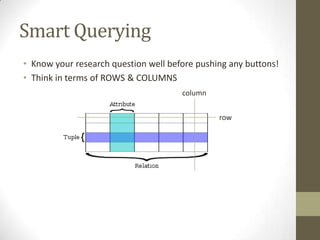
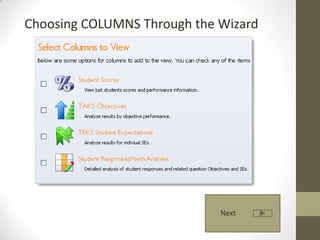
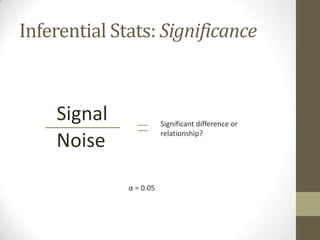
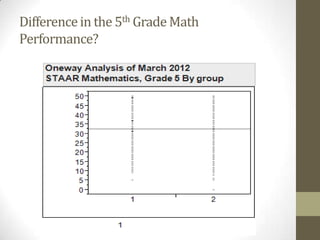
This document provides an overview of relational databases and how to query data using Eduphoria. It discusses that a relational database consists of tables that store sets of data. Relational databases allow users to upload data and query it. Querying can be done through writing SQL or R code, or using a graphical user interface. The document emphasizes thinking in terms of rows and columns when querying and provides examples of how to choose rows and columns through the Eduphoria wizard. It also covers exporting and analyzing data from Eduphoria.