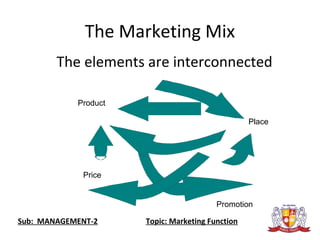
The document discusses key concepts in marketing, including the 4 P's of marketing (product, price, place, promotion), different marketing concepts (production, product, selling, marketing), and orientations (holistic, societal). It provides details on each of the 4 P's - what they refer to and examples. It also explains different management orientations like production, product, selling, and marketing concepts and how firms following these concepts operate. The document is meant to introduce students to fundamental marketing terminology and frameworks.