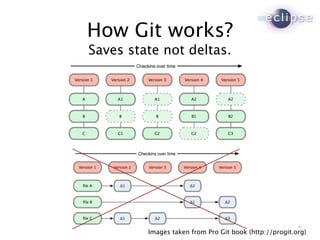
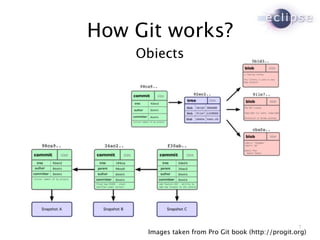
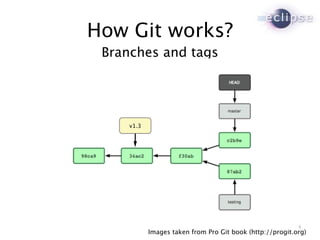
The document discusses Git and Eclipse tools for working with Git. It describes EGit, an Eclipse plugin that provides integration with Git repositories, and JGit, a Java library for Git. EGit and JGit are open source projects hosted by the Eclipse Foundation. The document outlines features and history of EGit releases and the goal of building a community around Git usage at Eclipse.