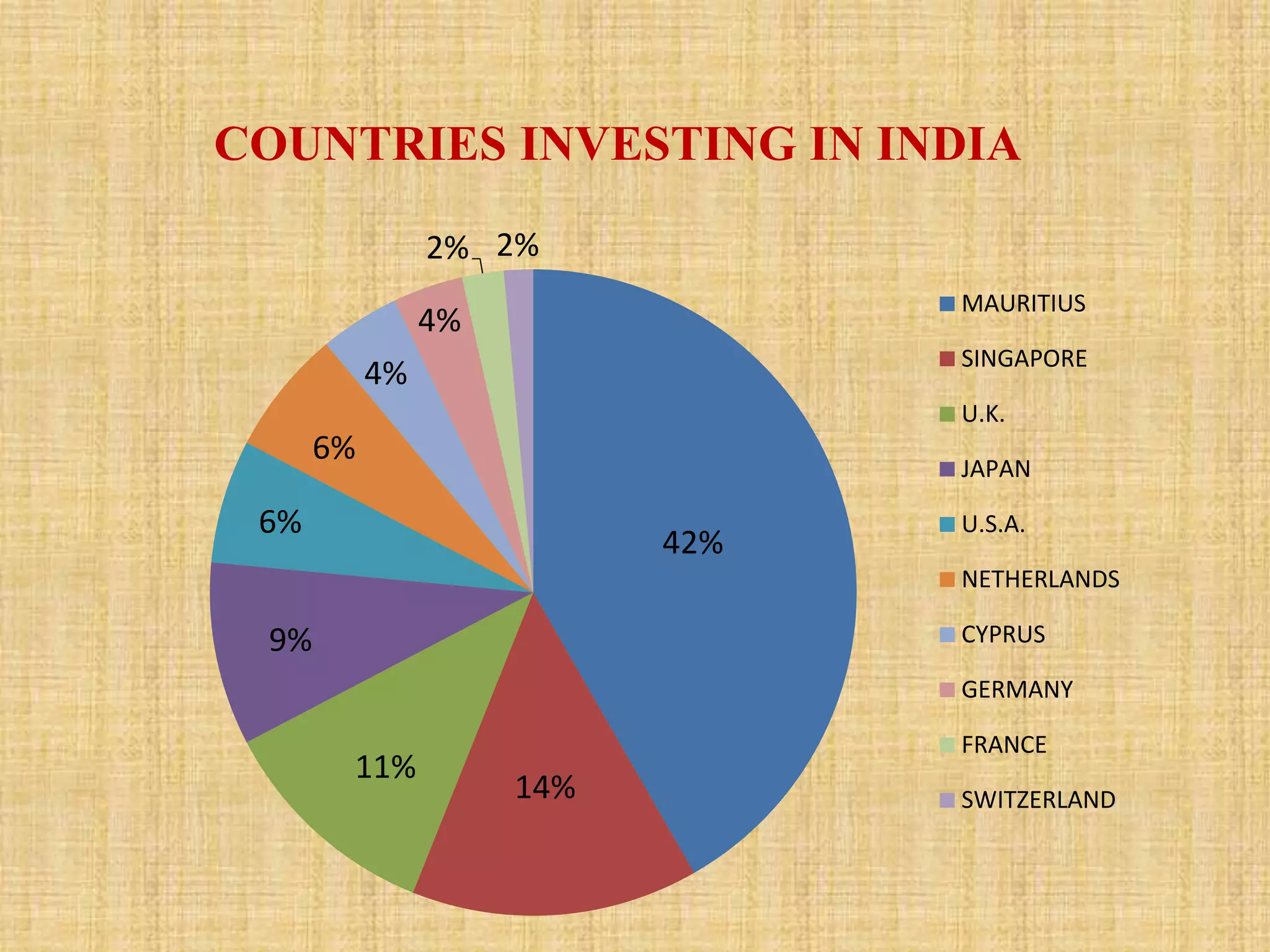
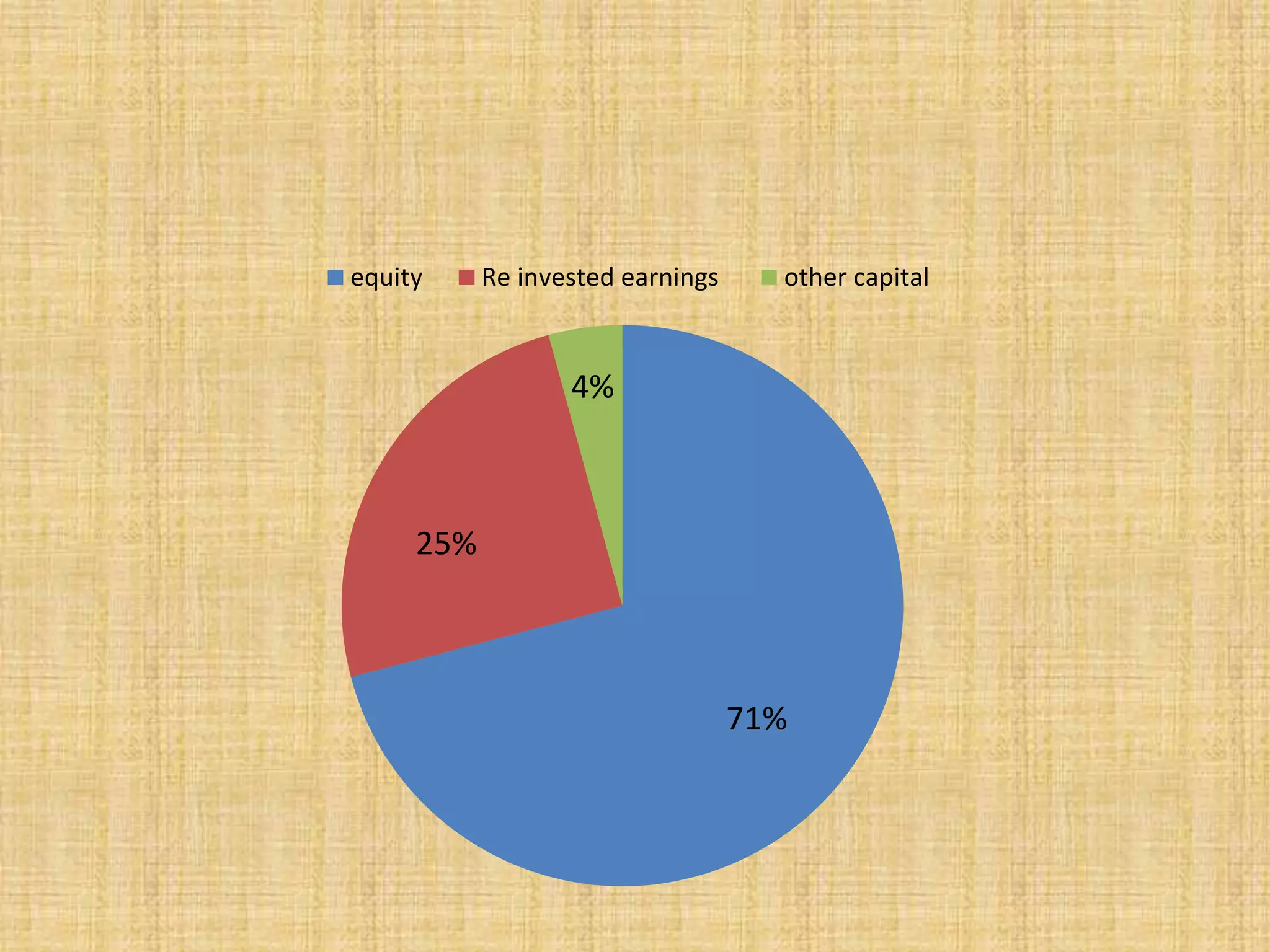
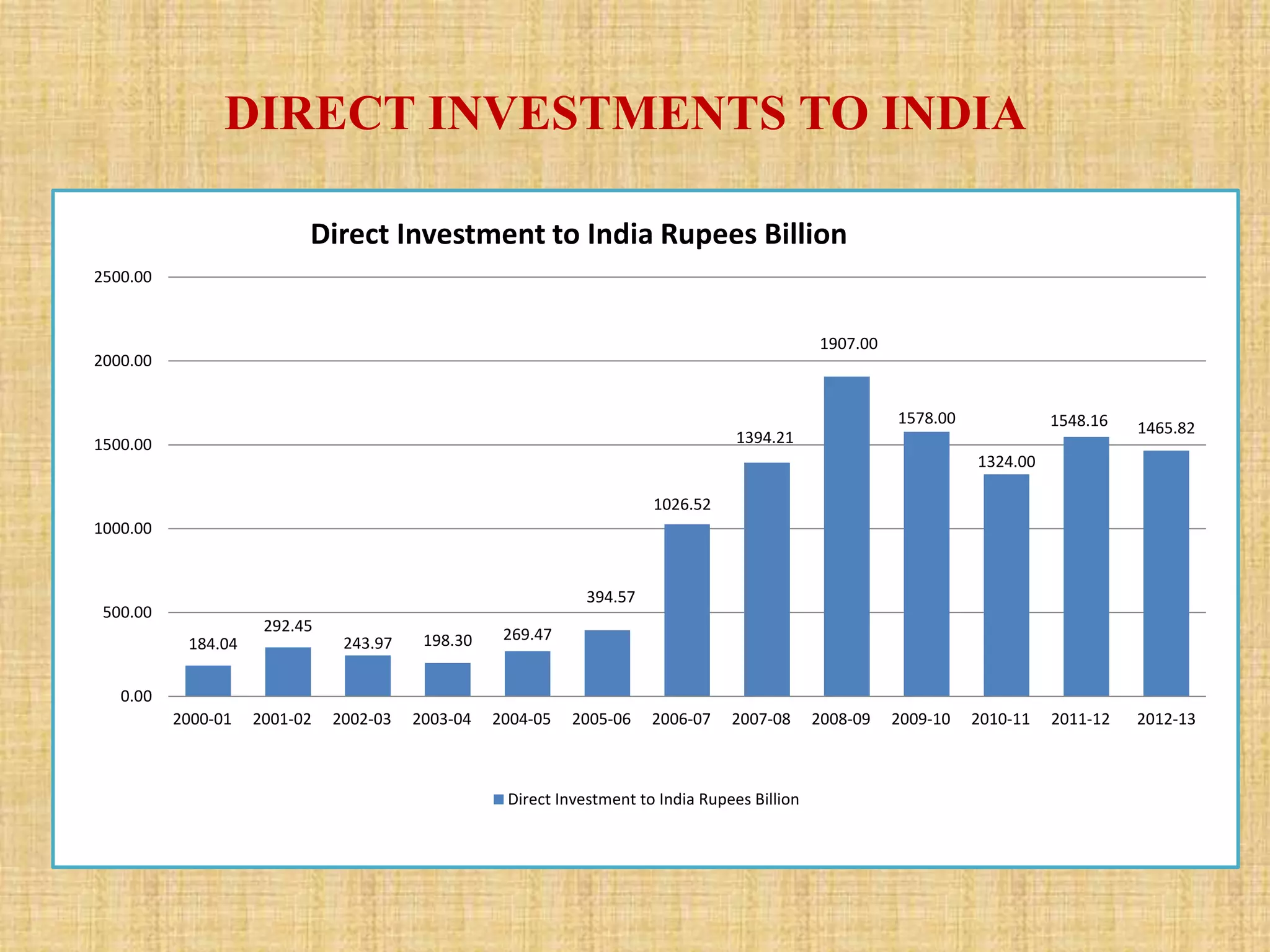
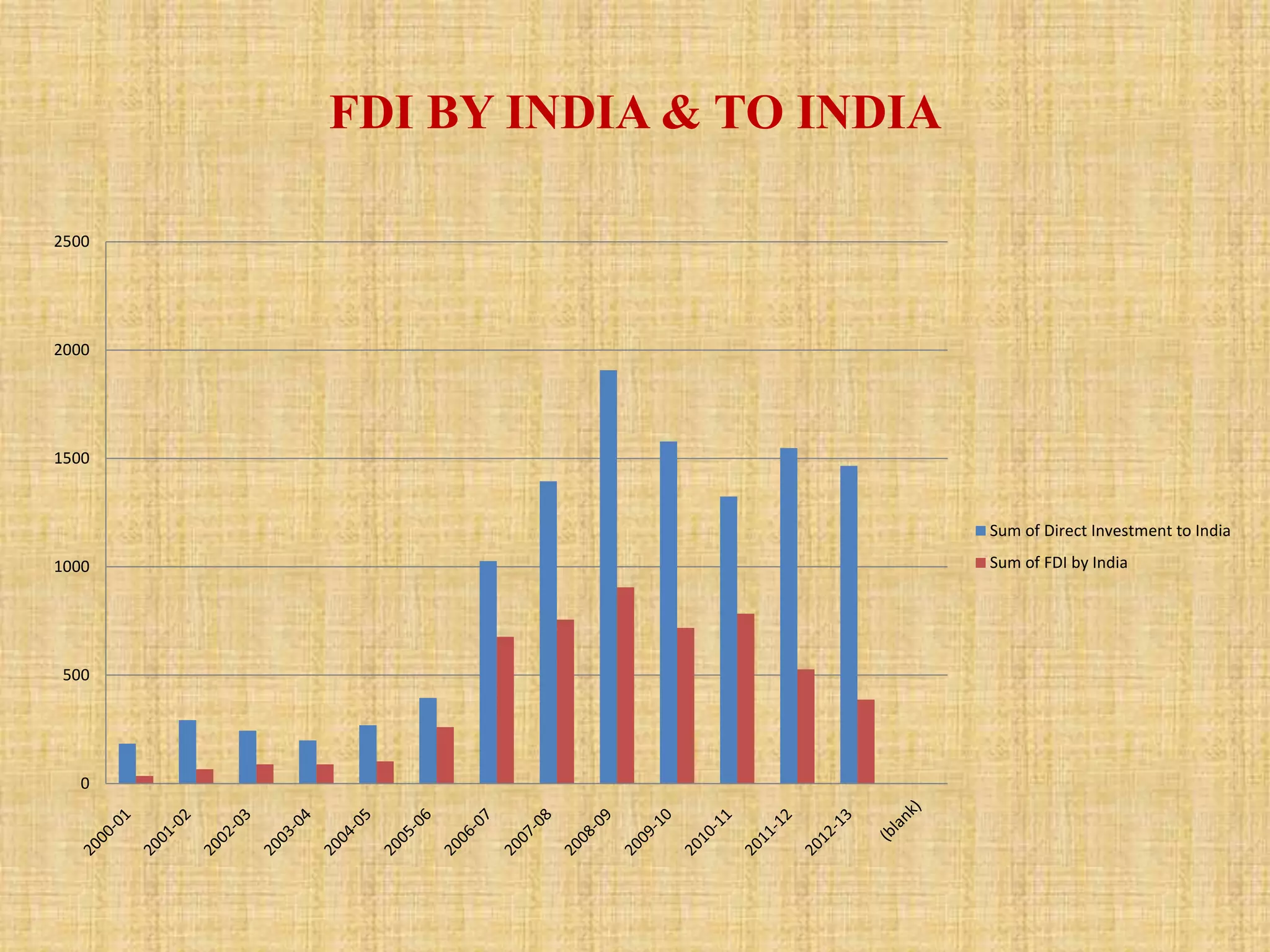
