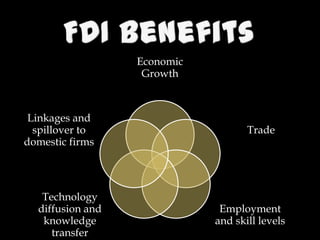
Foreign direct investment (FDI) refers to long-term cross-border investment made by a firm in business activities located in another economy. FDI can take several forms including mergers and acquisitions, joint ventures, and wholly owned subsidiaries. India allows FDI through various modes and sectors to promote economic growth. While FDI has benefits like job creation and technology transfers, it also poses risks such as inflation and loss of policy flexibility. Overall, FDI has played an important role in India's development but more can still be done to spread its benefits across sectors and regions.