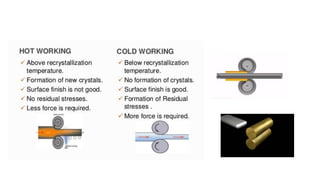
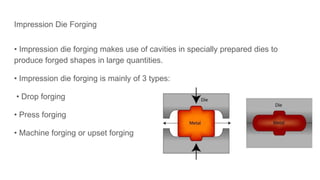
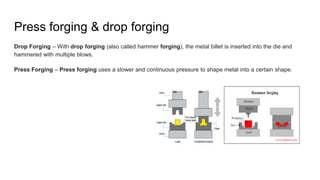
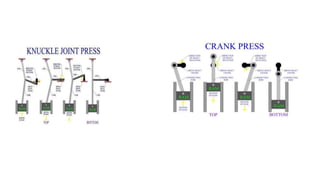
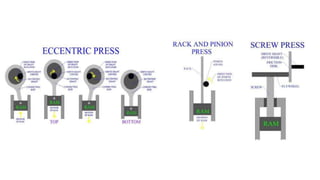
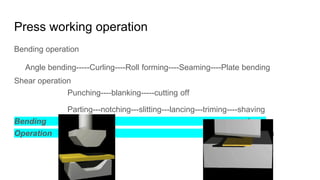
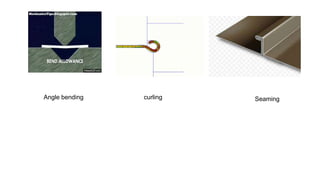
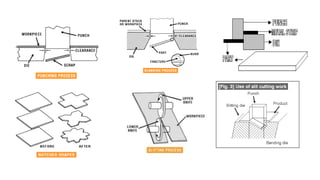
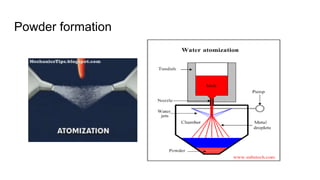
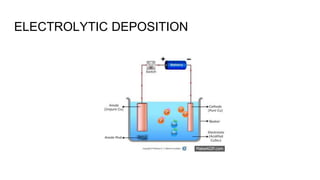
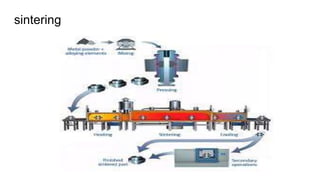
The document discusses metal forming technology, focusing on the mechanical deformation process utilized to shape metal components without altering mass. It outlines various forging methods such as smith forging and impression die forging, emphasizing their applications and classifications. Additionally, it covers powder metallurgy, detailing its procedural steps and significance in enhancing mechanical properties of metal powders.