The document provides an overview of animal form and function through a series of lecture slides. It discusses the following key points:
- Animal body plans follow patterns of symmetry like radial, bilateral, or asymmetrical. Bilateral symmetry allows for high mobility in land and aquatic animals.
- The size and shape of an animal's body is adapted to its environment and affects how it interacts with its surroundings.
- Animals obtain energy from food and convert nutrients to ATP. Their metabolic rate depends on being endothermic or ectothermic.
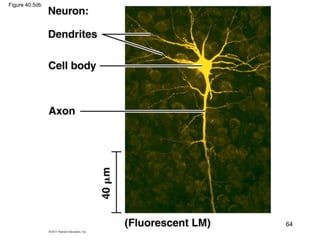
- The hierarchical organization of tissues, organs and systems allows for exchange of materials and maintenance of homeostasis. Epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous tissues each have