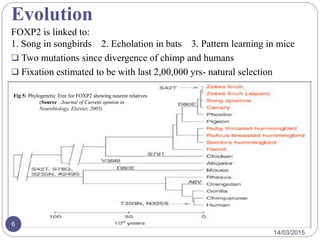
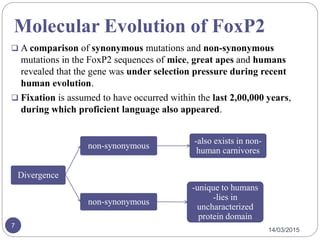
The document discusses the FOXP2 protein and its effects on cortico-basal ganglia circuits, speech, and language. It describes how FOXP2 is encoded in humans and expressed in the basal ganglia and frontal cortex. Mutations can cause reduced speech and developmental issues. Mouse models with FOXP2 disruptions show motor impairments and early death. Two amino acid changes in human FOXP2 occurred recently in evolution and may have enabled complex vocal learning abilities unique to humans. The document also reviews brain regions where FOXP2 is expressed and disorders like apraxia that have been linked to it.




![FACTS ABOUT FOXP2
14/03/20158
The human genome has undergone 17.5 million single nucleotide
changes and 2.5 million insertions and deletions since we split from the
lineage leading to chimpanzees some 6 million years ago.
The human capacity for vocal learning, that is to imitate complex
vocalizations… is absent or very limited in primates and mammals, so
the proficiency of all humans to learn vocalizations is very probably a
phenotype that required genetic changes.
Of the 708 aligned amino acids [in Foxp2] in mouse and human differ at
3 positions. Remarkably, 2 of these changes occurred in the short
timescale of human evolution after the human lineage split from the
lineage leading to chimpanzees.
Foxp2 ranks among the 5% most conserved proteins.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/effectsoffoxp2onbasalgnagliacircuitsspeechlanguage-161208161322/85/FoxP2-and-language-8-320.jpg)