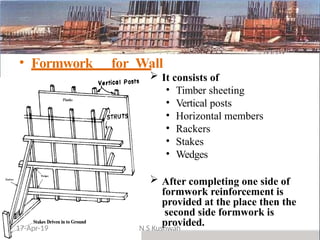
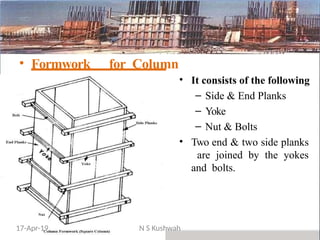
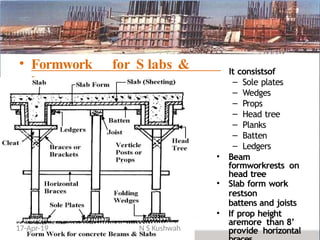
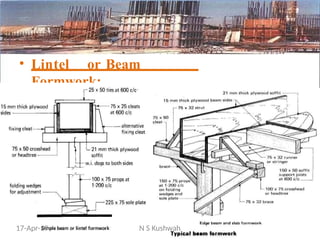
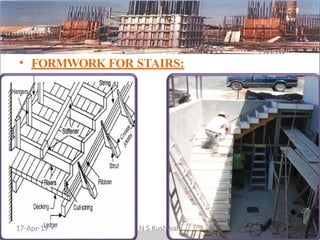
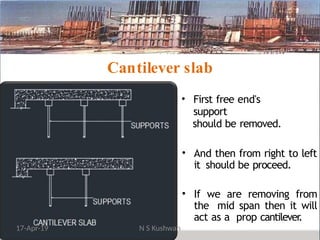
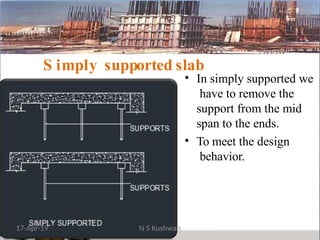
The document presents an overview of formwork construction techniques, detailing the materials, design, and requirements necessary for effective use, including quality, safety, and economy considerations. It outlines different types of formwork for various structural members such as walls, columns, and slabs, along with the importance of proper assembly, removal, and maintenance practices. Additionally, it discusses cost factors associated with formwork and highlights the advantages of using steel formwork over traditional materials.