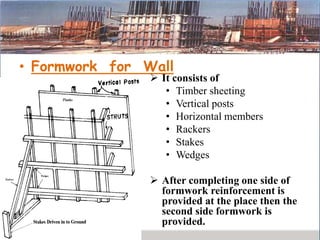
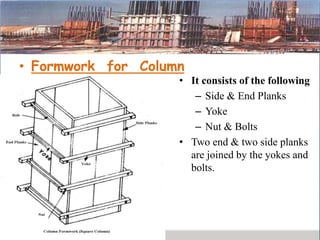
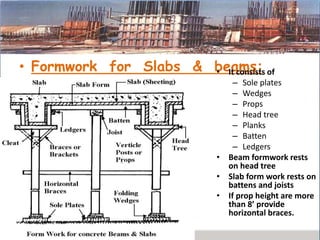
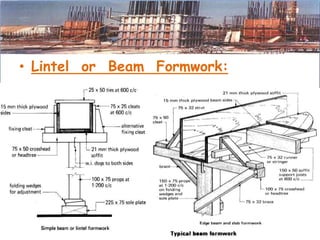
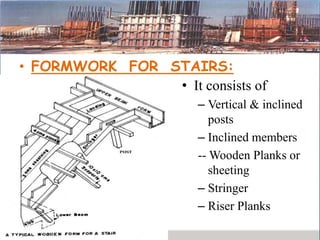
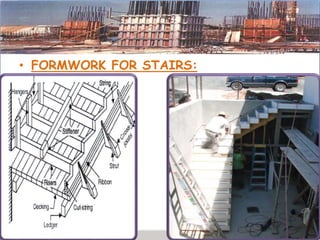
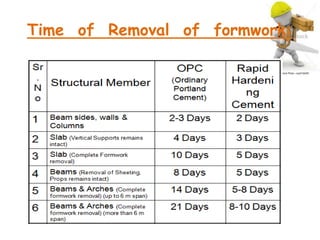
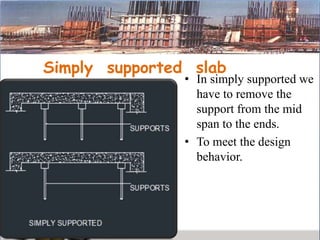
This presentation discusses formwork construction techniques. Formwork is a temporary mold used to contain and shape wet concrete until it hardens. It must be strong enough to support the weight of wet concrete and other loads. Common materials for formwork include timber and steel. Proper formwork design considers containment, strength, leakage resistance, accuracy, ease of handling, finish, access for concrete, and economy. Formwork is used for walls, columns, slabs, beams, stairs, chimneys, and other structural elements. Factors that influence when formwork can be removed include cement type, concrete mix ratio, and weather conditions. Maintenance and costs of formwork are also discussed.