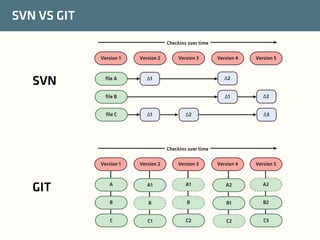
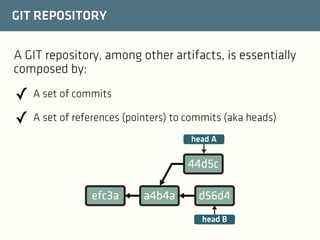
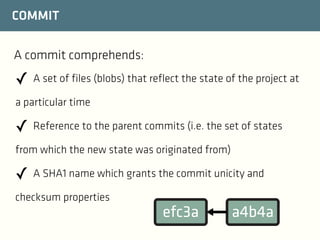
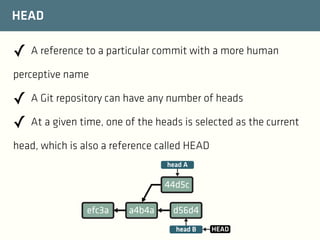
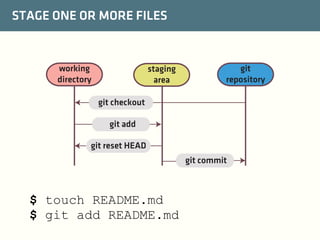
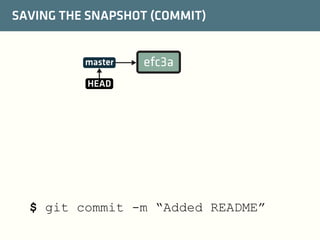
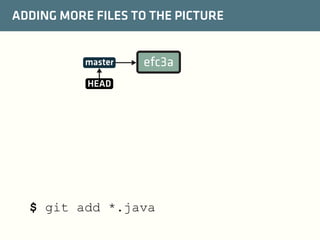
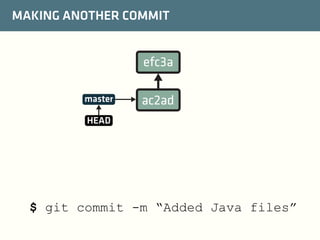
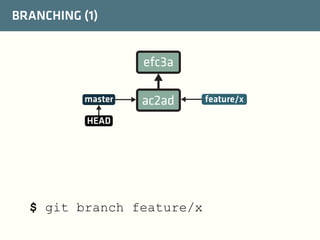
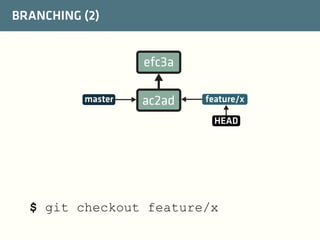
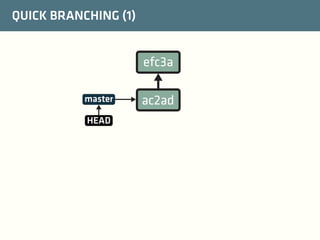
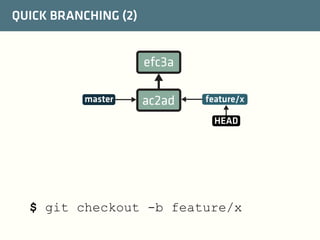
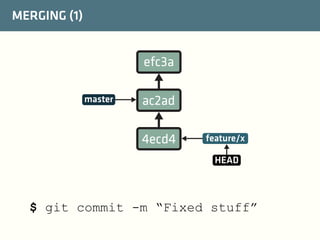
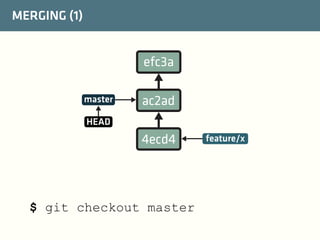
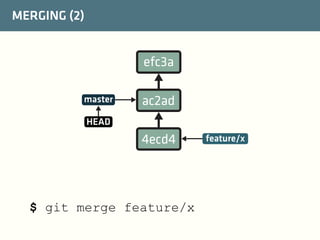
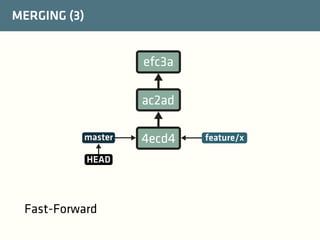
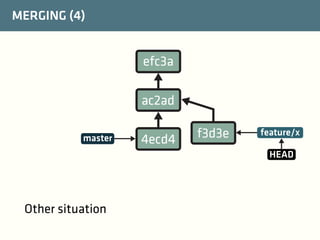
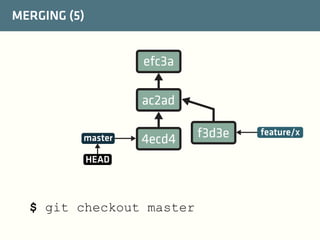
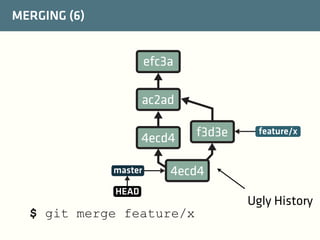
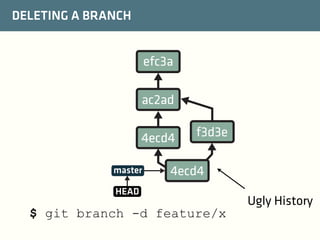
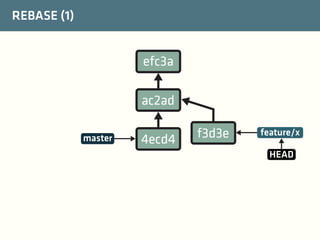