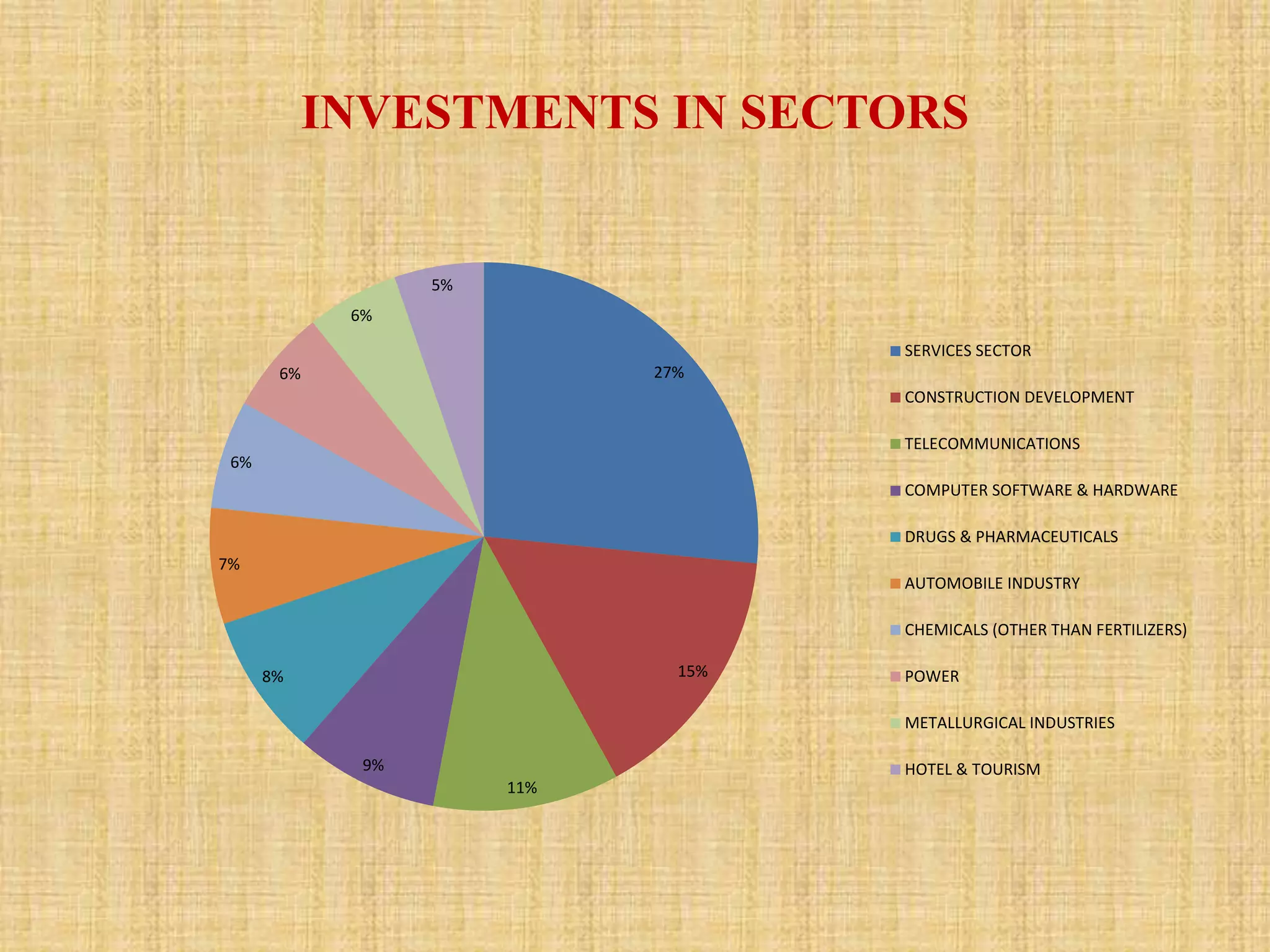
This document analyzes trends in foreign direct investment (FDI) flows to India from 2000-2014. It has two main objectives: 1) To study trends and patterns of FDI flows, and 2) To identify factors influencing FDI flows to India. The author collects data from secondary sources like RBI to analyze FDI magnitudes and factors. Key findings include that major investing countries are Mauritius, Singapore, and the UK, while most FDI goes to services, construction, and telecommunications. Factors found to affect FDI include profitability, costs, economic conditions, government policy, political stability, and ease of doing business.