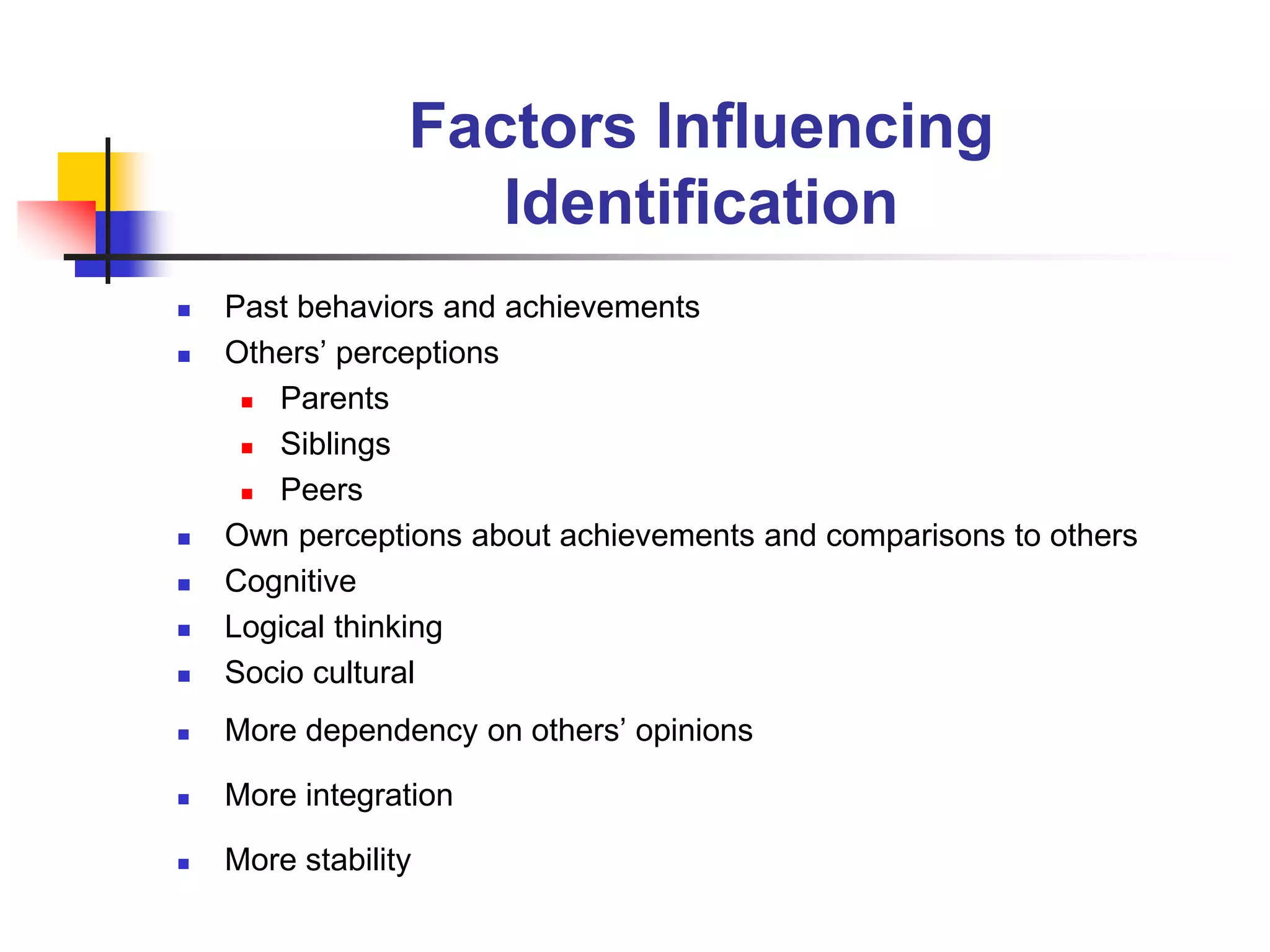
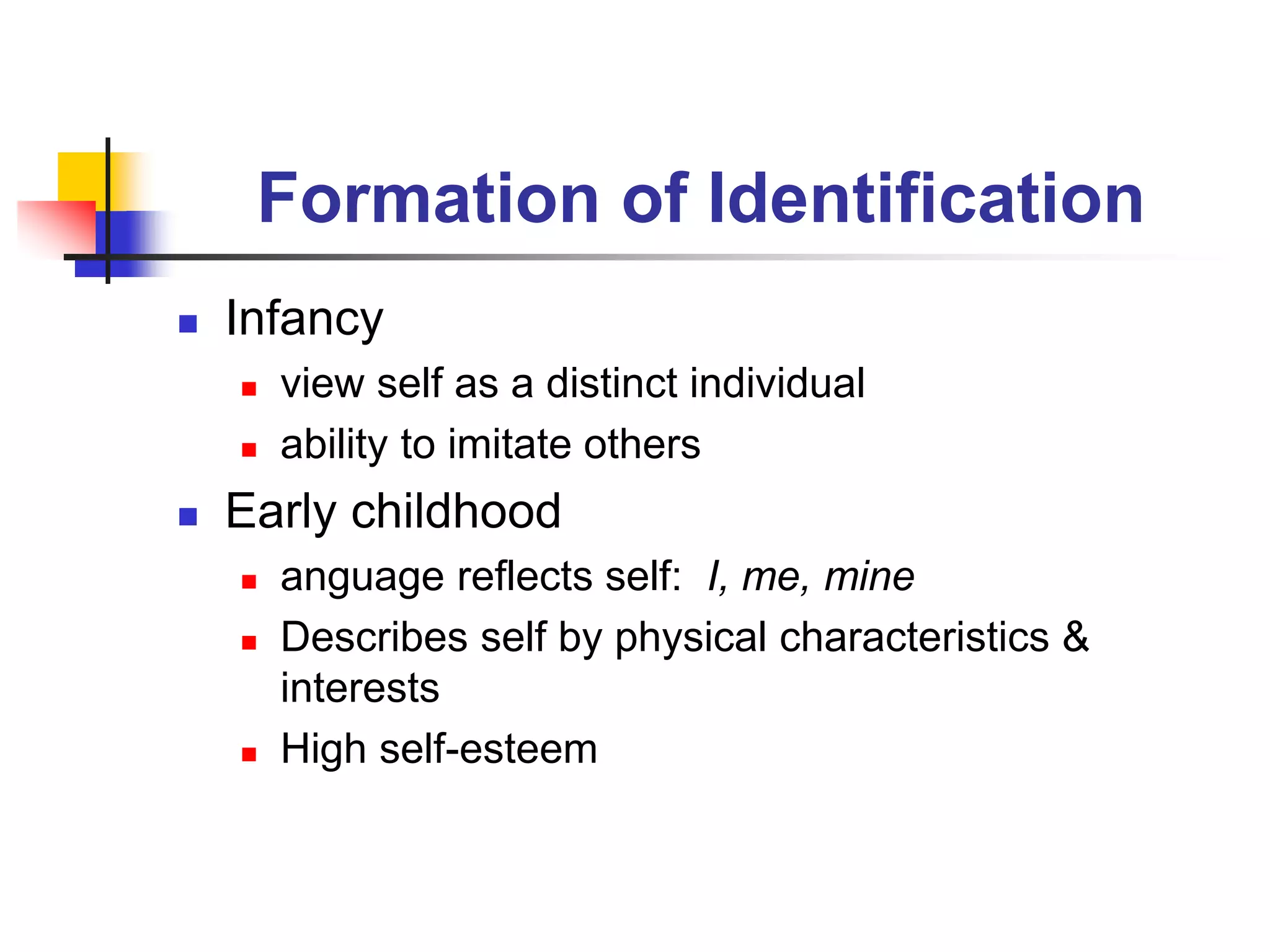
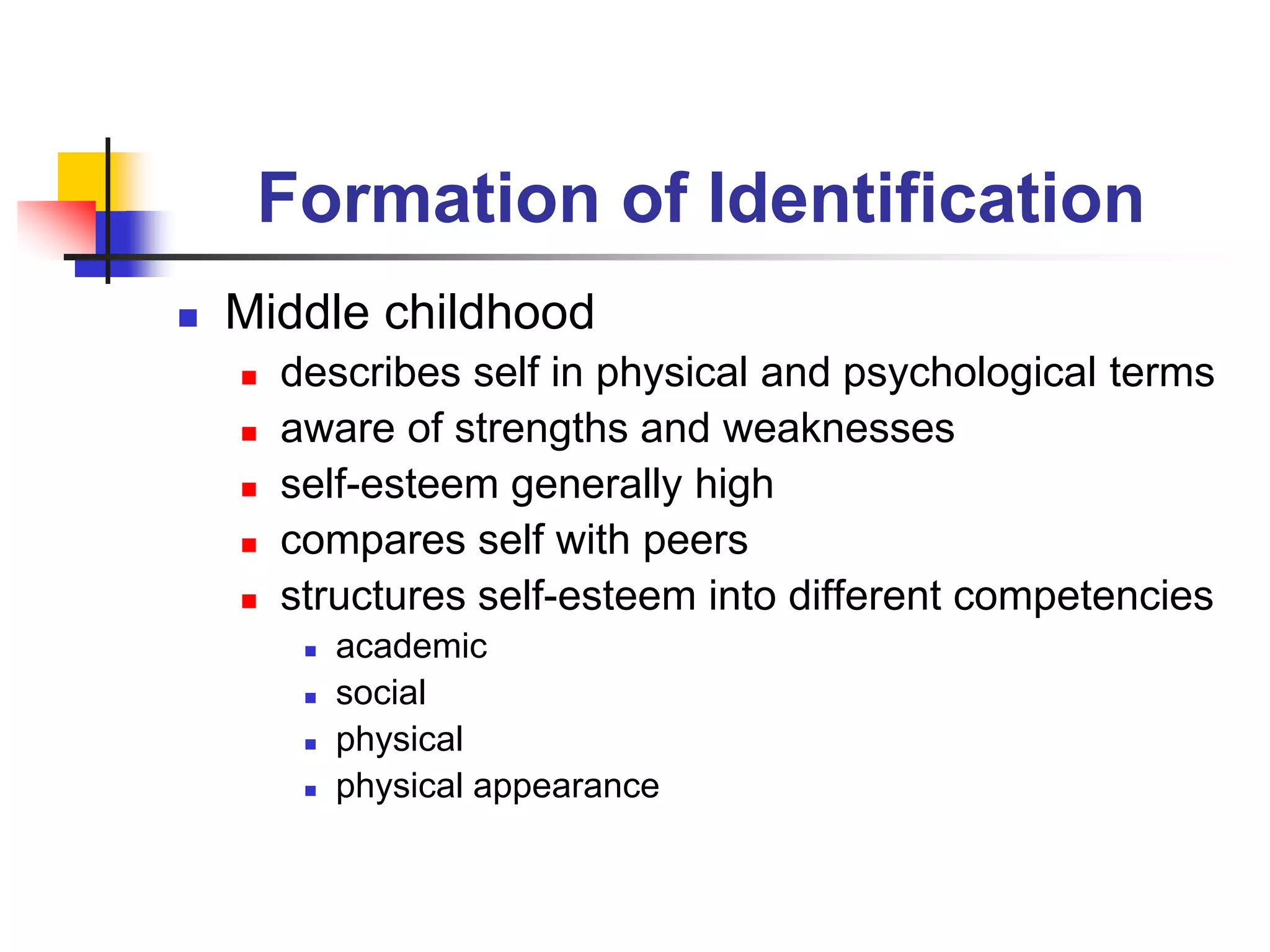
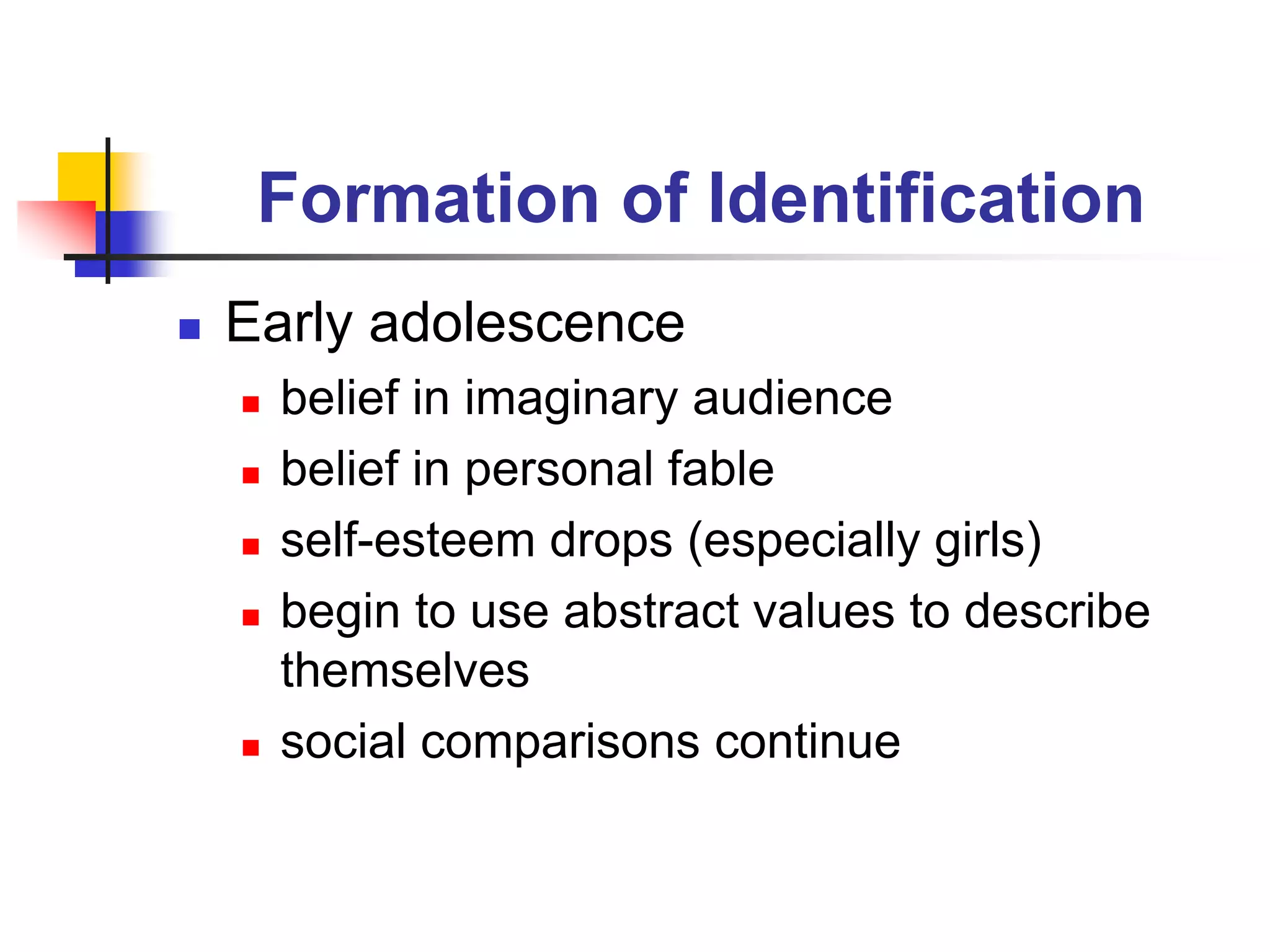
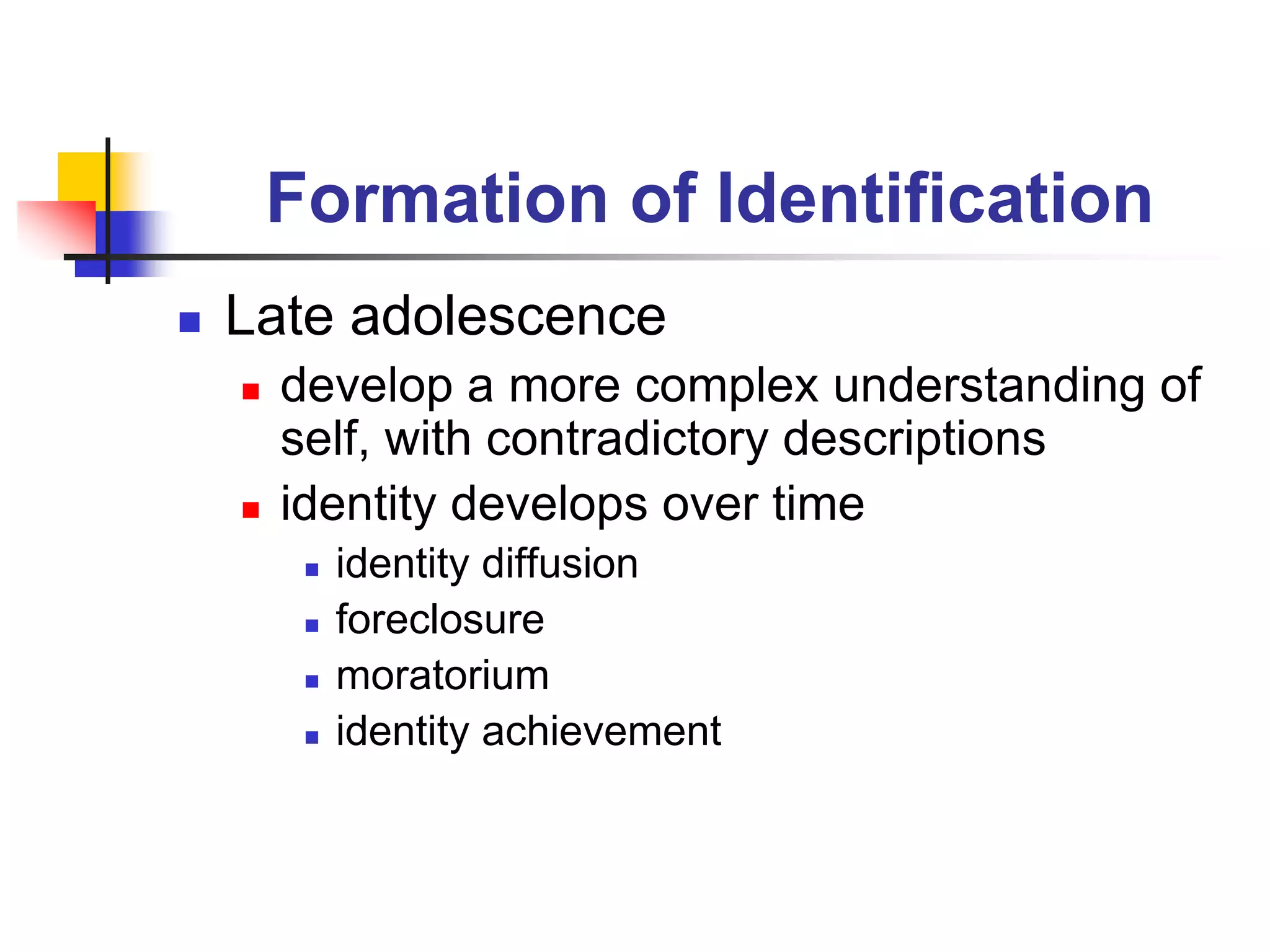
This document discusses identity formation and the factors that influence it. It explains that identity formation begins in infancy, when children begin to see themselves as distinct individuals. During early childhood, children describe themselves using physical characteristics and interests. In middle childhood, self-esteem is generally high as children compare themselves to peers. During early adolescence, self-esteem drops, especially in girls, as social comparisons increase. By late adolescence, identity has developed into a more complex understanding, with identities that can be diffuse, achieved through foreclosure or moratorium, or achieved. The document advocates for classrooms that foster identity formation through challenging learning environments, achievement, and developing positive habits and values.