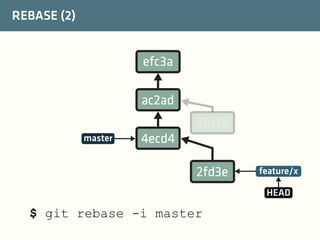
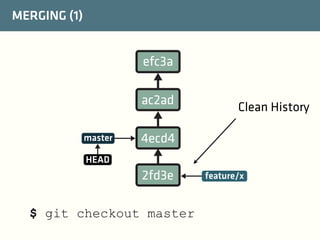
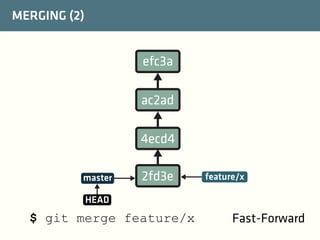
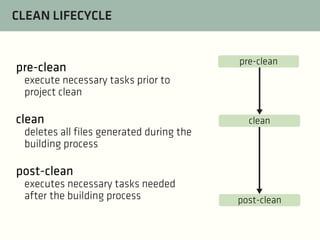
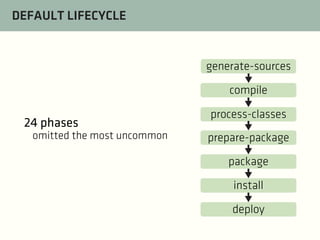
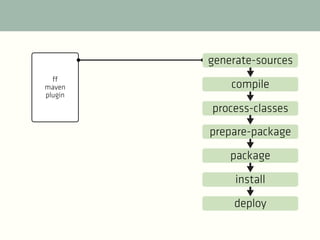
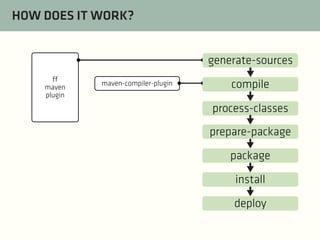
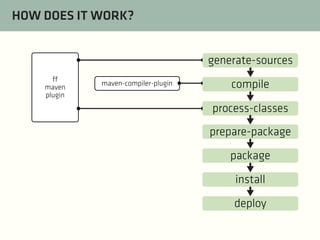
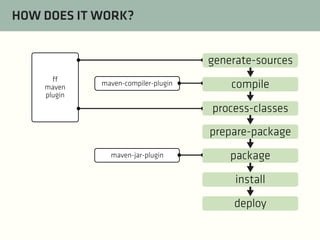
The document provides a comprehensive guide on best practices for coding in Eclipse, using Git for version control, and managing projects with Maven. It emphasizes the importance of adhering to code styles, utilizing shortcuts for productivity, understanding Git repository structures and workflows, and implementing Maven build lifecycles and plugins. Key rules include automatic formatting, effective branching and merging in Git, and managing dependencies within Maven to maintain a clean project environment.