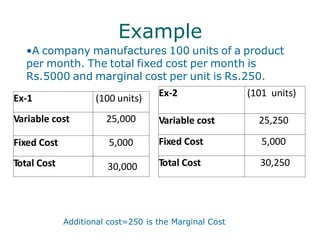
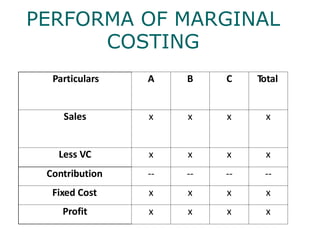
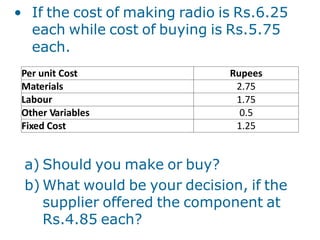
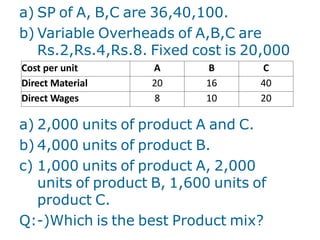
Marginal costing is a technique where only variable costs are treated as product costs and included in inventory valuation. Marginal cost is the additional cost of producing one additional unit of output. Marginal costing helps in decision making such as setting selling prices, exploring new markets, make or buy decisions, determining optimal product mix, and deciding whether to operate a plant or shut it down. An example shows how marginal costing can be used to determine whether a company should make or buy a component based on relevant costs.