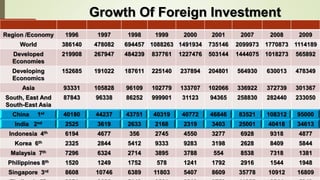
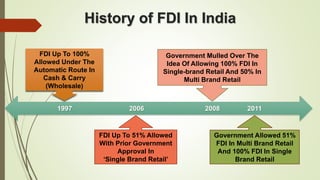
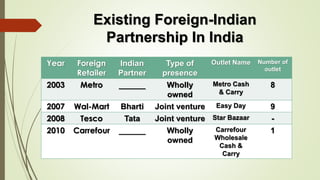
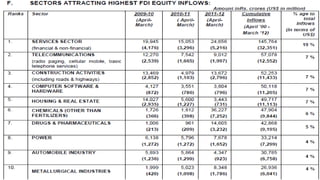
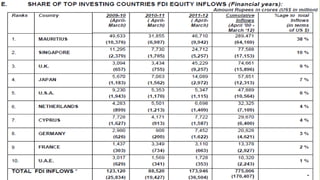
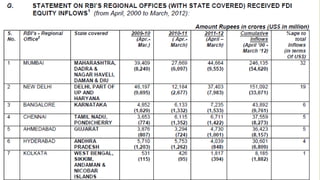
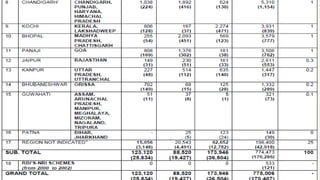
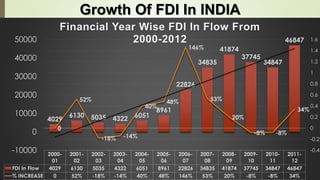
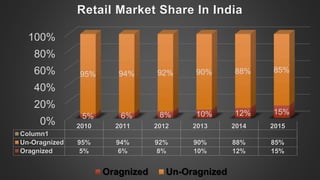
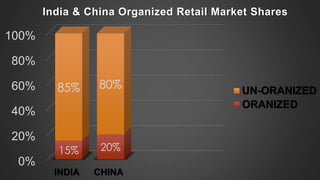
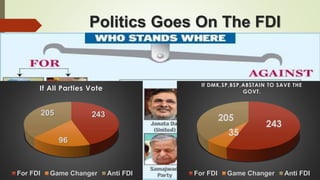
The document discusses foreign direct investment (FDI) in India. It defines FDI and explains that it refers to investment from foreign companies into domestic structures, equipment, and organizations in India. It outlines the types of FDI, factors affecting FDI, and the significance and limitations of FDI for India's economy. Additionally, it provides data on growth trends in FDI in India over time, popular destinations for FDI, and both advantages and limitations of allowing FDI in India's retail sector. Experts are cited discussing both benefits and risks of India's reliance on FDI.